Nanrilkefusp alfa (nanril; SOT101) is an interleukin (IL)-15 receptor βγ superagonist that stimulates natural killer (NK) and CD8+ T cells, thereby promoting an innate and adaptive anti-tumor inflammatory microenvironment in mouse tumor models either in monotherapy or combined with an anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibody. In cynomolgus monkeys, a clinical schedule was identified, which translated into the design of a phase 1/1b clinical trial, AURELIO-03 (NCT04234113). In 51 patients with advanced/metastatic solid tumors, nanril increased the proportions of CD8+ T cells and NK cells in peripheral blood and tumors. It had a favorable safety profile when administered subcutaneously on days 1, 2, 8, and 9 of each 21-day cycle as monotherapy (0.25-15 μg/kg) or combined (1.5-12 μg/kg) with the anti-PD-1 pembrolizumab (200 mg). The most frequent treatment-emergent adverse events were pyrexia, injection site reactions, and chills. Furthermore, early clinical efficacy was observed, including in immune checkpoint blockade-resistant/refractory patients.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 33
In Cell Reports Medicine on 18 February 2025 by Champiat, S., Garralda, E., et al.
A therapeutic regimen using neoantigen-specific TCR-T cells for HLA-A*2402-positive solid tumors.
In EMBO Molecular Medicine on 1 February 2025 by Bei, Y., Huang, Y., et al.
The adoptive transfer of TCR-T cells specific to neoantigens preferentially exhibits potent cytotoxicity to tumor cells and has shown promising efficacy in various preclinical human cancers. In this study, we first identified a functional TCR, Tcr-1, which selectively recognized the SYT-SSX fusion neoantigen shared by most synovial sarcomas. Engineered T-cell expressing Tcr-1 (Tcr-T1) demonstrated HLA-A*2402-restricted, antigen-specific anti-tumoral efficacy against synovial sarcoma cells, both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, to extend its application, we developed a cooperative therapeutic modality, in which exogenous SYT-SSX fusion neoantigen was loaded into stimuli-responsive nanoparticles (NPs) formed by mPEG-PVGLIG-PCL copolymers (Neo-AgNPs) for tumor targeting delivery. As expected, Neo-AgNPs were proven to have great tumor penetration and local release. In situ, the modification was able to direct engineered Tcr-T1 against other HLA-A*2402-positive malignant cancer cell lines with significant antigen-specific cytotoxicity despite their inherent mutation profiles. With these favorable data, our established cooperative therapeutic modality has great potential for further clinical investigation and provides new insight for future TCR-T cell therapy development.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Clinical Translational Immunology on 28 January 2025 by Messina, N. L., Germano, S., et al.
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination has off-target effects on disease risk for unrelated infections and immune responses to vaccines. This study aimed to determine the immunomodulatory effects of BCG vaccination on immune responses to vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.
Blood samples, from a subset of 275 SARS-CoV-2-naïve healthcare workers randomised to BCG vaccination (BCG group) or no BCG vaccination (Control group) in the BRACE trial, were collected before and 28 days after the primary course (two doses) of ChAdOx1-S (Oxford-AstraZeneca) or BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccination. SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies were measured using ELISA and multiplex bead array, whole blood cytokine responses to γ-irradiated SARS-CoV-2 (iSARS) stimulation were measured by multiplex bead array, and SARS-CoV-2-specific T-cell responses were measured by activation-induced marker and intracellular cytokine staining assays.
After randomisation (mean 11 months) but prior to COVID-19 vaccination, the BCG group had lower cytokine responses to iSARS stimulation than the Control group. After two doses of ChAdOx1-S, differences in iSARS-induced cytokine responses between the BCG group and Control group were found for three cytokines (CTACK, TRAIL and VEGF). No differences were found between the groups after BNT162b2 vaccination. There were also no differences between the BCG and Control groups in COVID-19 vaccine-induced antigen-specific antibody responses, T-cell activation or T-cell cytokine production.
BCG vaccination induced a broad and persistent reduction in ex vivo cytokine responses to SARS-CoV-2. Following COVID-19 vaccination, this effect was abrogated, and BCG vaccination did not influence adaptive immune responses to COVID-19 vaccine antigens.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical & Translational Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
RhCMV Expands CCR5 Memory T Cells and promotes SIV reservoir genesis in the Gut Mucosa
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 8 January 2025 by Perdios, C., Babu, N. S., et al.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a prevalent β-herpesvirus that persists asymptomatically in immunocompetent hosts. In people with HIV-1 (PWH), CMV is associated with persistence of the HIV-1 reservoir and particular inflammatory related co-morbidities. The true causative role of CMV in HIV-associated pathologies remains unclear given that nearly all PWH are coinfected with CMV. In this study, we examined acute phase SIV dynamics in cohorts of rhesus macaques that were seropositive or -negative for rhesus CMV (RhCMV). We observed expansion of CCR5+ target CD4+ T cells in gut and lymph nodes (LN) that existed naturally in RhCMV-seropositive animals, the majority of which did not react to RhCMV lysate. These cells expressed high levels of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 and a ligand for this receptor, CXCL9, was systemically elevated in RhCMV-seropositive animals. RhCMV+ RMs also exhibited higher peak SIV viremia. CCR5 target memory CD4 T cells in the gut of RhCMV+ RMs were maintained during acute SIV and this was associated with greater seeding of SIV DNA in the intestine. Overall, our data suggests the ability of RhCMV to regulate chemotactic axes that direct lymphocyte trafficking and promote seeding of SIV in a diverse, polyclonal pool of memory CD4+ T cells.
-
Macaca mulatta (Rhesus Monkey)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports Medicine on 19 November 2024 by Tay, T., Bommakanti, G., et al.
In cancer, chronic antigen stimulation drives effector T cells to exhaustion, limiting the efficacy of T cell therapies. Recent studies have demonstrated that epigenetic rewiring governs the transition of T cells from effector to exhausted states and makes a subset of exhausted T cells non-responsive to PD1 checkpoint blockade. Here, we describe an antigen-specific assay for T cell exhaustion that generates T cells phenotypically and transcriptionally similar to those found in human tumors. We perform a screen of human epigenetic regulators, identifying IKZF1 as a driver of T cell exhaustion. We determine that the IKZF1 degrader iberdomide prevents exhaustion by blocking chromatin remodeling at T cell effector enhancers and preserving the binding of AP-1, NF-κB, and NFAT. Thus, our study uncovers a role for IKZF1 as a driver of T cell exhaustion through epigenetic modulation, providing a rationale for the use of iberdomide in solid tumors to prevent T cell exhaustion.
Copyright © 2024. Published by Elsevier Inc.
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
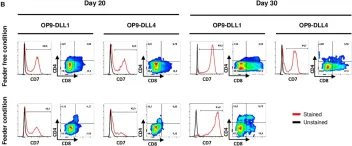
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 17 November 2020 by Flippe, L., Gaignerie, A., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
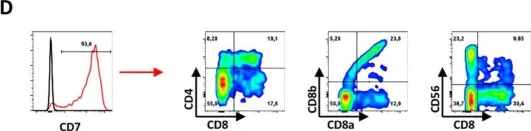
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 17 November 2020 by Flippe, L., Gaignerie, A., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2