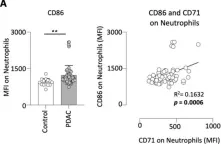
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most lethal malignancies, presenting a persisting global health burden. Neutrophils have a double-edged role in tumor progression exhibiting both pro-tumor and anti-tumor functions. CD71, also known as transferrin receptor 1, performs a critical role in cellular iron uptake and is highly expressed on proliferating cells, and especially on activated immune cells. CD71 is known to be elevated in various types of solid cancers and is associated with poor prognosis, however, the expression of CD71 on neutrophils in PDAC and its potential clinical impact is still unknown. Therefore, we analyzed CD71 on circulating neutrophils in PDAC and clinical control patients and found a significant increased expression in PDAC patients. High expression of CD71 on neutrophils in PDAC patients was associated with reduced outcome compared to low expression. CD71 on neutrophils correlated positively with the levels of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IFN-γ, and growth factor ligands CD40-L, and BAFF in plasma of PDAC patients. Finally, we have demonstrated that high expression of CD71 on neutrophils was also associated with an increased expression of CD39 and CD25 on circulating T-cells. Based on our findings, we hypothesize that CD71 on neutrophils is associated with tumor progression in PDAC. Further studies are required to investigate the distinct functionality of CD71 expressing neutrophils and their potential clinical application.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 4
In Scientific Reports on 10 September 2024 by Hansen, F. J., Mittelstädt, A., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Cell Reports Medicine on 20 February 2024 by Wang, L., Guo, W., et al.
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are the predominant cells that express programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) within human tumors in addition to cancer cells, and PD-L1+ TAMs are generally thought to be immunosuppressive within the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). Using single-cell transcriptomic and spatial multiplex immunofluorescence analyses, we show that PD-L1+ TAMs are mature and immunostimulatory with spatial preference to T cells. In contrast, PD-L1- TAMs are immunosuppressive and spatially co-localize with cancer cells. Either higher density of PD-L1+ TAMs alone or ratio of PD-L1+/PD-L1- TAMs correlate with favorable clinical outcome in two independent cohorts of patients with breast cancer. Mechanistically, we show that PD-L1 is upregulated during the monocyte-to-macrophage maturation and differentiation process and does not require external IFN-γ stimulus. Functionally, PD-L1+ TAMs are more mature/activated and promote CD8+ T cells proliferation and cytotoxic capacity. Together, our findings reveal insights into the immunological significance of PD-L1 within the TIME.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Cancers on 5 January 2023 by Hansen, F. J., David, P., et al.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) ranks among the most fatal cancer diseases, widely accepted to have the most dismal prognoses. Although immunotherapy has broadly revolutionized cancer treatment, its value in PDAC appears to be relatively low. Exhibiting protumoral effects, monocytes have recently been proposed as potential targets of such immunotherapeutic regimens. However, to date, the body of evidence on monocytes’ role in PDAC is scarce. Therefore, we analyzed monocytes in the peripheral blood of 58 PDAC patients prior to surgery and compared them to healthy individuals. PDAC patients showed increased levels of monocytes when compared to healthy controls In addition, patients with perineural infiltration demonstrated a higher percentage of monocytes compared to non-infiltrating tumors and PDAC G3 was associated with higher monocyte levels than PDAC G2. Patients with monocyte levels > 5% were found to have an 8.9-fold increased risk for a G3 and perineural infiltrated PDAC resulting in poorer survival compared to patients with <5% monocyte levels. Furthermore, PDAC patients showed increased expressions of CD86 and CD11c and decreased expressions of PD-L1 on monocytes compared to healthy individuals. Finally, levels of monocytes correlated positively with concentrations of IL-6 and TNF-α in plasma of PDAC patients. Based on our findings, we propose monocytes as a novel prognostic biomarker. Large-scale studies are needed to further decipher the role of monocytes in PDAC and investigate their potential as therapeutic targets.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In JCI Insight on 8 July 2022 by Patrick, D. M., de la Visitación, N., et al.
We describe a mechanism responsible for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In humans with SLE and in 2 SLE murine models, there was marked enrichment of isolevuglandin-adducted proteins (isoLG adducts) in monocytes and dendritic cells. We found that antibodies formed against isoLG adducts in both SLE-prone mice and humans with SLE. In addition, isoLG ligation of the transcription factor PU.1 at a critical DNA binding site markedly reduced transcription of all C1q subunits. Treatment of SLE-prone mice with the specific isoLG scavenger 2-hydroxybenzylamine (2-HOBA) ameliorated parameters of autoimmunity, including plasma cell expansion, circulating IgG levels, and anti-dsDNA antibody titers. 2-HOBA also lowered blood pressure, attenuated renal injury, and reduced inflammatory gene expression uniquely in C1q-expressing dendritic cells. Thus, isoLG adducts play an essential role in the genesis and maintenance of systemic autoimmunity and hypertension in SLE.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Sci Rep on 10 September 2024 by Hansen, F. J., Mittelstädt, A., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1