CD8 T cell differentiation is orchestrated by dynamic metabolic changes that direct activation, proliferation, cytotoxic function, and epigenetic changes. We report that the BTB-ZF family transcriptional repressor Zbtb20 negatively regulates CD8 T cell metabolism and memory differentiation in mice. Effector and memory CD8 T cells with conditional Zbtb20 deficiency displayed enhanced mitochondrial and glycolytic metabolism, and memory CD8 T cells had enhanced spare respiratory capacity. Furthermore, Zbtb20-deficient CD8 T cells displayed increased flexibility in the use of mitochondrial fuel sources. Phenotypic and transcriptional skewing toward the memory fate was observed during the CD8 T cell response to Listeria monocytogenes Memory cells mounted larger secondary responses and conferred better protection following tumor challenge. These data suggest that inactivation of Zbtb20 may offer an approach to enhance metabolic activity and flexibility and improve memory CD8 T cell differentiation, useful attributes for T cells used in adoptive immunotherapy.Copyright © 2020 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Product Citations: 5
In The Journal of Immunology on 15 November 2020 by Sun, Y., Preiss, N. K., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 10 September 2019 by Olson, W. J., Jakic, B., et al.
CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells are specialized in helping B cells during the germinal center (GC) reaction and ultimately promote long-term humoral immunity. Here we report that loss of the nuclear orphan receptor NR2F6 causes enhanced survival and accumulation of Tfh cells, GC B cells, and plasma cells (PCs) following T cell-dependent immunization. Nr2f6-deficient CD4 T cell dysfunction is the primary cause of cell accumulation. Cytokine expression in Nr2f6-deficient Tfh cells is dysregulated, and Il21 expression is enhanced. Mechanistically, NR2F6 binds directly to the interleukin 21 (IL-21) promoter and a conserved noncoding sequence (CNS) near the Il21 gene in resting CD4+ T cells. During Tfh cell differentiation, this direct NR2F6 DNA interaction is abolished. Enhanced Tfh cell accumulation in Nr2f6-deficient mice can be reverted by blocking IL-21R signaling. Thus, NR2F6 is a critical negative regulator of IL-21 cytokine production in Tfh cells and prevents excessive Tfh cell accumulation.Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
In Immunity on 16 July 2019 by Chisolm, D. A., Cheng, W., et al.
Genetic variation influences how the genome is interpreted in individuals and in mouse strains used to model immune responses. We developed approaches to utilize next-generation sequencing datasets to identify sequence variation in genes and enhancer elements in congenic and backcross mouse models. We defined genetic variation in the widely used B6-CD45.2 and B6.SJL-CD45.1 congenic model, identifying substantial differences in SJL genetic content retained in B6.SJL-CD45.1 strains on the basis of the vendor source of the mice. Genes encoding PD-1, CD62L, Bcl-2, cathepsin E, and Cxcr4 were within SJL genetic content in at least one vendor source of B6.SJL-CD45.1 mice. SJL genetic content affected enhancer elements, gene regulation, protein expression, and amino acid content in CD4+ T helper 1 cells, and mice infected with influenza showed reduced expression of Cxcr4 on B6.SJL-CD45.1 T follicular helper cells. These findings provide information on experimental variables and aid in creating approaches that account for genetic variables.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Follicular regulatory T cells impair follicular T helper cells in HIV and SIV infection.
In Nature Communications on 20 October 2015 by Miles, B., Miller, S. M., et al.
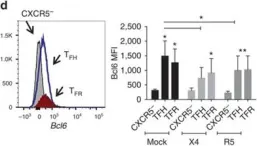
Human and simian immunodeficiency viruses (HIV and SIV) exploit follicular lymphoid regions by establishing high levels of viral replication and dysregulating humoral immunity. Follicular regulatory T cells (TFR) are a recently characterized subset of lymphocytes that influence the germinal centre response through interactions with follicular helper T cells (TFH). Here, utilizing both human and rhesus macaque models, we show the impact of HIV and SIV infection on TFR number and function. We find that TFR proportionately and numerically expand during infection through mechanisms involving viral entry and replication, TGF-β signalling, low apoptosis rates and the presence of regulatory dendritic cells. Further, TFR exhibit elevated regulatory phenotypes and impair TFH functions during HIV infection. Thus, TFR contribute to inefficient germinal centre responses and inhibit HIV and SIV clearance.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Macaca mulatta (Rhesus Monkey)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Leukocyte Biology on 1 January 2015 by Neumann, B., Klippert, A., et al.
B cells, as an important part of the humoral immune response, are generated in the BM, migrate to secondary lymphoid organs, and upon activation, differentiate into antibody-producing memory B cells or plasma cells. Despite the pivotal roles that they play in different diseases, a comprehensive characterization in healthy rhesus macaques, which serve as valuable models for a variety of human diseases, is still missing. With the use of multiparameter flow cytometry, we analyzed B cells in BM collected from two locations, i.e., the iliac crest (BMca) and the femur (BMfem), PB, as well as secondary lymphoid organs of healthy rhesus macaques. We assessed the frequencies of immature and mature B cells, as well as CD19(+) CD20(-) CD38(+/++) CD138(+/++) plasmablasts/plasma cells. Furthermore, we found site-specific differences in the expression of markers for B cell activation and proliferation, chemokine receptors and Igs, as well as the distribution of memory B cell subpopulations. As secondary lymphoid organs harbor the highest frequencies of naive B cells, expression of CD80, CD95, and Ki67 was lower compared with B cells in the periphery and BM, whereas expression of IgD, CXCR4 (CD184), and CCR7 (CD197) was higher. Interestingly, BMca differed from BMfem regarding frequencies of B cells, their expression of CD80 and CXCR4, T cells, and plasma cells. In summary, these data identify baseline values for the above-mentioned parameters and provide the foundation for future studies on B and plasma cells in different diseases.© Society for Leukocyte Biology.
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nat Commun on 20 October 2015 by Miles, B., Miller, S. M., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1