Multiple genetic associations suggest a causative relationship between Th17-related genes coding for proteins, such as IL-17A, IL-23 and STAT3, and psoriasis. Further support for this link comes from the findings that neutralizing antibodies directed against IL-17A, IL-17RA and IL-23 are efficacious in diseases like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. RORγt is a centrally positioned transcription factor driving Th17 polarization and cytokine secretion and modulation of RORγt may thus provide additional benefit to patients. However, RORγt also plays a role in the normal development of T cells in the thymus and genetic disruption of RORγt in the mouse leads to the development of lymphoma originating in the thymus. Whilst it is not established that down-regulation of RORγt activity would lead to the same consequence in humans, further understanding of the thymus effects is desirable to support progress of this target as a potential treatment of Th17-driven disease. Herein we present the characterisation of recently disclosed RORγt inverse agonists demonstrating target engagement and efficacy in vitro and in vivo against Th17 endpoints but requiring higher concentrations in vitro to affect thymocyte apoptosis.
Copyright: © 2025 Collins et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Product Citations: 54
RORγt inverse agonists demonstrating a margin between inhibition of IL-17A and thymocyte apoptosis.
In PLoS ONE on 17 January 2025 by Collins, M., Pehrson, R., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
The TLR7/8 agonist INI-4001 enhances the immunogenicity of a Powassan virus-like-particle vaccine
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 3 December 2024 by Crawford, M. W., Abdelwahab, W. M., et al.
Powassan virus (POWV) is a pathogenic tick-borne flavivirus that causes fatal neuroinvasive disease in humans. There are currently no approved therapies or vaccines for POWV infection. Here, we develop a POW virus-like-particle (POW-VLP) based vaccine adjuvanted with the novel synthetic Toll-like receptor 7/8 agonist INI-4001. We demonstrate that INI-4001 outperforms both alum and the Toll-like receptor 4 agonist INI-2002 in enhancing the immunogenicity of a dose-sparing POW-VLP vaccine in mice. INI-4001 increases the magnitude and breadth of the antibody response as measured by whole-virus ELISA, induces neutralizing antibodies measured by FRNT, reduces viral burden in the brain of infected mice measured by RT qPCR, and confers 100% protection from lethal challenge with both lineages of POWV. We show that the antibody response induced by INI-4001 is more durable than standard alum, and 80% of mice remain protected from lethal challenge 9-months post-vaccination. Lastly, we show that the protection elicited by INI-4001 adjuvanted POW-VLP vaccine is unaffected by either CD4 + or CD8 + T cell depletion and can be passively transferred to unvaccinated mice indicating that protection is mediated through humoral immunity. This study highlights the utility of novel synthetic adjuvants in VLP-based vaccines. Author summary Powassan virus (POWV) is an emerging pathogenic tick-borne flavivirus for which there is no vaccine. Current tick-borne flavivirus vaccines are less than ideal and use formalin-inactivated virus adjuvanted with alum. These vaccines require thorough inactivation of the antigen and frequent boosting to maintain immunity. In this study, we describe the development of a POWV vaccine using Powassan virus-like-particles (POW-VLPs) adjuvanted with either of two novel Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists, the TLR4 agonist INI-2002 or the TLR7/8 agonist INI-4001. We show that INI-4001 enhances the antibody response, reduces POWV neuroinvasion, and elicits full protection from lethal POWV infection in mice prime-boost vaccinated with low doses of POW-VLP. We further show that this protection is mediated by a humoral immune response which is both broader and more durable than a POW-VLP vaccine formulated with alum. These findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the novel synthetic TLR7/8 agonist INI-4001 as an adjuvant for low-dose VLP-based vaccines and the ability of this vaccine platform to improve upon current tick-borne flavivirus vaccine methodology.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 4 January 2024 by Alwithenani, A., Taha, Z., et al.
Immunotherapy and specifically oncolytic virotherapy has emerged as a promising option for cancer patients, with oncolytic herpes simplex virus-1 (oHSV-1) expressing granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor being the first OV to be approved by the FDA for treatment of melanoma. However, not all cancers are sensitive and responsive to oncolytic viruses (OVs). Our group has demonstrated that fumaric and maleic acid esters (FMAEs) are very effective in sensitizing cancer cells to OV infection. Of note, these FMAEs include dimethyl fumarate (DMF, also known as Tecfidera®), an approved treatment for multiple sclerosis and psoriasis. This study aimed to assess the efficacy of DMF in combination with oncolytic HSV-1 in preclinical cancer models. We demonstrate herewith that pre-treatment with DMF or other FMAEs leads to a significant increase in viral growth of oHSV-1 in several cancer cell lines, including melanoma, while decreasing cell viability. Additionally, DMF was able to enhance ex vivo oHSV-1 infection of mouse-derived tumor cores as well as human patient tumor samples but not normal tissue. We further reveal that the increased viral spread and oncolysis of the combination therapy occurs via inhibition of type I IFN production and response. Finally, we demonstrate that DMF in combination with oHSV-1 can improve therapeutic outcomes in aggressive syngeneic murine cancer models. In sum, this study demonstrates the synergistic potential of two approved therapies for clinical evaluation in cancer patients.
Copyright © 2023 Alwithenani, Taha, Thomson, Chen, Wong, Arulanandam and Diallo.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
mRNA-based VP8* nanoparticle vaccines against rotavirus are highly immunogenic in rodents.
In NPJ Vaccines on 22 December 2023 by Roier, S., Mangala Prasad, V., et al.
Despite the availability of live-attenuated oral vaccines, rotavirus remains a major cause of severe childhood diarrhea worldwide. Due to the growing demand for parenteral rotavirus vaccines, we developed mRNA-based vaccine candidates targeting the viral spike protein VP8*. Our monomeric P2 (universal T cell epitope)-VP8* mRNA design is equivalent to a protein vaccine currently in clinical development, while LS (lumazine synthase)-P2-VP8* was designed to form nanoparticles. Cyro-electron microscopy and western blotting-based data presented here suggest that proteins derived from LS-P2-VP8* mRNA are secreted in vitro and self-assemble into 60-mer nanoparticles displaying VP8*. mRNA encoded VP8* was immunogenic in rodents and introduced both humoral and cellular responses. LS-P2-VP8* induced superior humoral responses to P2-VP8* in guinea pigs, both as monovalent and trivalent vaccines, with encouraging responses detected against the most prevalent P genotypes. Overall, our data provide evidence that trivalent LS-P2-VP8* represents a promising mRNA-based next-generation rotavirus vaccine candidate.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 8 May 2023 by Taha, Z., Crupi, M. J. F., et al.
Established mouse models of HER2+ cancer are based on the over-expression of rodent Neu/Erbb2 homologues, which are incompatible with human HER2 (huHER2) targeted therapeutics. Additionally, the use of immune-deficient xenograft or transgenic models precludes assessment of native anti-tumour immune responses. These hurdles have been a challenge for our understanding of the immune mechanisms behind huHER2-targeting immunotherapies.
To assess the immune impacts of our huHER2-targeted combination strategy, we generated a syngeneic mouse model of huHER2+ breast cancer, using a truncated form of huHER2, HER2T. Following validation of this model, we next treated tumour-bearing with our immunotherapy strategy: oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus (VSVΔ51) with clinically approved antibody-drug conjugate targeting huHER2, trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1). We assessed efficacy through tumour control, survival, and immune analyses.
The generated truncated HER2T construct was non-immunogenic in wildtype BALB/c mice upon expression in murine mammary carcinoma 4T1.2 cells. Treatment of 4T1.2-HER2T tumours with VSVΔ51+T-DM1 yielded robust curative efficacy compared to controls, and broad immunologic memory. Interrogation of anti-tumour immunity revealed tumour infiltration by CD4+ T cells, and activation of B, NK, and dendritic cell responses, as well as tumour-reactive serum IgG.
The 4T1.2-HER2T model was used to evaluate the anti-tumour immune responses following our complex pharmacoviral treatment strategy. These data demonstrate utility of the syngeneic HER2T model for assessment of huHER2-targeted therapies in an immune-competent in vivo setting. We further demonstrated that HER2T can be implemented in multiple other syngeneic tumour models, including but not limited to colorectal and ovarian models. These data also suggest that the HER2T platform may be used to assess a range of surface-HER2T targeting approaches, such as CAR-T, T-cell engagers, antibodies, or even retargeted oncolytic viruses.
Copyright © 2023 Taha, Crupi, Alluqmani, Fareez, Ng, Sobh, Lee, Chen, Thomson, Spinelli, Ilkow, Bell, Arulanandam and Diallo.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
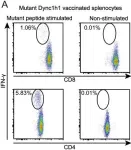
In PLoS One on 19 May 2016 by Martin, S. D., Brown, S. D., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1