Camel milk has demonstrated robust immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties in various clinical and experimental studies. However, no previous studies have characterized the cellular immunological effects of camel milk in the context of allergic asthma. Therefore, the present work aimed to evaluate the protective effects of camel milk in house dust mite induced asthma in mice, which emulate human pulmonary inflammation. Female BALB/c mice aged 8- to 10-week-old were intranasally sensitized with vehicle or HDM in 2.5 µl (5 µg) per nostril, 5 days a week for 3 weeks. On day 22, mice received an HDM challenge by a large volume but low dose into the lung (5 µg in 50µl) using intranasal inoculation. Using oral gavage technique, CM/HDM group mice received 0.5 ml of camel milk or vehicle five times a week, starting a day prior to sensitization. On day 23 following HDM challenge, mice were exposed to serial challenges with 10, 20, 40 and 100 mg/ml aerosolized methacholine to measure lung dynamics. Furthermore, BALF and whole lung samples were harvested to examine pulmonary inflammation. Camel milk effectively inhibited both HDM-induced infiltration of eosinophils and AHR. In addition to this, camel milk downregulates the number of pulmonary Th2 and Th17 cells and suppressed CCL17 expression in whole lung homogenates. Furthermore, camel milk reduced HDM-induced IL-4 and IL-13 expression following in vitro restimulation of pulmonary T cell subsets. Additionally, camel milk suppressed total concentrations of IL-5 and IL-13 in the lung. These results corroborate the asthma-preventive potential of camel milk and highlight the significance of diminished local concentrations of Th2- associated cytokines. In the present study, the observed downregulation of asthma progression by camel milk suggests its potential health benefits; however, further experimental and controlled clinical trials are needed before it can be considered a supplementary approach for allergic asthma management.
Copyright: © 2025 Rakhmatulina et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Product Citations: 63
The effect of camel milk on house dust mite allergen induced asthma model in BALB/C mice.
In PLoS ONE on 27 June 2025 by Rakhmatulina, A., Kenenbay, S., et al.
KLRG1 identifies regulatory T cells with mitochondrial alterations that accumulate with aging.
In Nature Aging on 1 May 2025 by Soto-Heredero, G., Gabandé-Rodríguez, E., et al.
Recent studies using single-cell RNA sequencing technology have uncovered several subpopulations of CD4+ T cells that accumulate with aging. These age-associated T cells are emerging as relevant players in the onset of inflammaging and tissue senescence. Here, based on information provided by single-cell RNA sequencing data, we present a flow cytometry panel that allows the identification of age-associated T cell subsets in systematic larger analysis in mice. We use this panel to evaluate at the single-cell level mitochondrial and senescence marks in the different age-associated CD4+ T cell subpopulations. Our analysis identifies a subpopulation of regulatory T (Treg) cells that is characterized by the extracellular expression of the co-inhibitory molecule killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G member 1 (KLRG1) and accumulates with aging in humans and mice. KLRG1-expressing Treg cells display senescence features such as mitochondrial alterations, increased expression of cell-cycle regulators and genomic DNA damage. Functionally, KLRG1+ Treg cells show a reduced suppressive activity in vivo accompanied by a pro-inflammatory phenotype.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
NETs-CD44-IL-17A Feedback Loop Drives Th17-Mediated Inflammation in Behçet's Uveitis.
In Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) on 1 April 2025 by Wu, Y., Ning, K., et al.
Behçet's uveitis (BU) is a severe ocular manifestation of Behçet's disease, typically accompanied by abnormal neutrophil infiltration and hyperactivation. However, the underlying causes of excessive neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) production and mechanisms by which NETs contribute to the pathogenesis of BU remain incompletely understood. Neutrophils from BU patients exhibit a higher propensity for NETs release compared to healthy controls. In the experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU), neutrophils are observed to exert pro-inflammatory effects through NETs. Clearing NETs can inhibit T helper 17 (Th17) cell differentiation and significantly alleviate EAU symptoms. In vivo and in vitro experiments demonstrate neutralizing IL-17A markedly reducing neutrophil infiltration and NETs formation in EAU. Single-cell RNA sequencing confirms that CD44 plays a key role in mediating interactions between NETs and Th17 cells. Antagonizing CD44 inhibits the proportion of Th17 cells and NETs formation. Multiplex immunofluorescence and cell communication analyses further demonstrate interactions and colocalization between NETs and CD44highCD4+T cells in EAU. NETs induce Th17 differentiation via upregulating CD44, and in turn, Th17 cells secrete IL-17A to recruit neutrophils and promote NETs formation. Interrupting NETs-CD44-IL-17A feedback loop may be a potential therapeutic target for BU.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In IScience on 21 March 2025 by Okoye, G. D., Kumar, A., et al.
Early immune dynamics during the initiation of fatal tularemia caused by Francisella tularensis infection remain unknown. Unto that end, we generated a transcriptomic map at single-cell resolution of the innate-like lymphocyte responses to F. tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS) infection of mice. We found that both interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-producing type 1 and interleukin-17 (IL-17)-producing type 3 innate-like lymphocytes expanded in the infected lungs. Natural killer (NK) and NKT cells drove the type 1 response, whereas mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) and γδ T cells drove the type 3 response. Furthermore, tularemia-like disease resistant NKT cell-deficient, Cd1d -/- mice accumulated more MAIT1 cells, MAIT17 cells, and cells with a hybrid phenotype between MAIT1 and MAIT17 cells than wild-type mice. Critically, adoptive transfer of LVS-activated MAIT cells from Cd1d -/- mice, which were enriched in MAIT17 cells, was sufficient to protect LVS-susceptible, immunodeficient RAG2 -/- mice from severe LVS infection-inflicted pathology. Collectively, our findings position MAIT cells as potential mediators of IL-17-dependent protection from pulmonary tularemia-like disease.
© 2025 The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
ITGAX promotes Th17-cell differentiation and drives pathogenesis in pediatric ulcerative colitis.
In Histology and Histopathology on 6 March 2025 by Xie, W. & Zhan, D.
Pediatric ulcerative colitis (UC) is an inflammatory bowel disease characterized by dysregulated immune responses and intestinal inflammation, often more severe than adult-onset UC. Th17 cells play a crucial role in UC pathogenesis but the mechanisms regulating their differentiation and recruitment in pediatric UC remain incompletely understood.
Transcriptomic analysis of pediatric UC patients and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were performed to identify key dysregulated genes. The functional role of the candidate gene ITGAX was investigated using in vitro Th17 differentiation assays with siRNA knockdown and an in vivo dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced UC mouse model with intrarectal siRNA administration.
WGCNA identified ITGAX, SOCS3, CXCL1, CASP1, and CXCL11 as core upregulated genes in pediatric UC, with ITGAX being a novel candidate regulator of Th17 cells. ITGAX knockdown in naive CD4+ T cells impaired Th17 differentiation and IL-17A production in vitro. In the DSS-induced UC mouse model, intrarectal ITGAX siRNA ameliorated colonic inflammation and ulceration, suppressed IL-17A levels, and selectively reduced the expansion of IFNγ-IL-17+ Th17 cells in the colon.
ITGAX is a key promoter of Th17-cell differentiation and expansion, contributing to the pathogenesis of pediatric UC. Targeting ITGAX may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for pediatric UC by modulating aberrant Th17 responses.
©The Author(s) 2025. Open Access. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons CC-BY International License.
-
FC/FACS
-
Pathology
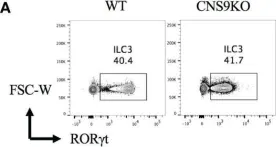
In Front Immunol on 28 March 2023 by Chang, D., Zhang, H., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1