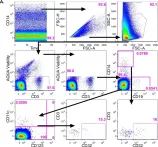
The majority of new Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-1 infections are acquired via sexual transmission at mucosal surfaces. Partial efficacy (31.2%) of the Thai RV144 HIV-1 vaccine trial has been correlated with Antibody-dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) mediated by non-neutralizing antibodies targeting the V1V2 region of the HIV-1 envelope. This has led to speculation that ADCC and other antibody-dependent cellular effector functions might provide an important defense against mucosal acquisition of HIV-1 infection. However, the ability of antibody-dependent cellular effector mechanisms to impact on early mucosal transmission events will depend on a variety of parameters including effector cell type, frequency, the class of Fc-Receptor (FcR) expressed, the number of FcR per cell and the glycoslyation pattern of the induced antibodies. In this study, we characterize and compare the frequency and phenotype of IgG (CD16 [FcγRIII], CD32 [FcγRII] and CD64 [FcγRI]) and IgA (CD89 [FcαR]) receptor expression on effector cells within male and female genital mucosal tissue, colorectal tissue and red blood cell-lysed whole blood. The frequency of FcR expression on CD14+ monocytic cells, myeloid dendritic cells and natural killer cells were similar across the three mucosal tissue compartments, but significantly lower when compared to the FcR expression profile of effector cells isolated from whole blood, with many cells negative for all FcRs. Of the three tissues tested, penile tissue had the highest percentage of FcR positive effector cells. Immunofluorescent staining was used to determine the location of CD14+, CD11c+ and CD56+ cells within the three mucosal tissues. We show that the majority of effector cells across the different mucosal locations reside within the subepithelial lamina propria. The potential implication of the observed FcR expression patterns on the effectiveness of FcR-dependent cellular effector functions to impact on the initial events in mucosal transmission and dissemination warrants further mechanistic studies.
Product Citations: 4
In PLoS ONE on 11 May 2016 by Cheeseman, H. M., Carias, A. M., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Scientific Reports on 24 February 2016 by Hogan, L. E., Jones, D. C., et al.
Antigen presenting cells (APC) are critical components of innate immunity and consequently shape the adaptive response. Leukocyte Ig Like Receptors (LILR) are innate immune receptors predominantly expressed on myeloid cells. LILR can influence the antigen presenting phenotype of monocytic cells to determine the nature of T cell responses in infections including Mycobaterium leprae. We therefore investigated the relevance of LILR in the context of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Real-time PCR studies indicated that the transcriptional profile of the orphan receptor LILRB5 was significantly up-regulated following exposure to mycobacteria. Furthermore, LILRA1 and LILRB5 were able to trigger signalling through direct engagement of mycobacteria using tranfectant cells incorporating a reporter system. We describe for the first time the expression of this receptor on T cells, and highlight the potential relevance to mycobacterial recognition. Furthermore, we demonstrate that crosslinking of this receptor on T cells increases proliferation of cytotoxic, but not helper, T cells.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology on 1 August 2014 by Blumchen, K., Beder, A., et al.
Threshold levels for peanut allergy determined by using oral challenges are important for the food industry with regard to allergen labeling. Moreover, the utility of biological markers in predicting threshold levels is uncertain.
We sought to use a modified oral food challenge regimen that might determine threshold levels for peanut allergy mimicking a more real-life exposure and to correlate the eliciting dose (ED) and severity of clinical reaction in children with peanut allergy with B-cell, T-cell, and effector cell markers.
A modified food challenge procedure with doses scheduled 2 hours apart was used in 63 children with peanut allergy. All children received a maximum of 8 semi-log increasing titration steps of roasted peanuts ranging from 3 to 4500 mg of peanut protein until objective allergic reactions occurred. Severity of symptoms was graded from I to V. Biological markers were measured before challenge.
Forty-five of 63 patients showed objective symptoms after greater than 30 minutes, with a median latency of clinical reaction of 55 minutes. By using a log-normal dose-distribution model, the ED5 was calculated to be 1.95 mg of peanut protein. The ED was significantly and inversely correlated with peanut- and Ara h 2-specific IgE levels, skin prick test responses, basophil activation, and TH2 cytokine production by PBMCs. Symptom severity did not correlate with any of the markers or the ED.
This modified food challenge procedure might better reflect threshold levels for peanut allergy than the standard procedure because most of the patients reacted at a time interval of greater than 30 minutes. By using this model, threshold levels, but not severity, could be correlated with biological markers.
Copyright © 2014 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology on 1 April 2009 by Wanich, N., Nowak-Wegrzyn, A., et al.
Children with milk allergy who tolerate heat-denatured milk (HM) have less severe reactions and outgrow the condition earlier than those who react to HM, which might be related to differences in IgE-dependent effector cell function.
We sought to apply a novel assay to test the hypothesis that HM-tolerant children have suppressed IgE-mediated basophil responses.
Allergic, HM-tolerant, outgrown, or control subjects were defined based on oral food challenges. Whole blood cells were stimulated in vitro with a range of milk allergen doses in the presence or absence of autologous serum or with dilutions of autologous serum. Activated basophils were identified by means of flow cytometry as CD63(bright)CD123+CD203c+HLA-DR(-)CD41a(-).
HM-tolerant subjects' basophils were significantly less responsive to milk allergen stimulation at all doses than were basophils from HM-reactive (allergic) individuals. In the absence of autologous serum, HM-tolerant subjects' basophils were significantly more reactive at low allergen concentrations. To a lesser extent, autologous serum also inhibited IL-3- and anti-IgE-induced, but not N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced, responses. The allergen-specific responsiveness of HM-tolerant subjects' basophils increased with dilution of autologous serum with normal pooled serum.
Children with milk allergy with a favorable prognosis have evidence of extrinsically suppressed allergen-specific effector cell reactivity.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS One on 11 May 2016 by Cheeseman, H. M., Carias, A. M., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1