ABSTRACT Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell (MSC) therapy holds great promise as both a therapeutic option and as a biofactory, as cells produce therapeutic proteins to augment their efficacy in disease treatment. This study investigates the therapeutic effects and the mechanistic insights of alpha-1 antitrypsin overexpressing MSCs (AAT-MSCs) in diabetes prevention and treatment. A single infusion of AAT-MSCs not only delayed diabetes onset but reversed new-onset type 1 diabetes (T1D) in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, flow cytometry, and functional analyses, we characterized the impact of AAT-MSCs on immune cells, particularly CD4 + and CD8 + T cells, in pancreatic lymph nodes (PLNs) and islets of NOD mice. AAT-MSCs enhanced the immunosuppressive function and the communication of regulatory T cells (Tregs) with other immune cells while reducing the numbers of T helper 1 (Th1) cells and CD8 + cytotoxic T cells. In vitro experiments further confirmed the capacity of AAT-MSCs to promote the proliferation of Tregs, which consequently fostered an exhausted phenotype in CD8 + T cells, thereby facilitating β cell survival and potentially aiding in diabetes remission. Thus, our findings underscore the significant protective effects of AAT-MSCs, delineate their novel mechanistic insight on recipient immune cells, and provide evidence for the clinical application of AAT-MSCs in treating T1D.
Product Citations: 27
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 21 April 2025 by Wei, H., Gou, W., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 7 February 2025 by Tomasello, L., Coppola, A., et al.
The primary outcome was the evaluation of the T-cell phenotype in autoimmune primary adrenal insufficiency (PAI). Secondary outcomes included the evaluation of the CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg population and the gene expression levels of IL-6, IL-17A, cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, heat shock proteins (HSP)-70, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and thioredoxin (TXN)-1.
We prospectively included 15 patients with PAI on conventional glucocorticoid (GC) replacement therapy, 15 switched to dual-release hydrocortisone (DR-HC), and 20 healthy controls. Serum inflammatory parameters and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were evaluated at baseline and after 12 months of treatment.
At baseline, significantly higher CD4+ and CD8+ (both p < 0.001) T-cell percentages, a lower CD4+/CD8+ ratio (p < 0.05), and higher CD25+ and CD4+/CD25+ T cells (both p < 0.001) were observed in PAI compared to controls. After 12 months of DR-HC treatment, we found significantly lower IL-6 (p = 0.019), IL-17A (p = 0.046), COX-2 (p < 0.001), HSP-70 (p = 0.006), and TXN-1 (p = 0.008) and higher PD-L1 (p < 0.001) and IDO (p < 0.001) mRNA values compared to baseline. After 12 months of DR-HC treatment, a significant increase in CD4+ T cells (p = 0.012), PD-L1 (p = 0.003), and IDO (p < 0.001) and a decrease in CD8+ T cells (p < 0.001), IL-6 (p = 0.003), IL-17A (p = 0.0014), COX-2 (p < 0.001), HSP-70 (p = 0.005), and TXN-1 (p = 0.0008), as well as a significantly higher conversion in the CD4+/CD8+ ratio (p = 0.033), were observed compared to conventional GCs.
The switch from conventional GCs to DR-HC treatment altered the T lymphocyte phenotype and CD4+/CD8+ ratio in a Treg-independent manner, inducing significant improvements in the immune and inflammatory profile in PAI.
Copyright © 2025 Tomasello, Coppola, Pizzolanti, Giordano, Arnaldi and Guarnotta.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Life Science Alliance on 1 October 2024 by Mori, L. P., Corley, M. J., et al.
Ongoing viral transcription from the reservoir of HIV-1 infected long-lived memory CD4+ T cells presents a barrier to cure and associates with poorer health outcomes for people living with HIV, including chronic immune activation and inflammation. We previously reported that didehydro-cortistatin A (dCA), an HIV-1 Tat inhibitor, blocks HIV-1 transcription. Here, we examine the impact of dCA on host immune CD4+ T-cell transcriptional and epigenetic states. We performed a comprehensive analysis of genome-wide transcriptomic and DNA methylation profiles upon long-term dCA treatment of primary human memory CD4+ T cells. dCA prompted specific transcriptional and DNA methylation changes in cell cycle, histone, interferon-response, and T-cell lineage transcription factor genes, through inhibition of both HIV-1 and Mediator kinases. These alterations establish a tolerogenic Treg/Th2 phenotype, reducing viral gene expression and mitigating inflammation in primary CD4+ T cells during HIV-1 infection. In addition, dCA suppresses the expression of lineage-defining transcription factors for Th17 and Th1 cells, critical HIV-1 targets, and reservoirs. dCA's benefits thus extend beyond viral transcription inhibition, modulating the immune cell landscape to limit HIV-1 acquisition and inflammatory environment linked to HIV infection.
© 2024 Mori et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Simultaneous blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm and myelofibrosis: A case report.
In Oncology Letters on 1 May 2024 by Luo, F., Li, B., et al.
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is an extremely rare and aggressive tumor with an unknown pathogenesis. Myelofibrosis (MF) is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm. MF can be secondary to several hematological malignancies, including chronic myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome and hairy cell leukemia. In the present report, a rare case of BPDCN secondary to MF is described. A 70-year-old male patient developed a large purplish-red rash with recurrent symptoms. BPDCN was confirmed by immunohistochemistry of a biopsy specimen and flow cytometry of bone marrow cells. Bone marrow histopathology revealed MF. Next-generation sequencing of peripheral blood revealed mutations in the Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 and NRAS proto-oncogene GTPase genes. The patient underwent one cycle of chemoimmunotherapy, but the condition progressed, an infection developed and the patient eventually died. The present case suggests that BPDCN can occur in conjunction with MF and that the prognosis of such patients is poor. Pathological examination and genetic testing aided in the diagnosis and treatment. This case emphasizes the need to raise awareness of BPDCN among clinicians and to be alert to the potential for fatal infection in patients with BPDCN combined with MF following myelosuppression triggered during chemotherapy.
Copyright: © 2024 Luo et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In JCI Insight on 10 July 2023 by Osei-Hwedieh, D. O., Sedlacek, A. L., et al.
T cells recognize tumor-derived mutated peptides presented on MHC by tumors. The recognition of these neo-epitopes leads to rejection of tumors, an event that is critical for successful cancer immunosurveillance. Determination of tumor-rejecting neo-epitopes in human tumors has proved difficult, though recently developed systems approaches are becoming increasingly useful at evaluating their immunogenicity. We have used the differential aggretope index to determine the neo-epitope burden of sarcomas and observed a conspicuously titrated antigenic landscape, ranging from the highly antigenic osteosarcomas to the low antigenic leiomyosarcomas and liposarcomas. We showed that the antigenic landscape of the tumors inversely reflected the historical T cell responses in the tumor-bearing patients. We predicted that highly antigenic tumors with poor antitumor T cell responses, such as osteosarcomas, would be responsive to T cell-based immunotherapy regimens and demonstrated this in a murine osteosarcoma model. Our study presents a potentially novel pipeline for determining antigenicity of human tumors, provides an accurate predictor of potential neo-epitopes, and will be an important indicator of which cancers to target with T cell-enhancing immunotherapy.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
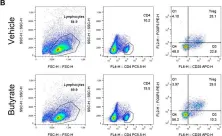
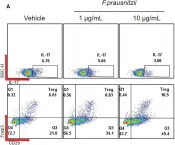
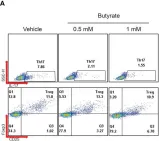
In Front Immunol on 5 May 2023 by Min, H. K., Na, H. S., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Front Immunol on 5 May 2023 by Min, H. K., Na, H. S., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Front Immunol on 5 May 2023 by Min, H. K., Na, H. S., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3