Glial cell dysfunction results in myelin loss and leads to subsequent motor and cognitive deficits throughout the demyelinating disease course.Therefore, in various therapeutic approaches, significant attention has been directed toward glial-restricted progenitor (GRP) transplantation for myelin repair and remyelination, and numerous studies using exogenous GRP injection in rodent models of hypomyelinating diseases have been performed. Previously, we proposed the transplantation of canine glial-restricted progenitors (cGRPs) into the double-mutant immunodeficient, demyelinated neonatal shiverer mice (shiverer/Rag2-/-). The results of our previous study revealed the myelination of axons within the corpus callosum of transplanted animals; however, the extent of myelination and lifespan prolongation depended on the transplantation site (anterior vs. posterior). The goal of our present study was to optimize the therapeutic effect of cGRP transplantation by using a multisite injection protocol to achieve a broader dispersal of donor cells in the host and obtain better therapeutic results. Experimental analysis of cGRP graft recipients revealed a marked elevation in myelin basic protein (MBP) expression and prominent axonal myelination across the brains of shiverer mice. Interestingly, the proportion of galactosyl ceramidase (GalC) positive cells was similar between the brains of cGRP recipients and control mice, implying a natural propensity of exogenous cGRPs to generate mature, myelinating oligodendrocytes. Moreover, multisite injection of cGRPs improved mice survival as compared to non-transplanted animals.
Product Citations: 3
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 1 October 2024 by Rogujski, P., Gewartowska, M., et al.
-
Neuroscience
-
Veterinary Research
In Stem Cell Research & Therapy on 13 June 2019 by Ahlfors, J. E., Azimi, A., et al.
Cell reprogramming is a promising avenue for cell-based therapies as it allows for the generation of multipotent, unipotent, or mature somatic cells without going through a pluripotent state. While the use of autologous cells is considered ideal, key challenges for their clinical translation include the ability to reproducibly generate sufficient quantities of cells within a therapeutically relevant time window.
We performed transfection of three distinct human somatic starting populations of cells with a non-integrating synthetic plasmid expressing Musashi 1 (MSI1), Neurogenin 2 (NGN2), and Methyl-CpG-Binding Domain 2 (MBD2). The resulting directly reprogrammed neural precursor cells (drNPCs) were examined in vitro using RT-qPCR, karyotype analysis, immunohistochemistry, and FACS at early and late time post-transfection. Electrophysiology (patch clamp) was performed on drNPC-derived neurons to determine their capacity to generate action potentials. In vivo characterization was performed following transplantation of drNPCs into two animal models (Shiverer and SCID/Beige mice), and the numbers, location, and differentiation profile of the transplanted cells were examined using immunohistochemistry.
Human somatic cells can be directly reprogrammed within two weeks to neural precursor cells (drNPCs) by transient exposure to Msi1, Ngn2, and MBD2 using non-viral constructs. The drNPCs generate all three neural cell types (astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons) and can be passaged in vitro to generate large numbers of cells within four weeks. drNPCs can respond to in vivo differentiation and migration cues as demonstrated by their migration to the olfactory bulb and contribution to neurogenesis in vivo. Differentiation profiles of transplanted cells onto the corpus callosum of myelin-deficient mice reveal the production of oligodendrocytes and astrocytes.
Human drNPCs can be efficiently and rapidly produced from donor somatic cells and possess all the important characteristics of native neural multipotent cells including differentiation into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes, and in vivo neurogenesis and myelination.
-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Scientific Reports on 21 April 2017 by Tokumoto, Y., Tamaki, S., et al.
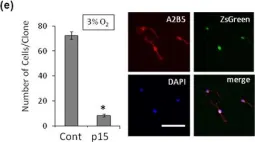
The adult mammalian central nervous system (CNS) contains a population of slowly dividing oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs), i.e., adult OPCs, which supply new oligodendrocytes throughout the life of animal. While adult OPCs develop from rapidly dividing perinatal OPCs, the mechanisms underlying their quiescence remain unknown. Here, we show that perinatal rodent OPCs cultured with thyroid hormone (TH) under hypoxia become quiescent and acquire adult OPCs-like characteristics. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p15/INK4b plays crucial roles in the TH-dependent cell cycle deceleration in OPCs under hypoxia. Klf9 is a direct target of TH-dependent signaling. Under hypoxic conditions, hypoxia-inducible factors mediates runt-related transcription factor 1 activity to induce G1 arrest in OPCs through enhancing TH-dependent p15/INK4b expression. As adult OPCs display phenotypes of adult somatic stem cells in the CNS, the current results shed light on environmental requirements for the quiescence of adult somatic stem cells during their development from actively proliferating stem/progenitor cells.
-
ICC-IF
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
-
Neuroscience
In Sci Rep on 21 April 2017 by Tokumoto, Y., Tamaki, S., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
ICC-IF
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1