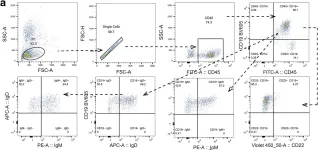
To study the expression of OX40 on T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and the ligand OX40L on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in peripheral blood of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and the role of OX40 signaling in promoting Tfh cells to assist B-cell differentiation.
Cross-sectional study.
Endocrinology department of a university hospital.
Twenty-five patients with T1DM and 35 with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from January 2021 to December 2021 (39 males, 21 females; mean age: 31.0 ± 4.5, range: 19-46 years).
None.
The peripheral blood proportion of CD4+CD25-CD127+CXCR5+PD1+ Tfh cells in patients with T1DM or T2DM and the OX40L expression in CD14+ monocytes and CD19+ B cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The OX40 signal effect on Tfh-cell function was analyzed by coincubating B cells with Tfh cells under different conditions. Flow cytometry detected the ratio of CD19-CD138+ plasmacytes.
The Tfh cells ratio and intracellular IL-21 expression in peripheral blood was significantly higher in patients with T1DM than with T2DM, and the OX40 expression in peripheral Tfh cells and OX40L expression in APC were significantly higher in T1DM. After adding OX40L protein, the CD19-CD138+-plasmacytes percentage was significantly increased and higher in T1DM. Blocking of anti-OX40L monoclonal antibodies significantly reduced the plasmacytes ratio.
The peripheral Tfh cells proportion increased and the OX40 expression in peripheral Tfh cells was upregulated in patients with T1DM vs patients with T2DM. OX40/OX40L signaling enhanced the Tfh-cell function to assist B-cell differentiation, which may contribute to the pathogenesis of T1DM.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Product Citations: 25
In The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism on 15 October 2024 by Du, X., Zhu, Y., et al.
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS Pathogens on 1 June 2024 by Warner van Dijk, F. A., Tong, O., et al.
AXL+ Siglec-6+ dendritic cells (ASDC) are novel myeloid DCs which can be subdivided into CD11c+ and CD123+ expressing subsets. We showed for the first time that these two ASDC subsets are present in inflamed human anogenital tissues where HIV transmission occurs. Their presence in inflamed tissues was supported by single cell RNA analysis of public databases of such tissues including psoriasis diseased skin and colorectal cancer. Almost all previous studies have examined ASDCs as a combined population. Our data revealed that the two ASDC subsets differ markedly in their functions when compared with each other and to pDCs. Relative to their cell functions, both subsets of blood ASDCs but not pDCs expressed co-stimulatory and maturation markers which were more prevalent on CD11c+ ASDCs, thus inducing more T cell proliferation and activation than their CD123+ counterparts. There was also a significant polarisation of naïve T cells by both ASDC subsets toward Th2, Th9, Th22, Th17 and Treg but less toward a Th1 phenotype. Furthermore, we investigated the expression of chemokine receptors that facilitate ASDCs and pDCs migration from blood to inflamed tissues, their HIV binding receptors, and their interactions with HIV and CD4 T cells. For HIV infection, within 2 hours of HIV exposure, CD11c+ ASDCs showed a trend in more viral transfer to T cells than CD123+ ASDCs and pDCs for first phase transfer. However, for second phase transfer, CD123+ ASDCs showed a trend in transferring more HIV than CD11c+ ASDCs and there was no viral transfer from pDCs. As anogenital inflammation is a prerequisite for HIV transmission, strategies to inhibit ASDC recruitment into inflamed tissues and their ability to transmit HIV to CD4 T cells should be considered.
Copyright: © 2024 Warner van Dijk et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
MYCT1 controls environmental sensing in human haematopoietic stem cells.
In Nature on 1 June 2024 by Aguadé-Gorgorió, J., Jami-Alahmadi, Y., et al.
The processes that govern human haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) self-renewal and engraftment are poorly understood and challenging to recapitulate in culture to reliably expand functional HSCs1-3. Here we identify MYC target 1 (MYCT1; also known as MTLC) as a crucial human HSC regulator that moderates endocytosis and environmental sensing in HSCs. MYCT1 is selectively expressed in undifferentiated human haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) and endothelial cells but becomes markedly downregulated during HSC culture. Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of MYCT1 prevented human fetal liver and cord blood (CB) HSPC expansion and engraftment. By contrast, restoring MYCT1 expression improved the expansion and engraftment of cultured CB HSPCs. Single-cell RNA sequencing of human CB HSPCs in which MYCT1 was knocked down or overexpressed revealed that MYCT1 governs important regulatory programmes and cellular properties essential for HSC stemness, such as ETS factor expression and low mitochondrial activity. MYCT1 is localized in the endosomal membrane in HSPCs and interacts with vesicle trafficking regulators and signalling machinery. MYCT1 loss in HSPCs led to excessive endocytosis and hyperactive signalling responses, whereas restoring MYCT1 expression balanced culture-induced endocytosis and dysregulated signalling. Moreover, sorting cultured CB HSPCs on the basis of lowest endocytosis rate identified HSPCs with preserved MYCT1 expression and MYCT1-regulated HSC stemness programmes. Our work identifies MYCT1-moderated endocytosis and environmental sensing as essential regulatory mechanisms required to preserve human HSC stemness. Our data also pinpoint silencing of MYCT1 as a cell-culture-induced vulnerability that compromises human HSC expansion.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In IScience on 15 December 2023 by Liu, S., Liu, Z. C., et al.
Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) plays prominent roles in mediating cell-cell adhesion which also facilitates B cell activation and differentiation with the help from CD4+ T cells. Here, we have reported a unique phenomenon that increased ICAM-1 on purified human CD4+ T cells upon anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation enhanced CD4+ T-B cell adhesion whereas induced less B cell differentiation and IgG production. This was largely due to increased PD-1 expression on CD19hi B cells after coculturing with hyperactivated CD4+ T cells. Consequently, ICAM-1 blockade during CD4+ T cell-B cell coculture promoted IgG production with the activation of ERK1/2 and Blimp-1/IRF4 upregulation. Consistently, CD4+ T cells from moderate-to-severe SLE patients with high ICAM-1 expression mediated less IgG production after T-B coculture. Therefore, ICAM-1-mediated human CD4+ T-B cell adhesion provides dual roles on B cell differentiation and IgG production partially depending on expression levels of PD-1 on B cells, supporting cell adhesion and subsequent PD-1 induction as an alternative intrinsic checkpoint for B cell differentiation.
© 2023 The Authors.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Clinical Cancer Research on 1 September 2023 by Roschewski, M., Patel, M. R., et al.
Novel targeted and immunotherapies have improved outcomes in relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but toxicities limit widespread use. The selective Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib has activity in patients with R/R DLBCL but durable responses are uncommon. STAT3 inhibition has demonstrated clinical activity in DLBCL.
Final results of the phase I study of acalabrutinib plus STAT3 inhibitor (danvatirsen; AZD9150) in patients with R/R DLBCL are reported. Danvatirsen 200 mg intravenous infusion [Days 1, 3, 5 (Cycle 1); weekly infusions starting Day 8, Cycle 1] was administered in combination with oral acalabrutinib 100 mg twice daily until progressive disease (PD) or unacceptable toxicity. Primary endpoints were safety and tolerability. Secondary endpoints included efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity.
Seventeen patients received combination treatment. One dose-limiting toxicity (Grade 3 liver transaminase) occurred in 1 patient. The most common reason for treatment discontinuation was PD (65%). In evaluable patients (n = 17), objective response rate was 24%; median duration of response was 1.9 months. All responders with available DLBCL cell-of-origin data were either activated B-cell or nongerminal center B-cell like subtype. Genetic subtype did not correlate with response. Baseline and longitudinal plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) concentrations were mostly higher in nonresponding patients. cfDNA changes were generally concordant with imaging. Pretreatment circulating B-cell levels were higher in responders versus nonresponders.
Targeting both STAT3 and BTK in combination is safe and tolerable but efficacy is limited in R/R DLBCL. Results support evaluation of circulating tumor DNA as a biomarker for clinical response.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In BMC Immunol on 7 January 2019 by Dagur, R. S., Branch-Woods, A., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from BMC Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In BMC Immunol on 7 January 2019 by Dagur, R. S., Branch-Woods, A., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from BMC Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2