The circular, double-stranded DNA genomes of Human papillomaviruses (HPV) exist in a nucleosomal state throughout the infectious cycle and rely on host histone epigenetic modifications and chromatin assembly processes to promote various phases of the viral life cycle. Here, we show that the histone H3.3 chaperone HIRA and its associated complex members are recruited to HPV replication factories during the late phase of the HPV life cycle. HIRA is also recruited to HPV replication factories generated by amplification of a replicon with a minimal origin and expression of the viral replication proteins E1 and E2, demonstrating that the E1 and E2 proteins are sufficient for HIRA recruitment. Downregulation of HIRA expression reduces HPV31 DNA amplification and viral transcription in differentiated keratinocytes. Histone H3.3 that is highly phosphorylated on serine residue 31 is also enriched at sites of HPV replication and this modification links the DNA damage response to chromatin that supports rapid gene activation. We propose that deposition of histone H3.3 generates viral minichromosomes which are highly primed to support the late stages of the HPV life cycle.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Product Citations: 45
Chromatin assembly by the histone chaperone HIRA facilitates Human Papillomavirus replication.
In Tumour Virus Research on 1 November 2025 by Della Fera, A. N., Chen, D., et al.
-
Genetics
In International Journal of Radiation Biology on 11 August 2025 by Hassan, E. M., Puzantian, B., et al.
Phosphorylation of the histone H2AX (γ-H2AX) is a rapid response to radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) and is a good biomarker for exposure to ionizing radiation. The signal has traditionally been detected by microscopy (spot counting) or by flow cytometry (fluorescent intensity). An imaging flow cytometry (IFC) method has been developed, which combines the high resolution of microscopy with the statistical power of flow cytometry methods to measure γ-H2AX in human lymphocytes.
The assay was optimized and validated for both sample acquisition and data analysis, in the dose range of 0-10 Gy. For data analysis, mean fluorescence intensity (MFI), spot count (foci per cell), and average area of the spots were used with the supervised machine learning (SML) K-Nearest Neighbors (K-NN) algorithm to estimate doses. These dose estimates were compared to the traditional flow cytometry method of estimating doses from an MFI-based dose response curve.
A statistical analysis of both methodologies showed that SML K-NN method was able to determine the dose delivered to blind, irradiated samples more accurately than when using a linear fit of the MFI response alone, especially in the 7-10 Gy dose range.
The efficiency of the γ-H2AX-IFC assay, 1 hour post-exposure, has been improved and validated using the SML K-NN methodology for dose estimation. This study could help establish the γ-H2AX assay as a triage tool for the rapid screening of a large number of samples.
p300 inhibition delays premature cellular senescence.
In Npj Aging on 10 July 2025 by Di Fede, E., Taci, E., et al.
Cellular senescence represents a permanent state of cell cycle arrest, also observed in neurodegenerative disorders. As p300 has been identified as an epigenetic driver of replicative senescence, we aimed to investigate whether in vitro p300 inhibition could rescue the stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS) phenotype. We exploited 2D and 3D (brain organoids) in vitro models of SIPS using two different stressor agents. In addition, we combined the treatment with a p300 inhibitor and validated p300 role in SIPS by analyzing different senescence markers and the transcriptome in our models. Interestingly, p300 inhibition can counteract the DNA damage and SIPS phenotype, detecting a dysregulation of gene expression and protein translation associated with the senescence program. These findings highlight both the molecular mechanisms underlying senescence and p300 as a possible pharmacological target. Thus, targeting p300 and, by extension, senescent cells could represent a promising therapeutic strategy for age-related diseases such as neurodegenerative disorders.
© 2025. The Author(s).
The anticancer potential of Origanum onites L. in gastric cancer through epigenetic alterations.
In BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies on 2 July 2025 by Sogutlu, F., Pekerbas, M., et al.
Epigenetic alterations are crucial in gastric cancer (GC) development and progression. As these modifications are reversible, targeting them may offer preventive and therapeutic benefits. Origanum onites L. essential oil (OOEO) has demonstrated anticancer properties in various cancers, but its epigenetic effects in GC remain unexplored.
OOEO was extracted by water distillation, and its effects on gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) and normal gastric epithelial (GES-1) cells were evaluated. Cytotoxicity was assessed via WST-8 assay, apoptosis by Annexin V staining, DNA damage by γ-H2AX test, and epigenetic modifications by methylation-specific PCR and histone modification analysis.
Compared to GES-1 cells, OOEO exhibited cytotoxic activity even at lower concentrations in AGS cells. OOEO treatment induced apoptosis and DNA double-strand breaks and arrested cell cycle at S and G2/M phases compared to the untreated group. OOEO also caused a decrease in promoter methylation of LOX, TIMP3, CDH1 and RARB genes and was found to globally alter 16 histone modifications in AGS cells and 19 histone modifications in GES-1 cells. OOEO contributed to the reorganization of H3K9ac modification in the promoters of CDKN1A, MYC, RUNX3, RASSF1 and CDH1 genes and H3K27me3 modification in the promoters of CDKN1A and MYC genes.
OOEO exhibits epigenetic regulatory properties that may contribute to GC prevention and treatment. Its potential in neoadjuvant or combinatory therapies warrants further investigation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
Chemical genetic screens reveal defective lysosomal trafficking as synthetic lethal with NF1 loss.
In Journal of Cell Science on 1 August 2024 by Bouley, S. J., Grassetti, A. V., et al.
Neurofibromatosis type 1, a genetic disorder caused by pathogenic germline variations in NF1, predisposes individuals to the development of tumors, including cutaneous and plexiform neurofibromas (CNs and PNs), optic gliomas, astrocytomas, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, high-grade gliomas and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs), which are chemotherapy- and radiation-resistant sarcomas with poor survival. Loss of NF1 also occurs in sporadic tumors, such as glioblastoma (GBM), melanoma, breast, ovarian and lung cancers. We performed a high-throughput screen for compounds that were synthetic lethal with NF1 loss, which identified several leads, including the small molecule Y102. Treatment of cells with Y102 perturbed autophagy, mitophagy and lysosome positioning in NF1-deficient cells. A dual proteomics approach identified BLOC-one-related complex (BORC), which is required for lysosome positioning and trafficking, as a potential target of Y102. Knockdown of a BORC subunit using siRNA recapitulated the phenotypes observed with Y102 treatment. Our findings demonstrate that BORC might be a promising therapeutic target for NF1-deficient tumors.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
-
ICC-IF
-
Cell Biology
-
Genetics
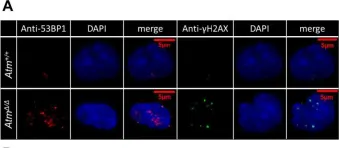
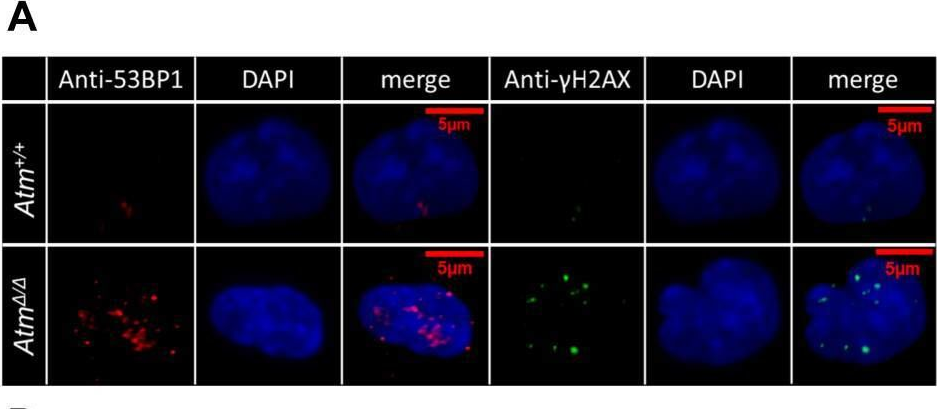
In J Biol Chem on 23 March 2021 by Sorimachi, Y., Karigane, D., et al.
Fig.4.A
-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from The Journal of Biological Chemistry by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1