In the intestinal epithelium, intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) coexist with intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). The IELs have an important role in defending the intestinal tract against pathogens and eliminating tumor cells. Anomalies in the absolute IEL count have been reported in various digestive diseases. IELs are typically counted using histologic techniques or under light microscopy after isolation of the epithelium. However, these techniques can introduce bias, which might account for the discrepancies in counts from one study to another. Here, we describe a flow cytometry assay for determining the absolute IEL count and the IEL/IEC ratio. We combined a conventional epithelial isolation method with a BD TruCountTM bead-based absolute counting technique to quantify IELs (CD45+ CD326/EpCAM- CD103+CD3+) and IECs (CD45- CD326/EpCAM+) in a C57BL/6 mouse model. Key features • Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) play a crucial role in maintaining mucosal integrity and defending against pathogens. • Conventional manual counting of IELs using a hemocytometer relies heavily on the operator's expertise. • Flow cytometry offers a more standardized approach to cell counting. • Using TruCountTM beads to quantify IELs and intraepithelial cells (IECs) by flow cytometry and assess their ratio ensures reproducibility and comparison with immunohistochemical methods. Graphical Overview.
©Copyright : © 2025 The Authors; This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license.
Product Citations: 60
In Bio-protocol on 5 May 2025 by Joulain, C., Bessoles, S., et al.
In IScience on 20 December 2024 by Shouse, A. N., Villarino, A. V., et al.
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) require IL-2 for survival in the periphery, yet how IL-2 shapes Treg heterogeneity remains poorly defined. Here we show that inhibition of IL-2R signaling in post-thymic Tregs leads to a preferential early loss of circulating Tregs (cTregs). Gene expression of cTregs was more dependent on IL-2R signaling than effector Tregs (eTregs). Unexpectedly, ablation of IL-2R signaling in cTregs resulted in increased proliferation, expression of eTreg genes, and enhanced capacity to develop into eTregs. Thus, IL-2R signaling normally acts as a checkpoint to maintain cTreg homeostasis while restraining their development into eTregs. Loss of IL-2R signaling also alters the distribution of eTreg subsets, with increased IFNγR1+ eTregs and CXCR5+ PD-1+ T follicular regulatory (TFR) cells but decreased intestinal RORγt+ TR17 cells. These changes lower eTreg suppressive function supporting expansion of IFNγ-secreting T effector cells. Thus, IL-2R signaling also safeguards Treg function and licenses differentiation of specialized eTregs.
© 2024 The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Non-homogenous intratumor ionizing radiation doses synergize with PD1 and CXCR2 blockade.
In Nature Communications on 14 October 2024 by Bergeron, P., Dos Santos, M., et al.
The efficacy and side effects of radiotherapy (RT) depend on parameters like dose and the volume of irradiated tissue. RT induces modulations of the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) that are dependent on the dose. Low dose RT (LDRT, i.e., single doses of 0.5-2 Gy) has been shown to promote immune infiltration into the tumor. Here we hypothesize that partial tumor irradiation combining the immunostimulatory/non-lethal properties of LDRT with cell killing/shrinkage properties of high dose RT (HDRT) within the same tumor mass could enhance anti-tumor responses when combined with immunomodulators. In models of colorectal and breast cancer in immunocompetent female mice, partial irradiation (PI) with millimetric precision to deliver LDRT (2 Gy) and HDRT (16 Gy) within the same tumor induces substantial tumor control when combined with anti-PD1. Using flow cytometry, cytokine profiling and single-cell RNA sequencing, we identify a crosstalk between the TIME of the differentially irradiated tumor volumes. PI reshapes tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells into more cytotoxic and interferon-activated phenotypes but also increases the infiltration of pro-tumor neutrophils driven by CXCR2. The combination of the CXCR2 antagonist SB225002 with PD1 blockade and PI improves tumor control and mouse survival. Our results suggest a strategy to reduce RT toxicity and improve the therapeutic index of RT and immune checkpoint combinations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Nat Cardiovasc Res on 1 June 2024 by Amoedo-Leite, C., Parv, K., et al.
Sterile inflammation after injury is important for tissue restoration. In injured human and mouse tissues, macrophages were recently found to accumulate perivascularly. This study investigates if macrophages adopt a mural cell phenotype important for restoration after ischemic injury. Single-cell RNA sequencing of fate-mapped macrophages from ischemic mouse muscles demonstrates a macrophage-toward-mural cell switch of a subpopulation of macrophages with downregulated myeloid cell genes and upregulated mural cell genes, including PDGFRβ. This observation was further strengthened when including unspliced transcripts in the analysis. The macrophage switch was proven functionally relevant, as induction of macrophage-specific PDGFRβ deficiency prevented their perivascular macrophage phenotype, impaired vessel maturation and increased vessel leakiness, which ultimately reduced limb function. In conclusion, macrophages in adult ischemic tissue were demonstrated to undergo a cellular program to morphologically, transcriptomically and functionally resemble mural cells while weakening their macrophage identity. The macrophage-to-mural cell-like phenotypic switch is crucial for restoring tissue function and warrants further exploration as a potential target for immunotherapies to enhance healing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Infection and Immunity on 13 February 2024 by Lahiri, P., Arrazuria, R., et al.
Digital dermatitis (DD) is a skin disease in cattle characterized by painful inflammatory ulcerative lesions in the feet, mostly associated with local colonization by Treponema spp., including Treponema phagedenis. The reason why most DD lesions remain actively inflamed and progress to chronic conditions despite antibiotic treatment remains unknown. Herein, we show an abundant infiltration of proinflammatory (CD14highCD16low) monocytes/macrophages in active DD lesions, a skin response that was not mitigated by topical treatment with oxytetracycline. The associated bacterium, T. phagedenis, isolated from DD lesions in cattle, when injected subcutaneously into mice, induced abscesses with a local recruitment of Ly6G+ neutrophils and proinflammatory (Ly6ChighCCR2+) monocytes/macrophages, which appeared at infection onset (4 days post challenge) and persisted for at least 7 days post challenge. When exploring the ability of macrophages to regulate inflammation, we showed that bovine blood-derived macrophages challenged with live T. phagedenis or its structural components secreted IL-1β via a mechanism dependent on the NLRP3 inflammasome. This study shows that proinflammatory characteristics of monocytes/macrophages and neutrophils dominate active non-healing ulcerative lesions in active DD, thus likely impeding wound healing after antibiotic treatment.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Veterinary Research
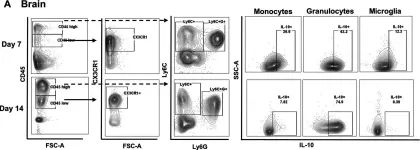
In J Neuroinflammation on 13 May 2023 by Kak, G., Van Roy, Z., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1