Invasive fungal infections (IFIs) are responsible for elevated rates of morbidity and mortality, causing around of 1.5 million deaths annually worldwide. One of the main causative agents of IFIs is Candida albicans, and non-albicans Candida species have emerged as a spreading global public health concernment. Furthermore, COVID-19 has contributed to a boost in the incidence of IFIs, such as mucormycosis, in which Rhizopus oryzae is the most prevalent causative agent. The effector host immune response against IFIs depends on the activity of T cells, which are susceptible to the regulatory effects triggered by fungal virulence factors. The fungal cell wall plays a crucial role as a virulence factor, and its remodeling compromises the development of a specific T-cell response. The redirection of Jurkat T cells to target Candida spp. by recognizing targets expressed on the fungal cell wall can be facilitated using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) technology. This study generated an M-CAR that contains an scFv with specificity to α-1,6 mannose backbone of fungal mannan, and the expression of M-CAR on the surface of modified Jurkat cells triggered a strong activation against Candida albicans (hyphae form), Candida tropicalis (hyphae form), Candida parapsilosis (pseudohyphal form), and Candida glabrata (yeast form). Moreover, M-CAR Jurkat cells recognized Rhizopus oryzae spores, which induced high expression of cell activation markers. Thus, a novel Mannan-specific CAR enabled strong signal transduction in modified Jurkat cells in the presence of Candida spp. or R. oryzae.
Product Citations: 25
In Bioengineered on 1 December 2025 by Guimarães, J. G., de Campos, G. Y., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In IScience on 18 April 2025 by Liu, H., Ge, W., et al.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) resists immunotherapy due to its immunosuppressive microenvironment. Sarcoma homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) inhibits T cell receptor signaling, and its pharmacological inhibition is limited by poor selectivity and membrane permeability. Here, we generated CRISPR-edited SHP-1-knockout (KO) CD8+ T cells to enhance adoptive therapy against HCC. Single-cell RNA sequencing of HCC patient T cells revealed elevated SHP-1 in exhausted subsets. SHP-1-KO T cells exhibited increased effector memory T cells (TEM) proportions and enhanced IFN-γ/Granzyme B/perforin secretion, improving cytotoxicity against HCC lines. In humanized PDX models, SHP-1-KO T cells demonstrated superior tumor-killing activity. Transcriptomics identified upregulated lipid metabolism pathways, with HMGCR as a hub gene. Combining SHP-1-KO T cells with simvastatin (HMGCR inhibitor) synergistically amplified anti-HCC efficacy. This study proposes a dual strategy combining SHP-1-targeted cell therapy and metabolic modulation to overcome immunotherapy resistance, offering a translatable approach for HCC treatment.
© 2025 The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 13 December 2024 by Guimarães, J. G., de Campos, G. Y., et al.
ABSTRACT Invasive fungal infections (IFIs) are responsible for elevated rates of morbidity and mortality, causing around of 1.5 million deaths annually worldwide. One of the main causative agents of IFIs is Candida albicans , and non-albicans Candida species have emerged as a spreading global public health concernment. Furthermore, COVID-19 has contributed to a boost in the incidence of IFIs, such as mucormycosis, in which Rhizopus oryzae is the most prevalent causative agent. The effector host immune response against IFIs depends on the activity of T cells, which are susceptible to the regulatory effects triggered by fungal virulence factors. The fungal cell wall plays a crucial role as a virulence factor, and its remodeling compromises the development of a specific T-cell response. The redirection of Jurkat T cells to target Candida spp. by recognizing targets expressed on the fungal cell wall can be facilitated using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) technology. This study generated an M-CAR that contains an scFv with specificity to α-1,6 mannose backbone of fungal mannan, and the expression of M-CAR on the surface of modified Jurkat cells triggered a strong activation against Candida albicans (hyphae form), Candida tropicalis (hyphae form), Candida parapsilosis (pseudohyphal form), and Candida glabrata (yeast form). Moreover, M-CAR Jurkat cells recognized Rhizopus oryzae spores, which induced high expression of cell activation markers. Thus, a novel Mannan-specific CAR enabled strong signal transduction in modified Jurkat cells in the presence of Candida spp. or R. oryzae .
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports Medicine on 19 November 2024 by Guerrero-Murillo, M., Rill-Hinarejos, A., et al.
The impact of phenotypic, clonal, and functional heterogeneity of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells on clinical outcome remains understudied. Here, we integrate clonal kinetics with transcriptomic heterogeneity resolved by single-cell omics to interrogate cellular dynamics of non-transduced (CARneg) and transduced (CARpos) T cells, in the infusion product (IP) and at the CAR-T cell expansion peak in five B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) patients treated with CD19CAR-T cells (varni-cel). We identify significant differences in cellular dynamics in response to therapy. CARpos T cells at IP of complete response patients exhibit a significantly higher CD4:CD8 ratio, validated in a larger cohort B-ALL patients (n = 47). Conversely, at the expansion peak, there is a clonal expansion of CD8+ effector memory and cytotoxic T cells. Cytotoxic CARpos γδ-T cells expansion correlates with treatment efficacy validated in a cohort of B-ALL (n = 18) and diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients (n = 58). Our data provide insights into the complexity of T cell responses following CAR-T cell therapy and suggest drivers of immunotherapy response.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 17 June 2024 by Chen, Y., Ouyang, D., et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a double-stranded DNA oncogenic virus. Several types of solid tumors, such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma, EBV-associated gastric carcinoma, and lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the lung, have been linked to EBV infection. Currently, several TCR-T-cell therapies for EBV-associated tumors are in clinical trials, but due to the suppressive immune microenvironment of solid tumors, the clinical application of TCR-T-cell therapy for EBV-associated solid tumors is limited. Figuring out the mechanism by which EBV participates in the formation of the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment will help T cells or TCR-T cells break through the limitation and exert stronger antitumor potential.
Flow cytometry was used for analyzing macrophage differentiation phenotypes induced by EBV-infected and EBV-uninfected tumors, as well as the function of T cells co-cultured with these macrophages. Xenograft model in mice was used to explore the effects of M2 macrophages, TCR-T cells, and matrix metalloprotein 9 (MMP9) inhibitors on the growth of EBV-infected tumors.
EBV-positive tumors exhibited an exhaustion profile of T cells, despite the presence of a large T-cell infiltration. EBV-infected tumors recruited a large number of mononuclear macrophages with CCL5 and induced CD163+M2 macrophages polarization through the secretion of CSF1 and the promotion of autocrine IL10 production by mononuclear macrophages. Massive secretion of MMP9 by this group of CD163+M2 macrophages induced by EBV infection was an important factor contributing to T-cell exhaustion and TCR-T-cell therapy resistance in EBV-positive tumors, and the use of MMP9 inhibitors improved the function of T cells cocultured with M2 macrophages. Finally, the combination of an MMP9 inhibitor with TCR-T cells targeting EBV-positive tumors significantly inhibited the growth of xenografts in mice.
MMP9 inhibitors improve TCR-T cell function suppressed by EBV-induced M2 macrophages. TCR-T-cell therapy combined with MMP9 inhibitors was an effective therapeutic strategy for EBV-positive solid tumors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Mol Oncol on 1 February 2017 by Liu, J. F., Ma, S. R., et al.
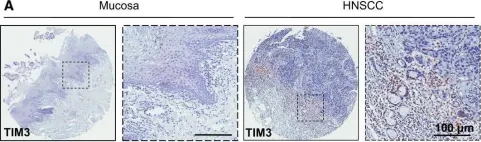
Fig.1.A

-
IHC
-
Collected and cropped from Mol Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Mol Oncol on 1 February 2017 by Liu, J. F., Ma, S. R., et al.
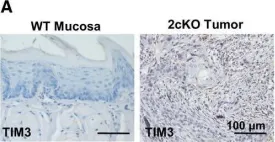
Fig.4.A

-
IHC
-
Collected and cropped from Mol Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Mol Oncol on 1 February 2017 by Liu, J. F., Ma, S. R., et al.
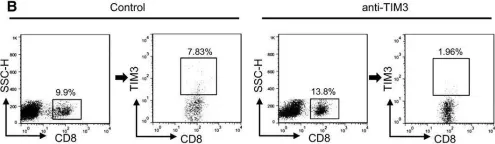
Fig.6.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Mol Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Mol Oncol on 1 February 2017 by Liu, J. F., Ma, S. R., et al.
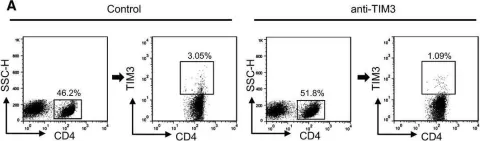
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Mol Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Mol Oncol on 1 February 2017 by Liu, J. F., Ma, S. R., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Mol Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5