Introduction: The classically defined two retinal microglia layers are distributed in inner and outer plexiform layers. Although there are some reports that retinal microglia are also superficially located around the ganglion cell layer (GCL) in contact with the vitreous, there has been a lack of detailed descriptions and not fully understood yet. Methods: We visualized the microglial layers by using CX3CR1-GFP (C57BL6) transgenic mice with both healthy and disease conditions including NaIO3-induced retinal degeneration models and IRBP-induced auto-immune uveitis models. Result: We found the GCL microglia has two subsets; peripheral (pph) microglia located on the retinal parenchyma and BAM (CNS Border Associated Macrophage) which have a special stretched phenotype only located on the surface of large retinal veins. First, in the pph microglia subset, but not in BAM, Galectin-3 and LYVE1 are focally expressed. However, LYVE1 is specifically expressed in the amoeboid or transition forms, except the typical dendritic morphology in the pph microglia. Second, BAM is tightly attached to the surface of the retinal veins and has similar morphology patterns in both the healthy and disease conditions. CD86+ BAM has a longer process which vertically passes the proximal retinal veins. Our data helps decipher the basic anatomy and pathophysiology of the retinal microglia in the GCL. Discussion: Our data helps decipher the basic anatomy and pathophysiology of the retinal microglia in the GCL.
Copyright © 2024 Jeon, Park, Kim, Kong, Kim, Yang, Lee, Kim, Kim and Kim.
Product Citations: 28
Deciphering perivascular macrophages and microglia in the retinal ganglion cell layers.
In Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology on 10 April 2024 by Jeon, J., Park, Y. S., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Neuroscience
In JCI Insight on 8 February 2024 by Fuseya, Y., Kadoba, K., et al.
Linear ubiquitin chains, which are generated specifically by the linear ubiquitin assembly complex (LUBAC) ubiquitin ligase, play crucial roles in immune signaling, including NF-κB activation. LUBAC comprises catalytic large isoform of heme-oxidized iron regulatory protein 2 ubiquitin ligase 1 (HOIL-1L) interacting protein (HOIP), accessory HOIL-1L, and SHANK-associated RH domain-interacting protein (SHARPIN). Deletion of the ubiquitin ligase activity of HOIL-1L, an accessory ligase of LUBAC, augments LUBAC functions by enhancing LUBAC-mediated linear ubiquitination, which is catalyzed by HOIP. Here, we show that HOIL-1L ΔRING1 mice, which exhibit augmented LUBAC functions upon loss of the HOIL-1L ligase, developed systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren's syndrome in a female-dominant fashion. Augmented LUBAC activity led to hyperactivation of both lymphoid and myeloid cells. In line with the findings in mice, we sought to identify missense single nucleotide polymorphisms/variations of the RBCK1/HOIL-1L gene in humans that attenuate HOIL-1L ligase activity. We found that the R464H variant, which is encoded by rs774507518 within the RBCK1/HOIL-1L gene, attenuated HOIL-1L ligase activity and augmented LUBAC-mediated immune signaling, including that mediated by Toll-like receptors. We also found that rs774507518 was enriched significantly in patients with SLE, strongly suggesting that RBCK1/HOIL-1L is an SLE susceptibility gene and that augmented linear ubiquitin signaling generated specifically by LUBAC underlies the pathogenesis of this prototype systemic autoimmune disease.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
mAb therapy controls CNS-resident lyssavirus infection via a CD4 T cell-dependent mechanism.
In EMBO Molecular Medicine on 11 October 2023 by Mastraccio, K. E., Huaman, C., et al.
Infections with rabies virus (RABV) and related lyssaviruses are uniformly fatal once virus accesses the central nervous system (CNS) and causes disease signs. Current immunotherapies are thus focused on the early, pre-symptomatic stage of disease, with the goal of peripheral neutralization of virus to prevent CNS infection. Here, we evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of F11, an anti-lyssavirus human monoclonal antibody (mAb), on established lyssavirus infections. We show that a single dose of F11 limits viral load in the brain and reverses disease signs following infection with a lethal dose of lyssavirus, even when administered after initiation of robust virus replication in the CNS. Importantly, we found that F11-dependent neutralization is not sufficient to protect animals from mortality, and a CD4 T cell-dependent adaptive immune response is required for successful control of infection. F11 significantly changes the spectrum of leukocyte populations in the brain, and the FcRγ-binding function of F11 contributes to therapeutic efficacy. Thus, mAb therapy can drive potent neutralization-independent T cell-mediated effects, even against an established CNS infection by a lethal neurotropic virus.
© 2023 Commonwealth of Australia and The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license. This article has been contributed to by U.S. Government employees and their work is in the public domain in the USA.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The β1-adrenergic receptor links sympathetic nerves to T cell exhaustion.
In Nature on 1 October 2023 by Globig, A. M., Zhao, S., et al.
CD8+ T cells are essential components of the immune response against viral infections and tumours, and are capable of eliminating infected and cancerous cells. However, when the antigen cannot be cleared, T cells enter a state known as exhaustion1. Although it is clear that chronic antigen contributes to CD8+ T cell exhaustion, less is known about how stress responses in tissues regulate T cell function. Here we show a new link between the stress-associated catecholamines and the progression of T cell exhaustion through the β1-adrenergic receptor ADRB1. We identify that exhausted CD8+ T cells increase ADRB1 expression and that exposure of ADRB1+ T cells to catecholamines suppresses their cytokine production and proliferation. Exhausted CD8+ T cells cluster around sympathetic nerves in an ADRB1-dependent manner. Ablation of β1-adrenergic signalling limits the progression of T cells towards the exhausted state in chronic infection and improves effector functions when combined with immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) in melanoma. In a pancreatic cancer model resistant to ICB, β-blockers and ICB synergize to boost CD8+ T cell responses and induce the development of tissue-resident memory-like T cells. Malignant disease is associated with increased catecholamine levels in patients2,3, and our results establish a connection between the sympathetic stress response, tissue innervation and T cell exhaustion. Here, we uncover a new mechanism by which blocking β-adrenergic signalling in CD8+ T cells rejuvenates anti-tumour functions.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
Core enhancers of the 3’RR optimize<i>IgH</i>nuclear position and loop conformation for oriented CSR
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 12 July 2023 by Bruzeau, C., Pollet, J., et al.
Class switch recombination is an essential process which enabling B cells to adapt immunoglobulin subtypes to antigens. Transcription plays a crucial role in regulating CSR in which the IgH 3’Regulatory Region ( 3’RR ) was identified as a key player. The 3’RR stands at the 3’ end of IgH locus and is composed of four core enhancers surrounded by inverted repeated sequences, forming a quasi-palindrome. In addition to transcriptional control, nuclear organization appears to be an important level in CSR regulation. Furthermore, the chromatin loops at IgH locus facilitate an efficient CSR recombination by bringing the donor and acceptor switch regions closer together. However, the precise control mechanisms governing both of these processes remain partially understood. Here, using the reference DNA 3D-FISH technique combined with various high throughput approaches, we showed that 3’RR core enhancers are necessary and sufficient to preorganize resting B cell nuclei to facilitate a deletional CSR mechanism at activated stage. We demonstrated that the 3’RR core enhancers regulate IgH locus addressing in the nuclei, control IgH locus accessibility and orchestrate IgH loops formation. Our findings pinpointed an additional regulation level of mechanisms underlying B cell diversification. Graphical abstract Position of IgH loci through B cell development (from transitional to stimulated stages) is represented by the red spots. In wt and c3’RR context, IgH loci get closer from each other and from nucleus center during evolution from transitional to mature resting stage and they relocates more at nuclear periphery, away one from each other, upon in vitro stimulation. In Δ3’RR model, this dynamic is lost and, moreover, IgH loci are more localized to pericentromeric heterochromatin (represented by green area) since the mature resting B cell stage and remain in after in vitro stimulation.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
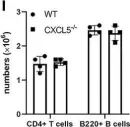
In Front Immunol on 7 December 2021 by Guo, L., Li, N., et al.
Fig.5.I

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1