Immune checkpoint inhibitors are associated with immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including arthritis (arthritis-irAE). Management of arthritis-irAE is challenging because immunomodulatory therapy for arthritis should not impede antitumor immunity. Understanding of the mechanisms of arthritis-irAE is critical to overcome this challenge, but the pathophysiology remains unknown. Here, we comprehensively analyze peripheral blood and/or synovial fluid samples from 20 patients with arthritis-irAE, and unmask a prominent Th1-CD8+ T cell axis in both blood and inflamed joints. CX3CR1hi CD8+ T cells in blood and CXCR3hi CD8+ T cells in synovial fluid, the most clonally expanded T cells, significantly share TCR repertoires. The migration of blood CX3CR1hi CD8+ T cells into joints is possibly mediated by CXCL9/10/11/16 expressed by myeloid cells. Furthermore, arthritis after combined CTLA-4 and PD-1 inhibitor therapy preferentially has enhanced Th17 and transient Th1/Th17 cell signatures. Our data provide insights into the mechanisms, predictive biomarkers, and therapeutic targets for arthritis-irAE.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 10
In Nature Communications on 12 April 2022 by Kim, S. T., Chu, Y., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 23 November 2021 by Perveen, K., Quach, A., et al.
Cord blood T cells (CBTC) from a proportion of newborns express low/deficient levels of some protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes, with low levels of PKCζ correlating with increased risk of developing allergy and associated decrease in interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) producing T cells. Interestingly, these lower levels of PKCζ were increased/normalized by supplementing women during pregnancy with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. However, at present, we have little understanding of the transient nature of the deficiency in the neonate and how PKCζ relates to other PKC isozymes and whether their levels influence maturation into IFN-γ producing T cells. There is also no information on PKCζ isozyme levels in the T cell subpopulations, CD4+ and CD8+ cells. These issues were addressed in the present study using a classical culture model of neonatal T cell maturation, initiated with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2). Of the isozymes evaluated, PKCζ, β2, δ, μ, ε, θ and λ/ι were low in CBTCs. The PKC isozyme deficiencies were also found in the CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subset levels of the PKC isozymes correlated between the two subpopulations. Examination of changes in the PKC isozymes in these deficient cells following addition of maturation signals showed a significant increase in expression within the first few hours for PKCζ, β2 and μ, and 1-2 days for PKCδ, ε, θ and λ/ι. Only CBTC PKCζ isozyme levels correlated with cytokine production, with a positive correlation with IFN-γ, interleukin (IL)-2 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF), and a negative association with IL-9 and IL-10. The findings reinforce the specificity in using CBTC PKCζ levels as a biomarker for risk of allergy development and identify a period in which this can be potentially 'corrected' after birth.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 5 May 2021 by Perveen, K., Quach, A., et al.
Low Protein Kinase C zeta (PKCζ) levels in cord blood T cells (CBTC) have been shown to correlate with the development of allergic sensitization in childhood. However, little is known about the mechanisms responsible. We have examined the relationship between the expression of different levels of PKCζ in CBTC and their development into mature T cell cytokine producers that relate to allergy or anti-allergy promoting cells. Maturation of naïve CBTC was initiated with anti-CD3/-CD28 antibodies and recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2). To stimulate lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production the cells were treated with Phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and Phorbol myristate acetate (PMA). Irrespective of the PKCζ levels expressed, immature CBTC showed no difference in lymphocyte proliferation and the production of T helper 2 (Th2) cytokine interleukin-4 (IL-4) and Th1 cytokine, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and influenced neither their maturation from CD45RA+ to CD45RO+ cells nor cell viability/apoptosis. However, upon maturation the low PKCζ expressing cells produced low levels of the Th1 cytokines, IFN-γ, IL-2 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF), no changes to levels of the Th2 cytokines, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13, and an increase in the Th9 cytokine, IL-9. Other cytokines, lymphotoxin-α (LT-α), IL-10, IL-17, IL-21, IL-22 and Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) were not significantly different. The findings support the view that low CBTC PKCζ levels relate to the increased risk of developing allergic diseases.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Therapeutic Targeting of Th17/Tc17 Cells Leads to Clinical Improvement of Lichen Planus.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 17 August 2019 by Solimani, F., Pollmann, R., et al.
Lichen planus (LP) is a common, chronic relapsing inflammatory disorder of the skin and mucous membranes which often poses a major therapeutic challenge due to its refractory course. Novel pathogenesis-based therapies are urgently needed. As several studies have shown that IL-17 may contribute to LP pathogenesis, we investigated whether therapeutic targeting of IL-17+ T cells leads to clinical improvement of mucosal and cutaneous LP lesions. A total of five patients with lichen planus were treated in a compassionate use trial with either secukinumab (anti-IL-17; 3 patients with acute and chronic recalcitrant muco-cutaneous LP), ustekinumab (anti-IL-12/IL-23; 1 patient with recalcitrant oral LP) or guselkumab (anti-IL-23; 1 patient with recalcitrant oral LP). The clinical course of the patients was assessed by the Autoimmune Bullous Skin Disorder Intensity Score (ABSIS) reflecting both extent and severity of disease and functional sequelae of oral involvement for at least 12 weeks. The inflammatory infiltrate in lesional and post-lesional skin was analyzed by immunohistochemistry before and after treatment. Furthermore, the cytokine profile of peripheral blood T cells from the treated patients was assessed by flow cytometry and/or ELISpot assay. Treatment with secukinumab induced rapid and prolonged clinical amelioration of muco-cutaneous LP. Clinical improvement was accompanied by a strong reduction of the Th1 and Th17/Tc17 cellular mucosal and cutaneous infiltrate. Moreover, long-term treatment of one patient with recalcitrant oral LP with ustekinumab led to healing of the ulcerative oral lesions and a reduction of peripheral blood and lesional IL-17+ T cells. Finally, treatment with guselkumab led to a marked clinical improvement in a patient with recalcitrant erosive oral LP. These findings show for the first time that therapeutic targeting of Th17/Tc17 cells leads to a pronounced clinical amelioration of mucosal and cutaneous LP and strongly suggests that IL-17-producing T cells are central to disease pathogenesis. Thus, therapeutic targeting of Th17/Tc17 cells opens new therapeutic avenues in the treatment of recalcitrant LP.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Virology on 15 February 2019 by Helmold Hait, S., Vargas-Inchaustegui, D. A., et al.
T follicular helper (TFH) cells are fundamental in germinal center (GC) maturation and selection of antigen-specific B cells within secondary lymphoid organs. GC-resident TFH cells have been fully characterized in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. However, the role of GC TFH cells in GC B cell responses following various simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) vaccine regimens in rhesus macaques (RMs) has not been fully investigated. We characterized GC TFH cells of RMs over the course of a mucosal/systemic vaccination regimen to elucidate GC formation and SIV humoral response generation. Animals were mucosally primed twice with replicating adenovirus type 5 host range mutant (Ad5hr)-SIV recombinants and systemically boosted with ALVAC-SIVM766Gag/Pro/gp120-TM and SIVM766&CG7V gD-gp120 proteins formulated in alum hydroxide (ALVAC/Env) or DNA encoding SIVenv/SIVGag/rhesus interleukin 12 (IL-12) plus SIVM766&CG7V gD-gp120 proteins formulated in alum phosphate (DNA&Env). Lymph nodes were biopsied in macaque subgroups prevaccination and at day 3, 7, or 14 after the 2nd Ad5hr-SIV prime and the 2nd vector/Env boost. Evaluations of GC TFH and GC B cell dynamics including correlation analyses supported a significant role for early GC TFH cells in providing B cell help during initial phases of GC formation. GC TFH responses at day 3 post-mucosal priming were consistent with generation of Env-specific memory B cells in GCs and elicitation of prolonged Env-specific humoral immunity in the rectal mucosa. GC Env-specific memory B cell responses elicited early post-systemic boosting correlated significantly with decreased viremia postinfection. Our results highlight the importance of early GC TFH cell responses for robust GC maturation and generation of long-lasting SIV-specific humoral responses at mucosal and systemic sites. Further investigation of GC TFH cell dynamics should facilitate development of an efficacious HIV vaccine.IMPORTANCE The modest HIV protection observed in the human RV144 vaccine trial associated antibody responses with vaccine efficacy. T follicular helper (TFH) cells are CD4+ T cells that select antibody secreting cells with high antigenic affinity in germinal centers (GCs) within secondary lymphoid organs. To evaluate the role of TFH cells in eliciting prolonged virus-specific humoral responses, we vaccinated rhesus macaques with a combined mucosal prime/systemic boost regimen followed by repeated low-dose intrarectal challenges with SIV, mimicking human exposure to HIV-1. Although the vaccine regimen did not prevent SIV infection, decreased viremia was observed in the immunized macaques. Importantly, vaccine-induced TFH responses elicited at day 3 postimmunization and robust GC maturation were strongly associated. Further, early TFH-dependent SIV-specific B cell responses were also correlated with decreased viremia. Our findings highlight the contribution of early vaccine-induced GC TFH responses to elicitation of SIV-specific humoral immunity and implicate their participation in SIV control.
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS One on 20 January 2016 by Li, L., Jiang, Y., et al.
Fig.8.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
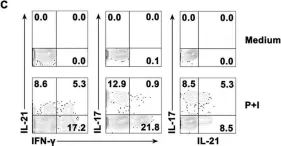
In Oncotarget on 6 October 2015 by Wu, C., Li, Z., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Oncotarget on 6 October 2015 by Wu, C., Li, Z., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3