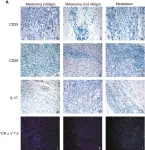
Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma (MEITL) is a rare and aggressive primary intestinal lymphoma with a poor prognosis. MEITL can metastasize to the central nervous system, liver and spleen, but gallbladder involvement has not yet been reported. The present study describes the case of a 57-year-old woman who presented with abdominal distention, pain and vomiting. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography revealed thickening and perforation of the small intestinal wall, and a gallbladder mass. Histopathological analysis of the affected small intestine and gallbladder revealed a dense infiltrate of medium-sized monomorphic lymphocytes with a CD3+, CD4-, CD8+ and TIA-1+ phenotype. Based on the absence of celiac disease, aggressive clinical course, and characteristic histopathological and immunophenotypic features, a diagnosis of MEITL with gallbladder involvement was established. The patient underwent small intestinal resection and cholecystectomy, followed by chemotherapy, which was completed without gastrointestinal or gallbladder perforation. Diagnostic resection is currently the best approach for suspected malignant lymphoma of the gallbladder. This rare case of MEITL with gallbladder involvement highlights the importance of considering this diagnosis in similar clinical scenarios and the role of cholecystectomy, which can serve both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Copyright: © 2025 Okuda et al.
Product Citations: 18
Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma with gallbladder involvement: A case report.
In Molecular and Clinical Oncology on 1 July 2025 by Okuda, T., Shirase, T., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Microorganisms on 15 October 2023 by Iloba, I., McGarry, S., et al.
Spore-forming probiotic bacteria, including Bacillus coagulans, are resilient and produce a variety of beneficial metabolites. We evaluated the immune-modulating effects of the novel probiotic strain Bacillus coagulans JBI-YZ6.3, where the germinated spores, metabolite fraction, and cell wall fraction were tested in parallel using human peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures under both normal and lipopolysaccharide-induced inflamed culture conditions. The expression of CD25 and CD69 activation markers was evaluated via flow cytometry. Supernatants were tested for cytokines, interferons, chemokines, and growth factors using Luminex arrays. The germinated spores were highly immunogenic; both the cell wall and metabolite fractions contributed significantly. Under normal culture conditions, increased levels of immune activation were observed as increased expressions of CD25 and CD69 relative to natural killer cells, suggesting an increased ability to attack virus-infected target cells. On monocytes, a complex effect was observed, where the expression of CD25 increased under normal conditions but decreased under inflamed conditions. This, in combination with increased interleukin-10 (IL-10) and decreased monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) production under inflamed conditions, points to anti-inflammatory effects. The production of the stem cell-related growth factor granulocyte colony-stimulating Factor (G-CSF) was enhanced. Further research is warranted to characterize the composition of the postbiotic metabolite fraction and document the characteristics of immunomodulating agents secreted by this probiotic strain.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 8 September 2023 by Carbone, M. L., Capone, A., et al.
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors is an efficient treatment for metastatic melanoma. Development of vitiligo upon immunotherapy represents a specific immune-related adverse event (irAE) diagnosed in 15% of patients and associated with a positive clinical response. Therefore, a detailed characterization of immune cells during vitiligo onset in melanoma patients would give insight into the immune mechanisms mediating both the irAE and the anti-tumor response.
To better understand these aspects, we analyzed T cell subsets from peripheral blood of metastatic melanoma patients undergoing treatment with anti-programmed cell death protein (PD)-1 antibodies. To deeply characterize the antitumoral T cell response concomitant to vitiligo onset, we analyzed T cell content in skin biopsies collected from melanoma patients who developed vitiligo. Moreover, to further characterize T cells in vitiligo skin lesion of melanoma patients, we sequenced T cell receptor (TCR) of cells derived from biopsies of vitiligo and primary melanoma of the same patient.
Stratification of patients for developing or not developing vitiligo during anti-PD-1 therapy revealed an association between blood reduction of CD8-mucosal associated invariant T (MAIT), T helper (h) 17, natural killer (NK) CD56bright, and T regulatory (T-reg) cells and vitiligo onset. Consistently with the observed blood reduction of Th17 cells in melanoma patients developing vitiligo during immunotherapy, we found high amount of IL-17A expressing cells in the vitiligo skin biopsy, suggesting a possible migration of Th17 cells from the blood into the autoimmune lesion. Interestingly, except for a few cases, we found different TCR sequences between vitiligo and primary melanoma lesions. In contrast, shared TCR sequences were identified between vitiligo and metastatic tissues of the same patient. These data indicate that T cell response against normal melanocytes, which is involved in vitiligo onset, is not typically mediated by reactivation of specific T cell clones infiltrating primary melanoma but may be elicited by T cell clones targeting metastatic tissues. Altogether, our data indicate that anti-PD-1 therapy induces a de novo immune response, stimulated by the presence of metastatic cells, and composed of different T cell subtypes, which may trigger the development of vitiligo and the response against metastatic tumor.
Copyright © 2023 Carbone, Capone, Guercio, Reddel, Silvestris, Lulli, Ramondino, Peluso, Quintarelli, Volpe and Failla.
-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) on 16 June 2023 by Jensen, G. S., Yu, L., et al.
The Nerium oleander extract PBI 05204 (PBI) and its cardiac glycoside constituent oleandrin have direct anti-viral properties. Their effect on the immune system, however, is largely unknown. We used an in vitro model of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to document effects under three different culture conditions: normal, challenged with the viral mimetic polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid Poly I:C, and inflamed by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Cells were evaluated for immune activation marks CD69, CD25, and CD107a, and culture supernatants were tested for cytokines. Both PBI and oleandrin directly activated Natural Killer (NK) cells and monocytes and triggered increased production of cytokines. Under viral mimetic challenge, PBI and oleandrin enhanced the Poly I:C-mediated immune activation of monocytes and NK cells and enhanced production of IFN-γ. Under inflammatory conditions, many cytokines were controlled at similar levels as in cultures treated with PBI and oleandrin without inflammation. PBI triggered higher levels of some cytokines than oleandrin. Both products increased T cell cytotoxic attack on malignant target cells, strongest by PBI. The results show that PBI and oleandrin directly activate innate immune cells, enhance anti-viral immune responses through NK cell activation and IFN-γ levels, and modulate immune responses under inflamed conditions. The potential clinical impact of these activities is discussed.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Immunobiology on 1 May 2023 by Kumari, D., Singh, S., et al.
SARS-CoV-2 has infected over 753 million individuals and caused more than 6.8 million deaths globally to date. COVID-19 disease severity has been associated with SARS-CoV-2 induced hyper inflammation and the immune correlation with its pathogenesis remains unclear. Acute viral infection is characterised by vigorous coordinated innate and adaptive activation, including an early cellular response that correlates well with the amplitude of virus specific humoral response.
The present study covers a wide spectrum of cellular immune response against COVID-19, irrespective of infection and vaccination.
We analysed immune status of (a) COVID-19 hospitalised patients including deceased and recovered patients, and compared with home isolated and non-infected healthy individuals, and (b) infected home isolated individuals with vaccinated individuals, using flow cytometry. We performed flow cytometry analysis of PBMCs to determine non-specific cell-mediated immune response.
The immune response revealed extensive induction and activation of multiple immune lineages, including T and B cells, Th17 regulatory subsets and M1, M2 macrophages in deceased and hospitalised recovered patients, vaccinated and healthy individuals. Compromised immune cell expression was observed in deceased patients even in later stages, while expression was restored in hospitalised recovered patients and home isolated individuals.
The findings associated with recovery and convalescence define a new signature of cellular immune response that persists in individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. The findings will help in providing a better understanding of COVID-19 disease and will aid in developing better therapeutic strategies for treatment.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier GmbH.
-
FC/FACS
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Immunol on 8 September 2023 by Carbone, M. L., Capone, A., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1