Tertiary lymphoid structures (TLSs) emerge as crucial determinants of anti-tumor immune responses and clinical outcomes. However, their clinical significance and formation mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unclear. Here, we demonstrate that hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) with oxaliplatin, leucovorin, and fluorouracil (FOLFOX) significantly enhances TLS formation in HCC tissues, correlating with improved therapeutic efficacy and prolonged progression-free survival in patients with HCC. Mechanistically, HAIC induces lymphotoxin β (LTβ)-expressing central memory T cell (TCM)-like CD4+ T cells, which activate MMP2+ fibroblasts and FOLR2+CCL4+ macrophages via the LTβ-LTβR axis to drive TLS development. Furthermore, the CXCL12-CXCR4 axis acts as a critical mediator in recruiting these cells to HAIC-treated tumors, thereby facilitating TLS formation and enhancing anti-tumor immunity. These findings highlight the pivotal role of TLSs in HAIC-induced anti-tumor immunity and their significance as robust prognostic biomarkers, offering potential therapeutic targets to optimize clinical outcomes for patients with HCC.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 12
In Cell Reports Medicine on 16 September 2025 by Xing, R., Mei, J., et al.
-
Cancer Research
In Nature Communications on 18 December 2023 by Pardons, M., Cole, B., et al.
The development of latency reversing agents that potently reactivate HIV without inducing global T cell activation would benefit the field of HIV reservoir research and could pave the way to a functional cure. Here, we explore the reactivation capacity of a lipid nanoparticle containing Tat mRNA (Tat-LNP) in CD4 T cells from people living with HIV undergoing antiretroviral therapy (ART). When combined with panobinostat, Tat-LNP induces latency reversal in a significantly higher proportion of latently infected cells compared to PMA/ionomycin (≈ 4-fold higher). We demonstrate that Tat-LNP does not alter the transcriptome of CD4 T cells, enabling the characterization of latently infected cells in their near-native state. Upon latency reversal, we identify transcriptomic differences between infected cells carrying an inducible provirus and non-infected cells (e.g. LINC02964, GZMA, CCL5). We confirm the transcriptomic differences at the protein level and provide evidence that the long non-coding RNA LINC02964 plays a role in active HIV infection. Furthermore, p24+ cells exhibit heightened PI3K/Akt signaling, along with downregulation of protein translation, suggesting that HIV-infected cells display distinct signatures facilitating their long-term persistence. Tat-LNP represents a valuable research tool for in vitro reservoir studies as it greatly facilitates the in-depth characterization of HIV reservoir cells' transcriptome and proteome profiles.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Genetics
In Nature Communications on 2 December 2023 by Schramm, C. A., Moon, D., et al.
As SARS-CoV-2 variants continue evolving, testing updated vaccines in non-human primates remains important for guiding human clinical practice. To date, such studies have focused on antibody titers and antigen-specific B and T cell frequencies. Here, we extend our understanding by integrating innate and adaptive immune responses to mRNA-1273 vaccination in rhesus macaques. We sorted innate immune cells from a pre-vaccine time point, as well as innate immune cells and antigen-specific peripheral B and T cells two weeks after each of two vaccine doses and used single-cell sequencing to assess the transcriptomes and adaptive immune receptors of each cell. We show that a subset of S-specific T cells expresses cytokines critical for activating innate responses, with a concomitant increase in CCR5-expressing intermediate monocytes and a shift of natural killer cells to a more cytotoxic phenotype. The second vaccine dose, administered 4 weeks after the first, elicits an increase in circulating germinal center-like B cells 2 weeks later, which are more clonally expanded and enriched for epitopes in the receptor binding domain. Both doses stimulate inflammatory response genes associated with elevated antibody production. Overall, we provide a comprehensive picture of bidirectional signaling between innate and adaptive components of the immune system and suggest potential mechanisms for the enhanced response to secondary exposure.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
AAV vectors displaying bispecific DARPins enable dual-control targeted gene delivery.
In Biomaterials on 1 December 2023 by Theuerkauf, S. A., Herrera-Carrillo, E., et al.
Precise delivery of genes to therapy-relevant cells is crucial for in vivo gene therapy. Receptor-targeting as prime strategy for this purpose is limited to cell types defined by a single cell-surface marker. Many target cells are characterized by combinations of more than one marker, such as the HIV reservoir cells. Here, we explored the tropism of adeno-associated viral vectors (AAV2) displaying designed ankyrin repeat proteins (DARPins) mono- and bispecific for CD4 and CD32a. Cryo-electron tomography revealed an unaltered capsid structure in the presence of DARPins. Surprisingly, bispecific AAVs transduced CD4/CD32a double-positive cells at much higher efficiencies than single-positive cells, even if present in low amounts in cell mixtures or human blood. This preference was confirmed when vector particles were systemically administered into mice. Cell trafficking studies revealed an increased cell entry rate for bispecific over monospecific AAVs. When equipped with an HIV genome-targeting CRISPR/Cas cassette, the vectors prevented HIV replication in T cell cultures. The data provide proof-of-concept for high-precision gene delivery through tandem-binding regions on AAV. Reminiscent of biological products following Boolean logic AND gating, the data suggest a new option for receptor-targeted vectors to improve the specificity and safety of in vivo gene therapy.Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
In STAR Protocols on 16 December 2022 by Mutavhatsindi, H. & Riou, C.
Monitoring antigen-specific T cell frequency, function, and phenotype is essential to assess the host immune response to pathogens or novel vaccines. Here, we describe a rapid and simple ex vivo whole blood assay to detect and phenotype the SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell response. We detail steps for whole blood stimulation with SARS-CoV-2 spike peptide and subsequent cell fixation and cryopreservation. We further describe thawing and cell staining steps for flow cytometry analysis. This approach minimizes sample manipulation and has a quick turnaround time. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Riou et al. (2021).
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
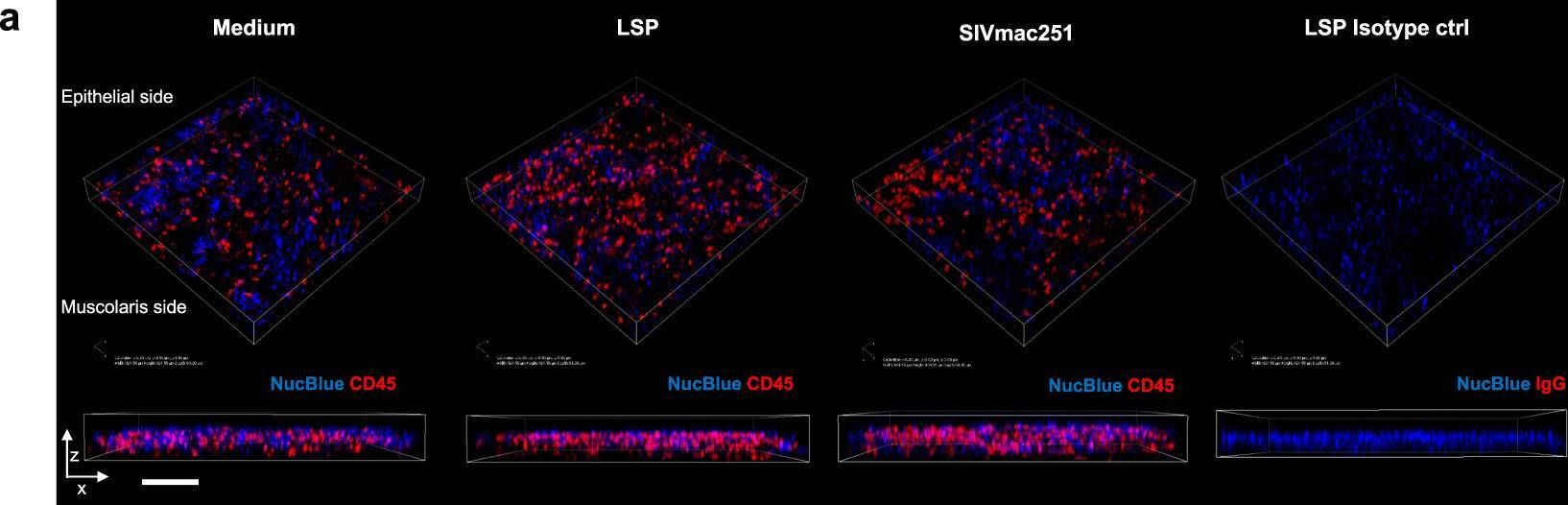
In Commun Biol on 12 July 2021 by Cavarelli, M., Hua, S., et al.
Fig.6.A
-
IHC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Communications Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1