The hormone and neurotransmitter serotonin regulates numerous physiological functions within the central nervous system and in the periphery upon binding to specific receptors. In the periphery, the serotonin receptor 7 (5-HT7R) is expressed on different immune cells including monocytes and macrophages. To investigate the impact of 5-HT7R-mediated signaling on macrophage properties, we used human THP-1 cells and differentiated them into pro-inflammatory M1- and anti-inflammatory M2-like macrophages. Pharmacological 5-HT7R activation with the specific agonist LP-211 especially modulates morphology of M1-like macrophages by increasing the number of rounded cells. Furthermore, 5-HT7R stimulation results in significantly reduced phagocytic and migratory ability of M1-like macrophages. Noteworthy, LP-211 treatment leads to changes in secretory properties of all macrophage types with the highest effects obtained for M0- and M2c-like macrophages. Finally, the importance of 5-HT7R for regulation of phagocytosis was confirmed in human primary CD14+ cells. These results indicate that 5-HT7R activation selectively impairs basic functions of macrophages and might thus be a new access point for the modulation of macrophage responses in the future treatment of inflammatory diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 15
Serotonin receptor 5-HT7 modulates inflammatory-associated functions of macrophages.
In Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS on 21 January 2025 by Bahr, F. S., Müller, F. E., et al.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Rep Methods on 17 June 2024 by Raffo-Romero, A., Ziane-Chaouche, L., et al.
3D tumoroids have revolutionized in vitro/ex vivo cancer biology by recapitulating the complex diversity of tumors. While tumoroids provide new insights into cancer development and treatment response, several limitations remain. As the tumor microenvironment, especially the immune system, strongly influences tumor development, the absence of immune cells in tumoroids may lead to inappropriate conclusions. Macrophages, key players in tumor progression, are particularly challenging to integrate into the tumoroids. In this study, we established three optimized and standardized methods for co-culturing human macrophages with breast cancer tumoroids: a semi-liquid model and two matrix-embedded models tailored for specific applications. We then tracked interactions and macrophage infiltration in these systems using flow cytometry and light sheet microscopy and showed that macrophages influenced not only tumoroid molecular profiles but also chemotherapy response. This underscores the importance of increasing the complexity of 3D models to more accurately reflect in vivo conditions.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Blood Advances on 23 January 2024 by Cai, S. F., Huang, Y., et al.
Enasidenib (ENA) is an inhibitor of isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) approved for the treatment of patients with IDH2-mutant relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In this phase 2/1b Beat AML substudy, we applied a risk-adapted approach to assess the efficacy of ENA monotherapy for patients aged ≥60 years with newly diagnosed IDH2-mutant AML in whom genomic profiling demonstrated that mutant IDH2 was in the dominant leukemic clone. Patients for whom ENA monotherapy did not induce a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi) enrolled in a phase 1b cohort with the addition of azacitidine. The phase 2 portion assessing the overall response to ENA alone demonstrated efficacy, with a composite complete response (cCR) rate (CR/CRi) of 46% in 60 evaluable patients. Seventeen patients subsequently transitioned to phase 1b combination therapy, with a cCR rate of 41% and 1 dose-limiting toxicity. Correlative studies highlight mechanisms of clonal elimination with differentiation therapy as well as therapeutic resistance. This study demonstrates both efficacy of ENA monotherapy in the upfront setting and feasibility and applicability of a risk-adapted approach to the upfront treatment of IDH2-mutant AML. This trial is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT03013998.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Cancer Cell International on 18 December 2023 by Xu, P., Feng, D. X., et al.
Increasing evidence highlights the potential role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the biological behaviors of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Here, we explored the mechanism of AGAP2-AS1 in the occurrence and development of clear cell RCC (ccRCC) involving IGF2BP3/miR-9-5p/THBS2.
The expressions of AGAP2-AS1, IGF2BP3, miR-9-5p, and THBS2 and their relationship were analyzed by bioinformatics. The targeting relationship between AGAP2-AS1 and miR-9-5p and between miR-9-5p and THBS2 was evaluated with their effect on cell biological behaviors and macrophage polarization assayed. Finally, we tested the effect of AGAP2-AS1 on ccRCC tumor formation in xenograft tumors.
IGF2BP3 could stabilize AGAP2-AS1 through m6A modification. AGAP2-AS1 was highly expressed in ccRCC tissues and cells. The lentivirus-mediated intervention of AGAP2-AS1 induced malignant behaviors of ccRCC cells and led to M2 polarization of macrophages. In addition, THBS2 promoted M2 polarization of macrophages by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. AGAP2-AS1 could directly bind with miR-9-5p and promote the expression of THBS2 downstream of miR-9-5p. These results were further verified by in vivo experiments.
AGAP2-AS1 stabilized by IGF2BP3 competitively binds to miR-9-5p to up-regulate THBS2, activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and inducing macrophage M2 polarization, thus facilitating the development of RCC.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Immunobiology on 1 May 2023 by Kumari, D., Singh, S., et al.
SARS-CoV-2 has infected over 753 million individuals and caused more than 6.8 million deaths globally to date. COVID-19 disease severity has been associated with SARS-CoV-2 induced hyper inflammation and the immune correlation with its pathogenesis remains unclear. Acute viral infection is characterised by vigorous coordinated innate and adaptive activation, including an early cellular response that correlates well with the amplitude of virus specific humoral response.
The present study covers a wide spectrum of cellular immune response against COVID-19, irrespective of infection and vaccination.
We analysed immune status of (a) COVID-19 hospitalised patients including deceased and recovered patients, and compared with home isolated and non-infected healthy individuals, and (b) infected home isolated individuals with vaccinated individuals, using flow cytometry. We performed flow cytometry analysis of PBMCs to determine non-specific cell-mediated immune response.
The immune response revealed extensive induction and activation of multiple immune lineages, including T and B cells, Th17 regulatory subsets and M1, M2 macrophages in deceased and hospitalised recovered patients, vaccinated and healthy individuals. Compromised immune cell expression was observed in deceased patients even in later stages, while expression was restored in hospitalised recovered patients and home isolated individuals.
The findings associated with recovery and convalescence define a new signature of cellular immune response that persists in individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. The findings will help in providing a better understanding of COVID-19 disease and will aid in developing better therapeutic strategies for treatment.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier GmbH.
-
FC/FACS
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Sci Rep on 21 July 2021 by Durlanik, S., Fundel-Clemens, K., et al.
Fig.2.D
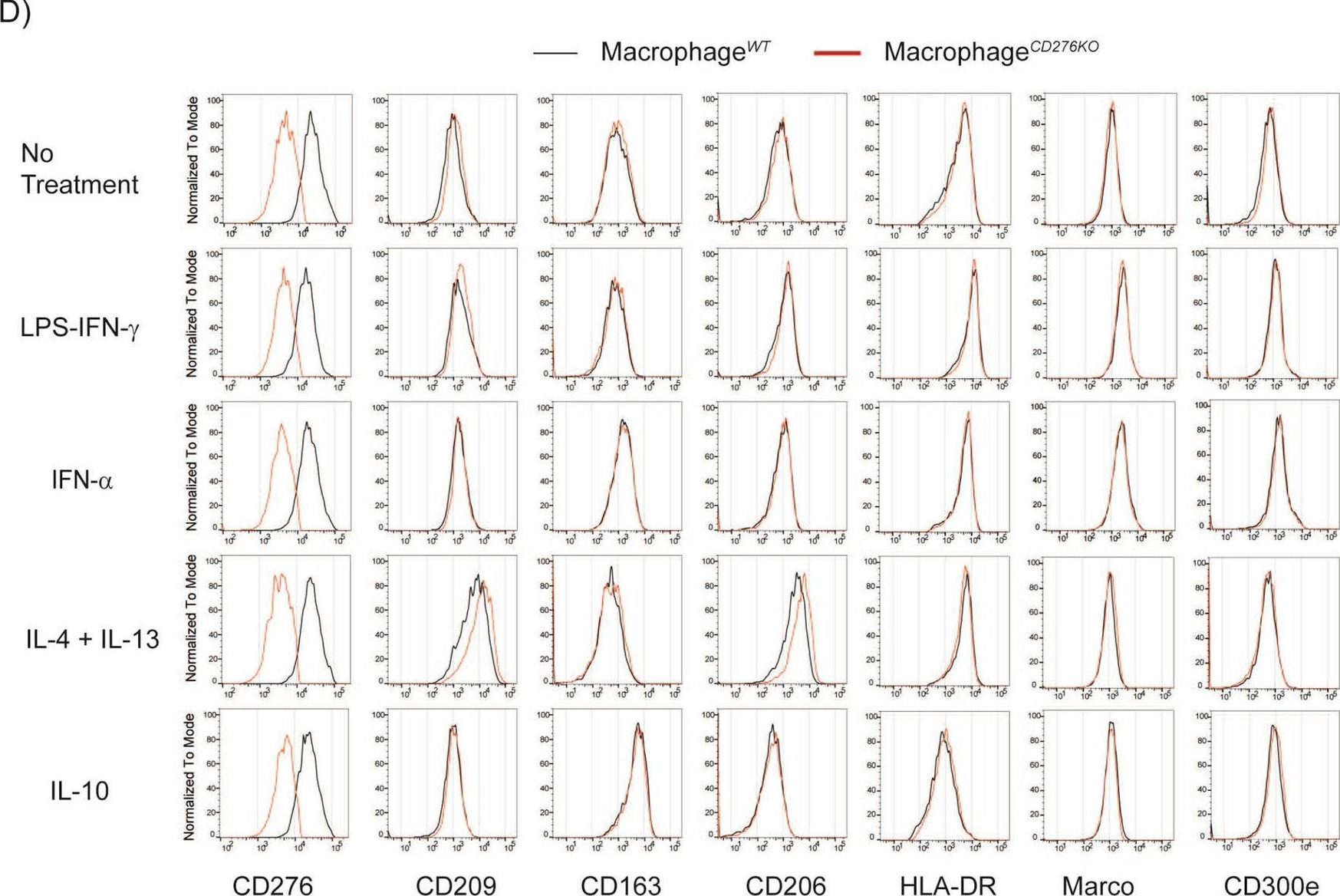
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1