Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) immunotherapy has revolutionized anticancer therapy, as it accurately targets cancer cells by recognizing specific antigens expressed in cancer cells. This innovative therapeutic strategy has attracted considerable attention. However, few therapeutics are available for treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for most lung cancer cases and is one of the deadliest cancers with low survival rates.
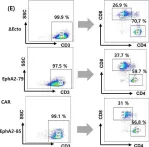
In this study, we developed a new antibody targeting erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular carcinoma A2 (EphA2), which is highly expressed in NSCLC, and established CAR-T/ natural killer (NK) immune cells to verify its potential for immune cell therapy. The killing capacity, cytokine secretion and solid tumor growth inhibition of EphA2 CAR-T/NK cells were compared to normal T/NK cells.
EphA2 CAR-T cells demonstrated superior killing capacity, enhanced cytokine secretion, and significant solid tumor growth inhibition. Additionally, they exhibited improved tumor infiltration in lung cancer models compared to normal T cells. The anticancer efficacy of the developed EphA2 CAR-NK cells was also confirmed, showcasing their potential as robust candidates for immune cell therapy.
The findings of this study highlight the potential of CAR-T/NK cell therapy targeting EphA2 as an effective treatment for lung cancer, particularly NSCLC with high EphA2 expression. By leveraging the specific targeting capabilities of CAR-T cells and the unique properties of CAR-NK cells, this approach provides a promising therapeutic strategy to address the unmet needs in NSCLC treatment.
Copyright © 2025 Kim, Lee, Kim, Bae, Hong, Jo, Kim, Chung and Kim.
Product Citations: 47
Developing CAR-T/NK cells that target EphA2 for non-small cell lung cancer treatment.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 4 April 2025 by Kim, S. M., Lee, S. Y., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 4 February 2023 by Janeczek, K., Kowalska, W., et al.
There are many drugs for allergic rhinitis (AR), however, these drugs show variable clinical effectiveness and some side effects. Therefore, new methods of AR pharmacotherapy are being sought.
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the efficacy of polyvalent mechanical bacterial lysate (PMBL) therapy in improving the clinical course of grass pollen-induced AR (seasonal AR, SAR) in children and its effect on changes in the blood level of the γδT, iNKT and cytotoxic T cell subsets.
Fifty children with SAR were enrolled in this study and were randomly assigned to either the PMBL group or the placebo group. The severity of SAR symptoms was assessed using the total nasal symptom score (TNSS) and visual analogue scale (VAS). During two visits (V1, V2), peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF) was measured and peripheral blood was collected for immunological analyses. The study also included 2 telephone contacts (TC1, TC2).
The severity of the nasal symptoms of SAR on the TNSS scale was revealed to have a significantly lower impact in the PMBL group vs the placebo group at measuring points TC1 and V2 (p = 0.01, p = 0.009, respectively). A statistically significantly lower mean severity of nasal symptoms of SAR on the VAS scale was recorded for children in the PMBL group compared to the placebo group at measuring points TC1, V2 and TC2 (p = 0.04, p = 0.04, p = 0.03, respectively). The compared groups do not show significant differences in terms of PNIF values at individual measuring points. There were no statistically significant changes in immune variables. For both groups, there was a statistically significant association between the level of Th1-like γδT cells and the severity of SAR symptoms expressed on the TNSS scale (p = 0.03) - the lower the level of Th1-like γδT cells, the higher the TNSS value.
Administration of sublingual PMBL tablets during the grass pollen season proves to have a high efficacy in alleviating SAR symptoms in children sensitized to grass pollen allergens. Th1-like γδT cells may be used as potential markers for SAR severity in children.
ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier (NCT04802616).
Copyright © 2023 Janeczek, Kowalska, Zarobkiewicz, Suszczyk, Mikołajczyk, Markut-Miotła, Morawska-Michalska, Bakiera, Tomczak, Kaczyńska, Emeryk, Roliński and Piotrowska-Weryszko.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 3 January 2023 by Balta, E., Janzen, N., et al.
Use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells to treat B cell lymphoma and leukemia has been remarkably successful. Unfortunately, the therapeutic efficacy of CAR T cells against solid tumors is very limited, with immunosuppression by the pro-oxidative tumor microenvironment (TME) a major contributing factor. High levels of reactive oxygen species are well-tolerated by tumor cells due to their elevated expression of antioxidant proteins; however, this is not the case for T cells, which consequently become hypo-responsive. The aim of this study was to improve CAR T cell efficacy in solid tumors by empowering the antioxidant capacity of CAR T cells against the pro-oxidative TME. To this end, HER2-specific human CAR T cells stably expressing two antioxidant systems: thioredoxin-1 (TRX1), and glutaredoxin-1 (GRX1) were generated and characterized. Thereafter, antitumor functions of CAR T cells were evaluated under control or pro-oxidative conditions. To provide insights into the role of antioxidant systems, gene expression profiles as well as global protein oxidation were analyzed. Our results highlight that TRX1 is pivotal for T cell redox homeostasis. TRX1 expression allows CAR T cells to retain their cytolytic immune synapse formation, cytokine release, proliferation, and tumor cell-killing properties under pro-oxidative conditions. Evaluation of differentially expressed genes and the first comprehensive redoxosome analysis of T cells by mass spectrometry further clarified the underlying mechanisms. Taken together, enhancement of the key antioxidant TRX1 in human T cells opens possibilities to increase the efficacy of CAR T cell treatment against solid tumors.
Copyright © 2022 Balta, Janzen, Kirchgessner, Toufaki, Orlik, Liang, Lairikyengbam, Abken, Niesler, Müller-Decker, Ruppert and Samstag.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Immunity & Ageing : I & A on 27 September 2022 by Liu, W., Xu, J., et al.
Assessment of immune function is of key importance in recognition of disease or healthy status, which still faces challenge in clinical practice. We conducted a 10-center study to investigate lymphocyte parameters including the number, phenotype and IFN-γ-producing ability, and routine laboratory indicators by using the standard method.
Although the heterogeneity of lymphocyte parameters was widely found, we have established the normal ranges of these parameters by using pooled data which showed no significant difference among centers. Cluster analysis of 35 parameters found 3 interesting clusters which represented different immunological status. Cluster 1 (parameters: IFN-γ+CD4+ T cell percentage and IFN-γ+CD8+ T cell percentage) represented current lymphocyte function, which was associated with indicators such as body mass index and red blood cell; Cluster 2 (parameters: NK cell number and CD45RA+CD4+ T cell percentage) represented potential of lymphocytes, which was associated with indicators such as albumin and high-density lipoprotein. Cluster 3 (parameters: HLA-DR+CD8+ T cell percentage) represented inflammatory status, which was associated with indicators such as low-density lipoprotein, globulin and age. Correlation analysis found that nutritional indicator albumin is significantly positively correlated with lymphocyte potential. Triglyceride and body mass index were positively correlated with current lymphocyte function rather than lymphocyte potential. The loss of CD8+ T cells was extremely pronounced with increasing age and was one of the most important factors to cause immunosenescence, which may be associated with increased glucose.
We have established the normal ranges of lymphocyte parameters in different areas. This study elucidates the key indicators used to reflect the current function or potential of lymphocytes, which may provide a valuable clue for how to keep immunity healthy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Properdin produced by dendritic cells contributes to the activation of T cells.
In Immunobiology on 1 July 2022 by van Essen, M. F., Schlagwein, N., et al.
The complement system does not only play an important role in the defence against microorganism and pathogens, but also contributes to the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Especially activation fragments C3a and C5a and complement activation at the interface of antigen presenting cell (APC) and T cell, were shown to have a role in T cell activation and proliferation. Whereas most complement factors are produced by the liver, properdin, a positive regulator of the C3 convertase, is mainly produced by myeloid cells. Here we show that properdin can be detected in myeloid cell infiltrate during human renal allograft rejection. In vitro, properdin is produced and secreted by human immature dendritic cells (iDCs), which is further increased by CD40-L-matured DCs (mDCs). Transfection with a specific properdin siRNA reduced properdin secretion by iDCs and mDCs, without affecting the expression of co-stimulatory markers CD80 and CD86. Co-culture of properdin siRNA-transfected iDCs and mDCs with human allogeneic T cells resulted in reduced T cell proliferation, especially under lower DC-T cell ratio's (1:30 and 1:90 ratio). In addition, T cell cytokines were altered, including a reduced TNF-α and IL-17 secretion by T cells co-cultured with properdin siRNA-transfected iDCs. Taken together, these results indicate a local role for properdin during the interaction of DCs and allogeneic T cells, contributing to the shaping of T cell proliferation and activation.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Immunol on 4 April 2025 by Kim, S. M., Lee, S. Y., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
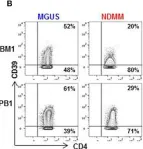
In Front Immunol on 21 August 2019 by Marsh-Wakefield, F., Kruzins, A., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
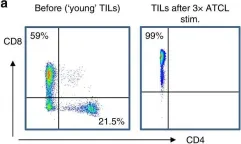
In Br J Cancer on 1 January 2019 by Meng, Q., Valentini, D., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Br J Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
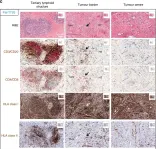
In Br J Cancer on 1 January 2019 by Meng, Q., Valentini, D., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
IHC
-
Collected and cropped from Br J Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4