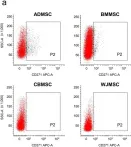
Human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) are isolated from a plethora of tissue sources for cell therapy purposes. In 2006, the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) published minimal guidelines to define MSC identity. Nevertheless, many independent studies demonstrated that cells meeting the ISCT criteria possessed heterogeneous phenotypes and functionalities, heavily influenced by culture conditions. In this study, human MSC derived from many adult (bone marrow and adipose tissue) or fetal (cord blood, Wharton's jelly, umbilical cord perivascular compartment and amniotic fluid) tissues were investigated. Their immunophenotype was analyzed to define consistent source-specific markers by extensive flow cytometry analysis and real-time qRT-PCR. CD271+ subpopulations were detected in adult MSC, whereas NG2 was significantly more expressed in fetal MSC but failed validation on independent samples coming from an external laboratory. The highest number of CD271+ adult MSC were detected soon after isolation in serum-based culture conditions. Furthermore, heterogeneous percentages of CD271 expression were found in platelet lysate-based or serum-free culture conditions. Finally, CD271+ adult MSC showed high clonogenic and osteogenic properties as compared to CD271- cells. To conclude, in this phenotype-function correlation study CD271+ subpopulation confers heterogeneity on adult MSC, confirming the need of more specific markers to address MSC properties.
Product Citations: 6
In Scientific Reports on 18 June 2018 by Barilani, M., Banfi, F., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Neuroscience
In Human Molecular Genetics on 15 June 2017 by Miller, E. E., Kobayashi, G. S., et al.
Biallelic loss-of-function mutations in the RNA-binding protein EIF4A3 cause Richieri-Costa-Pereira syndrome (RCPS), an autosomal recessive condition mainly characterized by craniofacial and limb malformations. However, the pathogenic cellular mechanisms responsible for this syndrome are entirely unknown. Here, we used two complementary approaches, patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and conditional Eif4a3 mouse models, to demonstrate that defective neural crest cell (NCC) development explains RCPS craniofacial abnormalities. RCPS iNCCs have decreased migratory capacity, a distinct phenotype relative to other craniofacial disorders. Eif4a3 haploinsufficient embryos presented altered mandibular process fusion and micrognathia, thus recapitulating the most penetrant phenotypes of the syndrome. These defects were evident in either ubiquitous or NCC-specific Eif4a3 haploinsufficient animals, demonstrating an autonomous requirement of Eif4a3 in NCCs. Notably, RCPS NCC-derived mesenchymal stem-like cells (nMSCs) showed premature bone differentiation, a phenotype paralleled by premature clavicle ossification in Eif4a3 haploinsufficient embryos. Likewise, nMSCs presented compromised in vitro chondrogenesis, and Meckel's cartilage was underdeveloped in vivo. These findings indicate novel and essential requirements of EIF4A3 for NCC migration and osteochondrogenic differentiation during craniofacial development. Altogether, complementary use of iPSCs and mouse models pinpoint unique cellular mechanisms by which EIF4A3 mutation causes RCPS, and provide a paradigm to study craniofacial disorders.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
-
FC/FACS
-
Genetics
Inheritable Silencing of Endogenous Genes by Hit-and-Run Targeted Epigenetic Editing.
In Cell on 22 September 2016 by Amabile, A., Migliara, A., et al.
Gene silencing is instrumental to interrogate gene function and holds promise for therapeutic applications. Here, we repurpose the endogenous retroviruses' silencing machinery of embryonic stem cells to stably silence three highly expressed genes in somatic cells by epigenetics. This was achieved by transiently expressing combinations of engineered transcriptional repressors that bind to and synergize at the target locus to instruct repressive histone marks and de novo DNA methylation, thus ensuring long-term memory of the repressive epigenetic state. Silencing was highly specific, as shown by genome-wide analyses, sharply confined to the targeted locus without spreading to nearby genes, resistant to activation induced by cytokine stimulation, and relieved only by targeted DNA demethylation. We demonstrate the portability of this technology by multiplex gene silencing, adopting different DNA binding platforms and interrogating thousands of genomic loci in different cell types, including primary T lymphocytes. Targeted epigenome editing might have broad application in research and medicine.
Copyright © 2016 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Genetics
Immunophenotypic characterization of ovine mesenchymal stem cells.
In Cytometry. Part A : the Journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology on 1 May 2016 by Khan, M. R., Chandrashekran, A., et al.
The clinical potential of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has led to the essential development of analytical tools such as antibodies against membrane-bound proteins for the immunophenotypic characterization of human and rodent cells. Such tools are frequently lacking for emerging large animal models like the sheep that have greater relevance for the study of human musculoskeletal diseases. The present study identified a set of commercial nonspecies specific monoclonal antibodies for the immunophenotypic characterization of ovine MSCs. A protocol combining the less destructive proteolytic activity of accutase and EDTA was initially developed for the detachment of cells from plastic with minimum loss of cell surface antigens. A range of commercially available antibodies against human or rodent MSC antigens were then tested in single and multistain-based assays for their cross-reactivity to bone marrow derived ovine MSCs. Antibody clones cross-reactive to ovine CD73 (96.9% ± 5.9), CD90 (99.6% ± 0.3), CD105 (99.1 ± 1.5), CD271 (97.7 ± 2.0), and MHC1 (94.0% ± 7.2) antigens were identified using previously reported CD29, CD44, and CD166 as positive controls. Multistaining analysis indicated the colocalization of these antigens on MSCs. Furthermore, antibody clones identified to cross-react against white blood cell antigens exhibited either negative (CD117 (0.1% ± 0.1)) or low (MHCII (10.5% ± 16.0); CD31 (14.6% ± 4.2), and CD45 (39.4% ± 31.8)) cross-reactivity with ovine MSCs. The validation of these antibody clones to sheep MSC antigens is essential for studies utilizing this large animal model for stem cell-based therapies. © 2016 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
© 2016 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
-
FC/FACS
-
Ovis aries (Sheep)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
-
Veterinary Research
Genetic approach to track neural cell fate decisions using human embryonic stem cells.
In Protein Cell on 1 January 2014 by Fu, X., Rong, Z., et al.
With their capability to undergo unlimited self-renewal and to differentiate into all cell types in the body, human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) hold great promise in human cell therapy. However, there are limited tools for easily identifying and isolating live hESC-derived cells. To track hESC-derived neural progenitor cells (NPCs), we applied homologous recombination to knock-in the mCherry gene into the Nestin locus of hESCs. This facilitated the genetic labeling of Nestin positive neural progenitor cells with mCherry. Our reporter system enables the visualization of neural induction from hESCs both in vitro (embryoid bodies) and in vivo (teratomas). This system also permits the identification of different neural subpopulations based on the intensity of our fluorescent reporter. In this context, a high level of mCherry expression showed enrichment for neural progenitors, while lower mCherry corresponded with more committed neural states. Combination of mCherry high expression with cell surface antigen staining enabled further enrichment of hESC-derived NPCs. These mCherry(+) NPCs could be expanded in culture and their differentiation resulted in a down-regulation of mCherry consistent with the loss of Nestin expression. Therefore, we have developed a fluorescent reporter system that can be used to trace neural differentiation events of hESCs.
-
FC/FACS
-
Genetics
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Sci Rep on 18 June 2018 by Barilani, M., Banfi, F., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1