Background: Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is a neuropathological condition marked by cognitive deterioration and chronic neuroinflammation. Previous investigations have unveiled a strong correlation between the gut microbiota and the progression of AD. In this study, our objective is to probe the effects of Parabacteroides distasonis ( P.distasonis ), previously found to be conspicuously diminished in AD patients, on the APP/PS1 mice model. Methods: : To assess the impact of orally administered P.distasonis on gut microbiota and metabolites, we utilized 16s rDNA sequencing and GC-MS to analyze gut composition and short-chain fatty acids in APP/PS1 mice after one month of P.distasonis gavage. To investigate the effects of P.distasonis administration over a six-month period on APP/PS1 mice, we evaluated cognitive function using novel object recognition and Y-maze tests, assessed intestinal barrier integrity and AD-related pathological features with immunofluorescence, and analyzed immune cell subpopulations in intestine, blood, spleen, and brain tissues via flow cytometry. The Luminex assay was employed to detect inflammatory cytokine secretion in the same regions. Results: : One-month oral administration of P.distasonis modulated the gut microbiota, elevated butyrate levels. Six-month oral administration of P.distasonis improved cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice, reducing Aβ deposition and inhibiting glial cell proliferation. It also amplified Treg cells within the gut, concomitant with the decreased Th1 proliferation and intestinal inflammation. Additionally, we observed the migration of peripheral CD4 + T cells to the brain through chemotaxis, accompanied by an increase in Treg cells and higher levels of anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-10 and TGF-β in the brain. Collectively, these multifaceted effects contributed to the alleviation of neuroinflammation. Conclusion: These findings underscore the potential of transplanting P.distasonis in alleviating AD-related pathology, suggesting a role for gut microbiota in neuroinflammation attenuation.
Product Citations: 4
Preprint on Research Square on 29 March 2024 by Jiang, J., He, Y., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In eLife on 12 August 2021 by Hirano, K. I., Hosokawa, H., et al.
Notch signaling primarily determines T-cell fate. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the maintenance of T-lineage potential in pre-thymic progenitors remain unclear. Here, we established two murine Ebf1-deficient pro-B cell lines, with and without T-lineage potential. The latter expressed lower levels of Lmo2; their potential was restored via ectopic expression of Lmo2. Conversely, the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of Lmo2 resulted in the loss of the T-lineage potential. Introduction of Bcl2 rescued massive cell death of Notch-stimulated pro-B cells without efficient LMO2-driven Bcl11a expression but was not sufficient to retain their T-lineage potential. Pro-B cells without T-lineage potential failed to activate Tcf7 due to DNA methylation; Tcf7 transduction restored this capacity. Moreover, direct binding of LMO2 to the Bcl11a and Tcf7 loci was observed. Altogether, our results highlight LMO2 as a crucial player in the survival and maintenance of T-lineage potential in T-cell progenitors via the regulation of the expression of Bcl11a and Tcf7.
© 2021, Hirano et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In RSC Advances on 27 May 2020 by Zhu, X., Ji, W., et al.
Immunometabolism determines the fate and function of regulatory T cells. The metabolic phenotype of regulatory T cells (Treg) is affected by various factors. The relationship between Treg metabolism and function of mice with sepsis is not clear. We used liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to analyze the metabolic profiles of freshly-isolated spleen Treg cells in mice with sepsis. It was found that in severe infection, activated Treg cells depend on glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation, and inhibition of metabolic pathways has a significant impact on the number and quality of Treg cells. Understanding the metabolic characteristics of Treg cells in the real environment in the body helps to grasp the function of Treg cells and even the overall immune status. Targeting the metabolic pathway of Treg may provide a new method for the treatment of sepsis.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 7 April 2017 by Dai, K., Huang, L., et al.
The mechanisms by which tumor-responsive CD8+ T cells are regulated are important for understanding the tumor immunity and for developing new therapeutic strategies. In current study, we identified the expression of 1810011o10 Rik, which is the homolog of human thyroid cancer 1, in intratumoral activated CD8+ T cells in a murine hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) implantation model. To investigate the role of 1810011o10 Rik in the regulation of antitumor activity of CD8+ T cells, normal CD8+ T cells were transduced with 1810011o10 Rik-expressing lentiviruses. Although 1810011o10 Rik overexpression did not influence agonistic antibody-induced CD8+ T cell activation in vitro, it inhibited the cytotoxic efficacy of CD8+ T cells on HCC cells in vivo. 1810011o10 Rik overexpression impeded CD8+ T cell-mediated HCC cell apoptosis and favored tumor cell growth in vivo. Further investigation revealed that 1810011o10 Rik blocked the nuclear translocation of Notch2 intracellular domain, which is crucial for CD8+ T cell activity. Furthermore, a brief in vitro experiment suggested that both antigen-presenting cells and TGF-β might be necessary for the upregulation of Rik expression in activated CD8+ T cells. In general, our study disclosed a novel mechanism underlying the negative regulation of antitumor CD8+ T cells during HCC progression.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
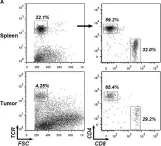
In Front Immunol on 7 April 2017 by Dai, K., Huang, L., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1