Multiple myeloma (MM) remains an incurable malignancy characterized by the proliferation of malignant plasma cells and significant dysregulation within the bone marrow microenvironment. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) play a crucial role in the immune landscape of MM, often being co-opted by MM cells to support tumor progression. In this study, we identified all-trans retinoic acid (RA) as a potent modulator of pDC function through a high-throughput screening of 2,000 small-molecule drugs. RA significantly enhances pDCs' capacity to secrete interferon (IFN)-α upon CpG or Resiquimod stimulation, reversing the MM-induced suppression of IFN-α secretion. Mechanistically, RA upregulates Toll-like receptor (TLR)7/9 expression in pDCs, amplifying TLR7/9 agonist-induced IFN-α production and enhancing retinoic acid-inducible gene Ⅰ (RIG-Ⅰ)-like signaling and IFN-stimulated gene expression. In vivo, RA combined with CpG or Resiquimod significantly improves the survival of MM-bearing mice, with even greater pro-survival benefits observed when RA, Resiquimod, and bortezomib are combined. These findings demonstrate that RA rejuvenates pDCs, leading to improved control of MM growth in preclinical models, offering novel insights into developing more effective MM therapies.
© 2025 The Authors.
Product Citations: 41
In Molecular Therapy. Oncology on 18 June 2025 by Yu, W., Tang, W., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
PD-1 blockade employed at the time CD8+ T cells are activated enhances their antitumor efficacy.
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 7 May 2025 by Moseman, J. E., Rastogi, I., et al.
We have previously shown that immune checkpoint receptors, including PD-1, are upregulated on T cells at the time of their activation, and that blockade of these receptors can improve the efficacy of antitumor vaccines. In the present study, we sought to determine whether, and by what mechanisms, the timing of PD-1 blockade with respect to vaccination affects antitumor T cell function.
TRAMP-C1 or E.G7-OVA tumor-bearing mice received PD-1 blockade at different timing intervals with a tumor-associated antigen vaccine. Tumor growth, survival, and immune-infiltrating populations were assessed. In vitro models of T cell activation using OT-I T cells and PD-(L)1 axis disruption with a PD-1 blocking antibody or PD-L1KO dendritic cells were used.
Mice receiving PD-1 blockade at the time of T cell activation with vaccine had better antitumor outcomes in comparison to mice receiving PD-1 blockade before or after immunization. T cells activated in vitro in the presence of PD-(L)1 axis disruption had a more differentiated, functional phenotype with decreased CD28 and CCR7 expression and increased production of the Tc1 cytokines IL-2, TNFα, and IFNγ. Intriguingly, a small subset of undifferentiated cells (CD28+) was of a stem-like Tc17 phenotype (IL-17α+, TCF1+). Tumor-bearing mice receiving T cells activated in the presence of PD-(L)1-axis disruption had better antitumor outcomes and a greater number of complete responses.
These data indicate that PD-1 blockade, when used with antitumor vaccines, acts primarily at the time of T cell activation, not exclusively within the tumor microenvironment. Consequently, PD-1 blockade may be best used when delivered concurrently with T cell activating agents such as vaccines.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Lymphatic platelet thrombosis limits bone repair by precluding lymphatic transporting DAMPs.
In Nature Communications on 18 January 2025 by Zheng, Y., Cong, L., et al.
In the musculoskeletal system, lymphatic vessels (LVs), which are interdigitated with blood vessels, travel and form an extensive transport network. Blood vessels in bone regulate osteogenesis and hematopoiesis, however, whether LVs in bone affect fracture healing is unclear. Here, we investigate the lymphatic draining function at the tibial fracture sites using near-infrared indocyanine green lymphatic imaging (NIR-ICG) and discover that lymphatic drainage insufficiency (LDI) starts on day one and persists for up to two weeks following the fracture in male mice. Sufficient lymphatic drainage facilitates fracture healing in male mice. Furthermore, we identify that lymphatic platelet thrombosis (LPT) blocks the draining lymphoid sinus and LVs, causes LDI, and inhibits fracture healing in male mice, which can be rescued by a blood thinner. Moreover, unblocked lymphatic drainage decreases neutrophils and increases M2-type macrophages of the hematoma niche to support osteoblast (OB) survival and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) proliferation via transporting damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in male rats. Lymphatic platelet thrombolysis also benefits senile fracture healing in female mice. These findings demonstrate that LPT limits bone regeneration by impeding lymphatic transporting DAMPs. Together, these findings represent a way forward in the treatment of bone repair.
© 2025. The Author(s).
In MedComm (2020) on 1 January 2025 by Wang, X., Zhan, Z., et al.
Agonists of the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway are increasingly being recognized as a promising new approach in the treatment of cancer. Although progress in clinical trials for STING agonists in antitumor applications has been slow, there is still an urgent need for developing new potent STING agonists with versatile potential applications. Herein, we developed and identified a non-nucleotide STING agonist called DW18343. DW18343 showed robust activation across different STING isoforms. Crystallography analysis revealed that DW18343 binds more deeply into the ligand binding domain (LBD) pocket of STING-H232 compared to other agonists such as MSA-2, SR-717, or cGAMP, which likely contributes to its high potency. DW18343 triggered downstream p-TBK1/p-IRF3 signaling, leading to the production of multiple cytokines. Additionally, DW18343 displayed broad and long-lasting antitumor effects in various syngeneic mouse tumor models, whether administered locally or systemically. Moreover, DW18343 induced immune memory to combat the growth of rechallenged tumors. Finally, DW18343 was shown to be an activator of both the innate and adaptive antitumor immunity in tumor tissue, potentially explaining its strong antitumor effects in vivo. In conclusion, DW18343 serves as a novel non-nucleotide STING agonist with systemic antitumor effect through the activation of antitumor immunity.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
-
Genetics
In Molecular Cancer Therapeutics on 3 December 2024 by Singh, S. S., Calvo, R., et al.
As tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) exercise a plethora of protumor and immune evasive functions, novel strategies targeting TAMs to inhibit tumor progression have emerged within the current arena of cancer immunotherapy. Activation of the mannose receptor 1 (CD206) is a recent approach that recognizes immunosuppressive CD206high M2-like TAMs as a drug target. Ligation of CD206 both induces reprogramming of CD206high TAMs toward a proinflammatory phenotype and selectively triggers apoptosis in these cells. CD206-activating therapeutics are currently limited to the linear, 10mer peptide RP-182, 1, which is not a drug candidate. In this study, we sought to identify a better suitable candidate for future clinical development by synthesizing and evaluating a series of RP-182 analogs. Surprisingly, fatty acid derivative 1a [RP-182-PEG3-K(palmitic acid)] not only showed improved stability but also increased affinity to the CD206 receptor through enhanced interaction with a hydrophobic binding motif of CD206. Peptide 1a showed superior in vitro activity in cell-based assays of macrophage activation which was restricted to CD206high M2-polarized macrophages. Improvement in responses was disproportionally skewed toward improved induction of phagocytosis including cancer cell phagocytosis. Peptide 1a reprogrammed the immune landscape in genetically engineered murine KPC pancreatic tumors toward increased innate immune surveillance and improved tumor control and effectively suppressed tumor growth of murine B16 melanoma allografts.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Cancer Research
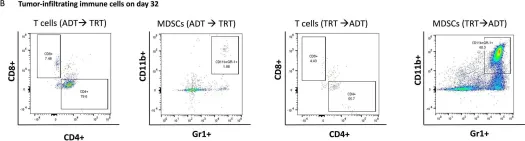
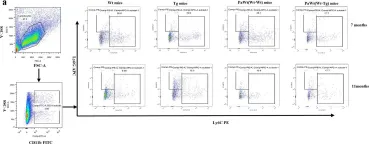
In J Immunother Cancer on 24 April 2024 by Muralidhar, A., Hernandez, R., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Immunother Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
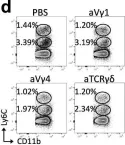
In Immun Ageing on 31 July 2023 by Li, C., Liu, K., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immun Ageing by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Immun Ageing on 31 July 2023 by Li, C., Liu, K., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immun Ageing by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Immun Ageing on 31 July 2023 by Li, C., Liu, K., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immun Ageing by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Immun Ageing on 31 July 2023 by Li, C., Liu, K., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immun Ageing by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
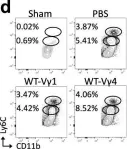
In Nat Commun on 18 July 2023 by Abou-El-Hassan, H., Rezende, R. M., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
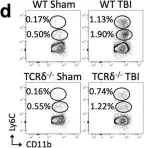
In Nat Commun on 18 July 2023 by Abou-El-Hassan, H., Rezende, R. M., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Nat Commun on 18 July 2023 by Abou-El-Hassan, H., Rezende, R. M., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8