Human induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) are increasingly used to identify potential factors capable of inducing endogenous cardiomyocyte proliferation to regenerate the injured heart. L-type calcium channel blockers have previously been identified as a class of factors capable of inducing matured hiPSC-CMs to proliferate. However, the mechanism by which L-type calcium channel blockers promote hiPSC-CM proliferation remains unclear. Here we provide evidence that matured hiPSC-CMs possess plasticity to undergo dematuration in response to certain pharmacological compounds. Consistent with primary cardiomyocyte maturation during perinatal development, we found that centrosome disassembly occurs in hiPSC-CMs during plate-based, temporal, maturation. A small molecule screen identified nitrendipine, an L-type calcium channel blocker, and 1-NA-PP1, a Src kinase inhibitor, as factors capable of inducing centrosome reassembly in a subpopulation of hiPSC-CMs. Furthermore, centrosome-positive hiPSC-CMs were more likely to exhibit cell cycle activity than centrosome-negative hiPSC-CMs. In contrast, neither nitrendipine or 1-NA-PP1 induced centrosome reassembly, or cell cycle activity, in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs). Differential bulk transcriptome analysis indicated that matured hiPSC-CMs, but not NRVMs, treated with nitrendipine or 1-NA-PP1 undergo dematuration. ScRNA transcriptome analysis supported that matured hiPSC-CMs treated with either nitrendipine or 1-NA-PP1 undergo dematuration. Collectively, our results indicate that matured hiPSC-CMs, but not primary NRVMs, possess plasticity to undergo dematuration in response to certain pharmacological compounds such as L-type calcium channel blockers and Src-kinase inhibitors. This study shows that once mature, hiPSC-CMs may not maintain their maturity under experimental conditions which may have implications for experimental systems where the state of hiPSC-CM maturation is relevant.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Product Citations: 55
Matured hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes possess dematuration plasticity.
In Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology Plus on 1 June 2025 by Meng, F., Kwok, M., et al.
In CNS Neuroscience Therapeutics on 1 January 2025 by Wu, Y., Liu, L., et al.
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a common and highly aggressive brain tumor with a poor prognosis. However, the prognostic value of ferroptosis-related genes (FRGs) and their classification remains insufficiently studied.
This study aims to explore the significance of ferroptosis classification and its risk model in GBM using multi-omics approaches and to evaluate its potential in prognostic assessment.
Ferroptosis-related genes (FRGs) were retrieved from databases such as FerrDB. The TCGA-GBM and CGGA-GBM datasets were used as training and testing cohorts, respectively. Univariate Cox regression and LASSO regression analyses were performed to establish a risk model comprising five genes (OSMR, G0S2, IGFBP6, IGHG2, FMOD). A Meta-analysis of integrated TCGA and GTEx data was conducted to examine the differential expression of these genes between GBM and normal tissues. Key gene protein expression differences were analyzed using CPTAC and HPA databases. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis was employed to explore the cell type-specific distribution of these genes.
The five-gene risk model demonstrated significant prognostic value in GBM. Meta-analysis revealed distinct expression patterns of the identified genes between GBM and normal tissues. Protein expression analysis confirmed these differences. scRNA-seq analysis highlighted the diverse distribution of these genes across different cell types, offering insights into their biological roles.
The ferroptosis-based risk model provides valuable prognostic insights into GBM and highlights potential therapeutic targets, emphasizing the biological significance of ferroptosis-related genes in tumor progression.
© 2025 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Concomitant loss of TET2 and TET3 results in T cell expansion and genomic instability in mice.
In Communications Biology on 3 December 2024 by Gioulbasani, M., Äijö, T., et al.
Ten eleven translocation (TET) proteins are tumor suppressors that through their catalytic activity oxidize 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, to promote DNA demethylation and to regulate gene expression. Notably, TET2 is one of the most frequently mutated genes in hematological malignancies, including T cell lymphomas. However, murine models with deletion of TET2 do not exhibit T cell expansion, presumably due to redundancy with other members of the TET family of proteins. In order to gain insight on the TET mediated molecular events that safeguard T cells from aberrant proliferation we performed serial adoptive transfers of murine CD4 T cells that lack concomitantly TET2 and TET3 to fully immunocompetent congenic mice. Here we show a progressive acquisition of malignant traits upon loss of TET2 and TET3 that is characterized by loss of genomic integrity, acquisition of aneuploidy and upregulation of the protooncogene Myc.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CRISPR-Cas9 immune-evasive hESCs are rejected following transplantation into immunocompetent mice.
In Front Genome Ed on 12 June 2024 by Frederiksen, H. R., Glantz, A., et al.
Although current stem cell therapies exhibit promising potential, the extended process of employing autologous cells and the necessity for donor-host matching to avert the rejection of transplanted cells significantly limit the widespread applicability of these treatments. It would be highly advantageous to generate a pluripotent universal donor stem cell line that is immune-evasive and, therefore, not restricted by the individual's immune system, enabling unlimited application within cell replacement therapies. Before such immune-evasive stem cells can be moved forward to clinical trials, in vivo testing via transplantation experiments in immune-competent animals would be a favorable approach preceding preclinical testing. By using human stem cells in immune competent animals, results will be more translatable to a clinical setting, as no parts of the immune system have been altered, although in a xenogeneic setting. In this way, immune evasiveness, cell survival, and unwanted proliferative effects can be assessed before clinical trials in humans. The current study presents the generation and characterization of three human embryonic stem cell lines (hESCs) for xenogeneic transplantation in immune-competent mice. The major histocompatibility complexes I- and II-encoding genes, B2M and CIITA, have been deleted from the hESCs using CRISPR-Cas9-targeted gene replacement strategies and knockout. B2M was knocked out by the insertion of murine CD47. Human-secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase (hSEAP) was inserted in a safe harbor site to track cells in vivo. The edited hESCs maintained their pluripotency, karyotypic normality, and stable expression of murine CD47 and hSEAP in vitro. In vivo transplantation of hESCs into immune-competent BALB/c mice was successfully monitored by measuring hSEAP in blood samples. Nevertheless, transplantation of immune-evasive hESCs resulted in complete rejection within 11 days, with clear immune infiltration of T-cells on day 8. Our results reveal that knockout of B2M and CIITA together with species-specific expression of CD47 are insufficient to prevent rejection in an immune-competent and xenogeneic context.
Copyright © 2024 Frederiksen, Glantz, Vøls, Skov, Tveden-Nyborg, Freude and Doehn.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Scientific Reports on 17 January 2024 by Singla, N., Nirschl, T. R., et al.
Novel perioperative strategies are needed to reduce recurrence rates in patients undergoing nephrectomy for high-risk, non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). We conducted a prospective, phase I trial of neoadjuvant nivolumab prior to nephrectomy in 15 evaluable patients with non-metastatic ccRCC. We leveraged tissue from that cohort to elucidate the effects of PD-1 inhibition on immune cell populations in ccRCC and correlate the evolving immune milieu with anti-PD-1 response. We found that nivolumab durably induces a pro-inflammatory state within the primary tumor, and baseline immune infiltration within the primary tumor correlates with nivolumab responsiveness. Nivolumab increases CTLA-4 expression in the primary tumor, and subsequent nephrectomy increases circulating concentrations of sPD-L1, sPD-L3 (sB7-H3), and s4-1BB. These findings form the basis to consider neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) for high-risk ccRCC while the tumor remains in situ and provide the rationale for perioperative strategies of novel ICI combinations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
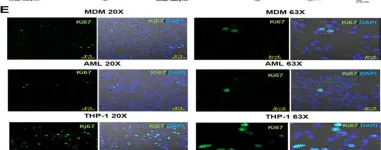
In MBio on 31 August 2023 by Pahari, S., Arnett, E., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from MBio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
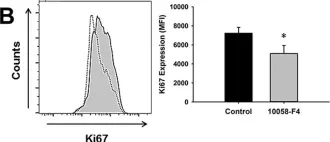
In Sci Rep on 29 August 2017 by Bellio, M. A., Pinto, M. T., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2