The chronic inflammatory component of asthma is propagated by granulocytes, including neutrophils and eosinophils, in the peripheral circulation and airway. Previous studies have suggested that these cells have an altered expression of adhesion-related molecules and a propensity for the release of granule contents that may contribute to tissue damage and enhance inflammatory complications in patients with status asthmaticus. The goal of this prospective cohort study at a tertiary care pediatric hospital with a large population of asthma patients was to assess the role of granulocyte-based inflammation in the development of asthma exacerbation. Subjects were enrolled from two patient populations: those with mild-to-moderate asthma exacerbations seen in the emergency department and those with severe asthma admitted to the intensive care unit (PICU). Clinical data were collected, and blood was drawn. Granulocytes were immediately purified, and the phenotype was assessed, including the expression of cell surface markers, elastase release, and cytokine production. Severe asthmatics admitted to the PICU displayed a significantly higher total neutrophil count when compared with healthy donors. Moreover, little to no eosinophils were found in granulocyte preparations from severe asthmatics. Circulating neutrophils from severe asthmatics admitted to the PICU displayed significantly increased elastase release ex vivo when compared with the PMN from healthy donors. These data suggest that the neutrophil-based activation and release of inflammatory products displayed by severe asthmatics may contribute to the propagation of asthma exacerbations.
Product Citations: 10
In Cells on 18 March 2024 by Henley, K., Tresselt, E., et al.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cell Biology
In Nature Communications on 18 December 2023 by Pardons, M., Cole, B., et al.
The development of latency reversing agents that potently reactivate HIV without inducing global T cell activation would benefit the field of HIV reservoir research and could pave the way to a functional cure. Here, we explore the reactivation capacity of a lipid nanoparticle containing Tat mRNA (Tat-LNP) in CD4 T cells from people living with HIV undergoing antiretroviral therapy (ART). When combined with panobinostat, Tat-LNP induces latency reversal in a significantly higher proportion of latently infected cells compared to PMA/ionomycin (≈ 4-fold higher). We demonstrate that Tat-LNP does not alter the transcriptome of CD4 T cells, enabling the characterization of latently infected cells in their near-native state. Upon latency reversal, we identify transcriptomic differences between infected cells carrying an inducible provirus and non-infected cells (e.g. LINC02964, GZMA, CCL5). We confirm the transcriptomic differences at the protein level and provide evidence that the long non-coding RNA LINC02964 plays a role in active HIV infection. Furthermore, p24+ cells exhibit heightened PI3K/Akt signaling, along with downregulation of protein translation, suggesting that HIV-infected cells display distinct signatures facilitating their long-term persistence. Tat-LNP represents a valuable research tool for in vitro reservoir studies as it greatly facilitates the in-depth characterization of HIV reservoir cells' transcriptome and proteome profiles.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Genetics
In PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases on 1 May 2022 by Bhuiyan, T. R., Rahman, M. A., et al.
Mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are unconventional T lymphocytes with a semi-conserved TCRα, activated by the presentation of vitamin B metabolites by the MHC-I related protein, MR1, and with diverse innate and adaptive effector functions. The role of MAIT cells in acute intestinal infections, especially at the mucosal level, is not well known. Here, we analyzed the presence and phenotype of MAIT cells in duodenal biopsies and paired peripheral blood samples, in patients during and after culture-confirmed Vibrio cholerae O1 infection. Immunohistochemical staining of duodenal biopsies from cholera patients (n = 5, median age 32 years, range 26-44, 1 female) identified MAIT cells in the lamina propria of the crypts, but not the villi. By flow cytometry (n = 10, median age 31 years, range 23-36, 1 female), we showed that duodenal MAIT cells are more activated than peripheral MAIT cells (p < 0.01 across time points), although there were no significant differences between duodenal MAIT cells at day 2 and day 30. We found fecal markers of intestinal permeability and inflammation to be correlated with the loss of duodenal (but not peripheral) MAIT cells, and single-cell sequencing revealed differing T cell receptor usage between the duodenal and peripheral blood MAIT cells. In this preliminary report limited by a small sample size, we show that MAIT cells are present in the lamina propria of the duodenum during V. cholerae infection, and more activated than those in the blood. Future work into the trafficking and tissue-resident function of MAIT cells is warranted.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Bispecific antibody targeting TROP2xCD3 suppresses tumor growth of triple negative breast cancer.
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 1 October 2021 by Liu, H., Bai, L., et al.
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a subtype of breast cancers with poor prognosis and targeted drug therapies are limited. To develop novel and efficacious therapies for TNBC, we developed a bispecific antibody F7AK3 that recognizes both trophoblast cell surface antigen 2 (TROP2) and CD3 and evaluated its antitumor activities both in vitro and in vivo.
The binding affinities of F7AK3 to the two targets, TROP2 and CD3, were evaluated by surface plasmon resonance. Binding of F7AK3 to TNBC cells and T cells were evaluated by flow cytometry. Immunofluorescent staining was performed to demonstrate the interactions between T cells with TNBC cells. The cytotoxicity of T cells against TNBC cell lines and primary tumor cells mediated by F7AK3 were determined in vitro. In vivo antitumor activity of F7AK3 was investigated in a xenograft TNBC tumor model, using immunodeficient mice that were reconstituted with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
We demonstrated that F7AK3 binds specifically to human TROP2 and CD3 antigens, as well as TNBC cell lines and primary tumor cells. Human T cells can only be activated by F7AK3 in the presence of target tumor cells. F7AK3 recruits T cells to TROP2+ tumor cells in vitro and into tumor tissues in vivo. Antitumor growth activity of F7AK3 is observed in a xenograft TNBC tumor model.
This study showed the antitumor potential of an anti-TROP2xCD3 bispecific antibody F7AK3 to TNBC tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. These data demonstrate that F7AK3 has the potential to treat TNBC patients, which warrants further preclinical and clinical evaluation of the F7AK3 in advanced or metastatic TNBC patients.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Nature Communications on 10 February 2021 by Ye, Z., Shen, Y., et al.
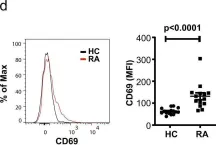
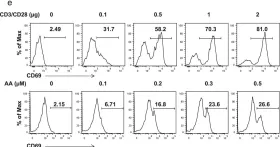
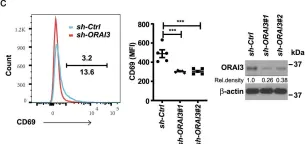
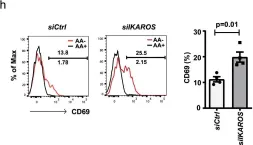
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are two distinct autoimmune diseases that manifest with chronic synovial inflammation. Here, we show that CD4+ T cells from patients with RA and PsA have increased expression of the pore-forming calcium channel component ORAI3, thereby increasing the activity of the arachidonic acid-regulated calcium-selective (ARC) channel and making T cells sensitive to arachidonic acid. A similar increase does not occur in T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Increased ORAI3 transcription in RA and PsA T cells is caused by reduced IKAROS expression, a transcriptional repressor of the ORAI3 promoter. Stimulation of the ARC channel with arachidonic acid induces not only a calcium influx, but also the phosphorylation of components of the T cell receptor signaling cascade. In a human synovium chimeric mouse model, silencing ORAI3 expression in adoptively transferred T cells from patients with RA attenuates tissue inflammation, while adoptive transfer of T cells from healthy individuals with reduced expression of IKAROS induces synovitis. We propose that increased ARC activity due to reduced IKAROS expression makes T cells more responsive and contributes to chronic inflammation in RA and PsA.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nat Commun on 10 February 2021 by Ye, Z., Shen, Y., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Nat Commun on 10 February 2021 by Ye, Z., Shen, Y., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Nat Commun on 10 February 2021 by Ye, Z., Shen, Y., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Nat Commun on 10 February 2021 by Ye, Z., Shen, Y., et al.
Fig.7.H

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Nat Commun on 3 August 2018 by Ye, Z., Li, G., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5