Abstract Despite considerable advances to improve colorectal cancer (CRC) survival over the last decade, therapeutic challenges remain due to the rapid metastatic dissemination of primary tumors and screening limitations. Meanwhile, the rise of CRC in younger adults (Early-onset CRC), commonly diagnosed with a metastatic form of the disease, shows the pressing need to develop more effective targeted therapies to decrease the high mortality rates associated with metastatic disease. Hyperactivation of the Rictor-mTORC2-AKT signaling pathway drives key metastatic players in diverse malignant tumors, including early- and late-onset colorectal cancer. Selective mTORC2 inhibitors are becoming a potential treatment strategy for CRC due to the therapeutic limitations of mTORC1 inhibitors. Veratridine (VTD), a lipid-soluble alkaloid extracted from Liliaceae plants, can transcriptionally increase UBXN2A, which induces 26S proteasomal degradation of the Rictor protein, a key member in the mTORC2 complex. Destabilization of Rictor protein by VTD decreases Akt phosphorylation on Ser473, which is responsible for metastatic signaling downstream of the mTORC2 pathway in diverse malignant tumors. VTD decreases the population of metastatic colon cancer stem cells and functions as an angiogenesis inhibitor. VTD effectively reduces the spheroid growth rate and restricts cell migration. Live cell migration and invasion assays alongside biomechanical-force-based experiments revealed that VTD suppresses colon cancer cell invasiveness and the ensuing risk of tumor metastasis. A CRC mouse model that mimics the natural stages of human sporadic CRC revealed that VTD treatment significantly decreases tumor growth in a UBXN2A-dependent manner. This study showed a novel mechanistic connection between a ubiquitin-like protein and mTORC2-dependent migration and invasion in CRC tumors. This study revealed the therapeutic benefit of selective inhibition of Rictor in CRC, particularly in tumors with a hyperactive Rictor-mTORC2 signaling pathway. Finally, this study opened a new platform for repurposing VTD, a supplemental anti-hypertension molecule, into an effective targeted therapy in CRC tumors.
Product Citations: 4
Preprint on Research Square on 25 October 2024 by Eikanger, M. M., Sane, S., et al.
-
Cancer Research
In Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) on 1 April 2021 by Wang, H., Gong, P., et al.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) presumably contribute to tumor progression and drug resistance, yet their definitive features have remained elusive. Here, simultaneous measurement of telomere length and transcriptome in the same cells enables systematic assessment of CSCs in primary colorectal cancer (CRC). The in-depth transcriptome profiled by SMART-seq2 is independently validated by high-throughput scRNA-seq using 10 × Genomics. It is found that rare CSCs exist in dormant state and display plasticity toward cancer epithelial cells (EPCs) that essentially are presumptive tumor-initiating cells (TICs), while both retaining the prominent signaling pathways including WNT, TGF-β, and HIPPO/YAP. Moreover, CSCs exhibit chromosome copy number variation (CNV) pattern resembling cancer EPCs but distinct from normal stem cells, suggesting the phylogenetic relationship between CSCs and cancer EPCs. Notably, CSCs maintain shorter telomeres and possess minimal telomerase activity consistent with their nonproliferative nature, unlike cancer EPCs. Additionally, the specific signature of CSCs particularly NOTUM, SMOC2, BAMBI, PHLDA1, and TNFRSF19 correlates with the prognosis of CRC. These findings characterize the heterogeneity of CSCs and their linkage to cancer EPCs/TICs, some of which are conventionally regarded as CSCs.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
LGR5 promotes cancer stem cell traits and chemoresistance in cervical cancer.
In Cell Death & Disease on 7 September 2017 by Cao, H. Z., Liu, X. F., et al.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs), also known as tumor-initiating cells, contribute to tumorigenesis, resistance to chemoradiotherapy and recurrence in human cancers, suggesting targeting CSCs may represent a potential therapeutic strategy. Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (LGR5) has recently been found to be a bona fide marker of colorectal CSCs. Our previous study showed that LGR5 functions as a tumor promoter in cervical cancer by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. However, very little is known about the function or contribution of LGR5 to cervical CSCs. Here, we have modulated the expression of LGR5 using an overexpression vector or short hairpin RNA in cervical cancer cell lines. We demonstrated that elevated LGR5 expression in cervical cancer cells increased tumorsphere-forming efficiency; conferred chemoresistance to cisplatin treatment; augmented cell migration, invasion and clonogenicity; and elevated the levels of stem cell-related transcription factors in vitro. Furthermore, modulated LGR5+ cells, unlike LGR5- cells, were highly tumorigenic in vivo. In addition, the modulated LGR5+ cells could give rise to both LGR5+ and LGR5- cells in vitro and in vivo, thereby establishing a cellular hierarchy. Finally, we found that the increased tumorsphere-forming efficiency induced by LGR5 could be regulated through the inhibition or activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in cervical cancer cells. Taken together, these results indicate that LGR5 has a vital oncogenic role by promoting cervical CSC traits and may represent a potential clinical target.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Oncotarget on 1 January 2015 by Jonchère, B., Vétillard, A., et al.
Induction of senescence by chemotherapy was initially characterized as a suppressive response that prevents tumor cell proliferation. However, in response to treatment, it is not really known how cells can survive senescence and how irreversible this pathway is. In this study, we analyzed cell escape in response to irinotecan, a first line treatment used in colorectal cancer that induced senescence. We detected subpopulations of cells that adapted to chemotherapy and resumed proliferation. Survival led to the emergence of more transformed cells that induced tumor formation in mice and grew in low adhesion conditions. A significant amount of viable polyploid cells was also generated following irinotecan failure. Markers such as lgr5, CD44, CD133 and ALDH were downregulated in persistent clones, indicating that survival was not associated with an increase in cancer initiating cells. Importantly, malignant cells which resisted senescence relied on survival pathways induced by Mcl-1 signaling and to a lesser extent by Bcl-xL. Depletion of Mcl-1 increased irinotecan efficiency, induced the death of polyploid cells, prevented cell emergence and inhibited growth in low-adhesion conditions. We therefore propose that Mcl-1 targeting should be considered in the future to reduce senescence escape and to improve the treatment of irinotecan-refractory colorectal cancers.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Cell Death Dis on 7 September 2017 by Cao, H. Z., Liu, X. F., et al.
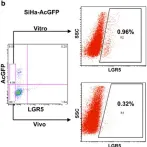
Fig.4.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Cell Death Dis on 7 September 2017 by Cao, H. Z., Liu, X. F., et al.
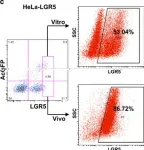
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Cell Death Dis on 7 September 2017 by Cao, H. Z., Liu, X. F., et al.
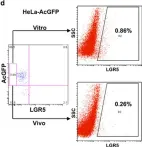
Fig.4.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Cell Death Dis on 7 September 2017 by Cao, H. Z., Liu, X. F., et al.
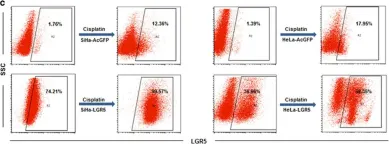
Fig.4.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Cell Death Dis on 7 September 2017 by Cao, H. Z., Liu, X. F., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5