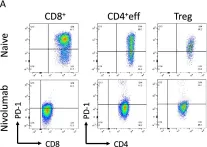
Novel perioperative strategies are needed to reduce recurrence rates in patients undergoing nephrectomy for high-risk, non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). We conducted a prospective, phase I trial of neoadjuvant nivolumab prior to nephrectomy in 15 evaluable patients with non-metastatic ccRCC. We leveraged tissue from that cohort to elucidate the effects of PD-1 inhibition on immune cell populations in ccRCC and correlate the evolving immune milieu with anti-PD-1 response. We found that nivolumab durably induces a pro-inflammatory state within the primary tumor, and baseline immune infiltration within the primary tumor correlates with nivolumab responsiveness. Nivolumab increases CTLA-4 expression in the primary tumor, and subsequent nephrectomy increases circulating concentrations of sPD-L1, sPD-L3 (sB7-H3), and s4-1BB. These findings form the basis to consider neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) for high-risk ccRCC while the tumor remains in situ and provide the rationale for perioperative strategies of novel ICI combinations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 5
In Scientific Reports on 17 January 2024 by Singla, N., Nirschl, T. R., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In The EMBO Journal on 18 September 2023 by Karger, A., Mansouri, S., et al.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) influence the transcription of gene networks in many cell types, but their role in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) is still largely unknown. We found that the lncRNA ADPGK-AS1 was substantially upregulated in artificially induced M2-like human macrophages, macrophages exposed to lung cancer cells in vitro, and TAMs from human lung cancer tissue. ADPGK-AS1 is partly located within mitochondria and binds to the mitochondrial ribosomal protein MRPL35. Overexpression of ADPGK-AS1 in macrophages upregulates the tricarboxylic acid cycle and promotes mitochondrial fission, suggesting a phenotypic switch toward an M2-like, tumor-promoting cytokine release profile. Macrophage-specific knockdown of ADPGK-AS1 induces a metabolic and phenotypic switch (as judged by cytokine profile and production of reactive oxygen species) to a pro-inflammatory tumor-suppressive M1-like state, inhibiting lung tumor growth in vitro in tumor cell-macrophage cocultures, ex vivo in human tumor precision-cut lung slices, and in vivo in mice. Silencing ADPGK-AS1 in TAMs may thus offer a novel therapeutic strategy for lung cancer.
© 2023 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY NC ND 4.0 license.
-
FC/FACS
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 23 August 2022 by Alfonso-Dunn, R., Lin, J., et al.
Immunocompromised individuals, including multiple sclerosis (MS) patients on certain immunotherapy treatments, are considered susceptible to complications from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and specific vaccination regimens have been recommended for suitable protection. MS patients receiving anti-CD20 therapy (aCD20-MS) are considered especially vulnerable due to acquired B-cell depletion and impaired antibody production in response to virus infection and COVID-19 vaccination. Here, the humoral and cellular responses are analyzed in a group of aCD20-MS patients (n=43) compared to a healthy control cohort (n=34) during the first 6 months after a 2-dose cycle mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccination. Both IgG antibodies recognizing receptor binding domain (RBD) from CoV-2 spike protein and their blocking activity against RBD-hACE2 binding were significantly reduced in aCD20-MS patients, with a seroconversion rate of only 23.8%. Interestingly, even under conditions of severe B-cell depletion and failed seroconversion, a significantly higher polyfunctional IFNγ+ and IL-2+ T-cell response and strong T-cell proliferation capacity were detected compared to controls. Moreover, no difference in T-cell response was observed between forms of disease (relapsing remitting- vs progressive-MS), anti-CD20 therapy (Rituximab vs Ocrelizumab) and type of mRNA-based vaccine received (mRNA-1273 vs BNT162b2). These results suggest the generation of a partial adaptive immune response to COVID-19 vaccination in B-cell depleted MS individuals driven by a functionally competent T-cell arm. Investigation into the role of the cellular immune response is important to identifying the level of protection against SARS-CoV-2 in aCD20-MS patients and could have potential implications for future vaccine design and application.
Copyright © 2022 Alfonso-Dunn, Lin, Kirschner, Lei, Feuer, Malin, Liu, Roche and Sadiq.
-
FC/FACS
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 7 July 2020 by Gomez-Lopez, N., Arenas-Hernandez, M., et al.
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been exhaustively investigated during early pregnancy; however, their role later in gestation is poorly understood. Herein, we report that functional Tregs are reduced at the maternal-fetal interface in a subset of women with idiopathic preterm labor/birth, which is accompanied by a concomitant increase in Tc17 cells. In mice, depletion of functional Tregs during late gestation induces preterm birth and adverse neonatal outcomes, which are rescued by the adoptive transfer of such cells. Treg depletion does not alter obstetrical parameters in the mother, yet it increases susceptibility to endotoxin-induced preterm birth. The mechanisms whereby depletion of Tregs induces adverse perinatal outcomes involve tissue-specific immune responses and mild systemic maternal inflammation, together with dysregulation of developmental and cellular processes in the placenta, in the absence of intra-amniotic inflammation. These findings provide mechanistic evidence supporting a role for Tregs in the pathophysiology of idiopathic preterm labor/birth and adverse neonatal outcomes.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy : CII on 1 December 2016 by van Poelgeest, M. I., Visconti, V. V., et al.
Adoptive transfer of tumor-specific T cells, expanded from tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes or from peripheral blood, is a promising immunotherapeutic approach for the treatment of cancer. Here, we studied whether the tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLN) of patients with human papillomavirus (HPV)-induced cervical cancer can be used as a source for ACT. The objectives were to isolate lymph node mononuclear cells (LNMC) from TDLN and optimally expand HPV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells under clinical grade conditions. TDLN were isolated from 11 patients with early-stage cervical cancer during radical surgery. Isolated lymphocytes were expanded in the presence of HPV16 E6 and E7 clinical grade synthetic long peptides and IL-2 for 22 days and then analyzed for HPV16 specificity by proliferation assay, multiparameter flow cytometry and cytokine analysis as well as for CD25 and FoxP3 expression. Stimulation of LNMC resulted in expansion of polyclonal HPV-specific T cells in all patients. On average a 36-fold expansion of a CD4+ and/or CD8+ HPV16-specific T cell population was observed, which maintained its capacity for secondary expansion. The T helper type 1 cytokine IFNγ was produced in all cell cultures and in some cases also the Th2 cytokines IL-10 and IL-5. The procedure was highly reproducible, as evidenced by complete repeats of the stimulation procedures under research and under full good manufacturing practice conditions. In conclusion, TDLN represent a rich source of polyclonal HPV16 E6- and E7-specific T cells, which can be expanded under clinical grade conditions for adoptive immunotherapy in patients with cervical cancer.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2024 by Singla, N., Nirschl, T. R., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1