Lung adenocarcinoma is a common aggressive cancer and a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Here, we report an important in vivo role for mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number during lung adenocarcinoma progression in the mouse. We found that lung tumors induced by KRASG12D expression have increased mtDNA levels and enhanced mitochondrial respiration. To experimentally assess a possible causative role in tumor progression, we induced lung cancer in transgenic mice with a general increase in mtDNA copy number and found that they developed a larger tumor burden, whereas mtDNA depletion in tumor cells reduced tumor growth. Immune cell populations in the lung and cytokine levels in plasma were not affected by increased mtDNA levels. Analyses of large cancer databases indicate that mtDNA copy number is also important in human lung cancer. Our study thus reports experimental evidence for a tumor-intrinsic causative role for mtDNA in lung cancer progression, which could be exploited for development of future cancer therapies.
Product Citations: 7
High mitochondrial DNA levels accelerate lung adenocarcinoma progression.
In Science Advances on 1 November 2024 by Mennuni, M., Wilkie, S. E., et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Genetics
GPR92 activation in islet macrophages controls β cell function in a diet-induced obesity model.
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 1 November 2022 by de Souza, C. O., Paschoal, V. A., et al.
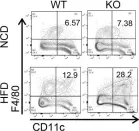
The molecular mechanisms underlying obesity-induced increases in β cell mass and the resulting β cell dysfunction need to be elucidated further. Our study revealed that GPR92, expressed in islet macrophages, is modulated by dietary interventions in metabolic tissues. Therefore, we aimed to define the role of GPR92 in islet inflammation by using a high-fat diet-induced (HFD-induced) obese mouse model. GPR92-KO mice exhibited glucose intolerance and reduced insulin levels - despite the enlarged pancreatic islets - as well as increased islet macrophage content and inflammation level compared with WT mice. These results indicate that the lack of GPR92 in islet macrophages can cause β cell dysfunction, leading to disrupted glucose homeostasis. Alternatively, stimulation with the GPR92 agonist farnesyl pyrophosphate results in the inhibition of HFD-induced islet inflammation and increased insulin secretion in WT mice, but not in GPR92-KO mice. Thus, our study suggests that GPR92 can be a potential target to alleviate β cell dysfunction via the inhibition of islet inflammation associated with the progression of diabetes.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Tet2 deficiency drives liver microbiome dysbiosis triggering Tc1 cell autoimmune hepatitis.
In Cell Host & Microbe on 13 July 2022 by Pandey, S. P., Bender, M. J., et al.
The triggers that drive interferon-γ (IFNγ)-producing CD8 T cell (Tc1 cell)-mediated autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) remain obscure. Here, we show that lack of hematopoietic Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 (Tet2), an epigenetic regulator associated with autoimmunity, results in the development of microbiota-dependent AIH-like pathology, accompanied by hepatic enrichment of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligand-producing pathobionts and rampant Tc1 cell immunity. We report that AIH-like disease development is dependent on both IFNγ and AhR signaling, as blocking either reverts ongoing AIH-like pathology. Illustrating the critical role of AhR-ligand-producing pathobionts in this condition, hepatic translocation of the AhR ligand indole-3-aldehyde (I3A)-releasing Lactobacillus reuteri is sufficient to trigger AIH-like pathology. Finally, we demonstrate that I3A is required for L. reuteri-induced Tc1 cell differentiation in vitro and AIH-like pathology in vivo, both of which are restrained by Tet2 within CD8 T cells. This AIH-disease model may contribute to the development of therapeutics to alleviate AIH.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 19 May 2020 by Moorlag, S. J. C. F. M., Khan, N., et al.
β-glucan is a potent inducer of epigenetic and functional reprogramming of innate immune cells, a process called "trained immunity," resulting in an enhanced host response against secondary infections. We investigate whether β-glucan exposure confers protection against pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. β-glucan induces trained immunity via histone modifications at gene promoters in human monocytes, which is accompanied by the enhanced production of proinflammatory cytokines upon secondary Mtb challenge and inhibition of Mtb growth. Mice treated with β-glucan are significantly protected against pulmonary Mtb infection, which is associated with the expansion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the bone marrow and increased myelopoiesis. The protective signature of β-glucan is mediated via IL-1 signaling, as β-glucan shows no protection in mice lacking a functional IL-1 receptor (IL1R-/-). The administration of β-glucan may be used as a novel strategy in the treatment of mycobacterial infections and possibly as an adjuvant to improve anti-tuberculosis vaccines.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
RIPK3 Activation Leads to Cytokine Synthesis that Continues after Loss of Cell Membrane Integrity.
In Cell Reports on 27 August 2019 by Orozco, S. L., Daniels, B. P., et al.
Necroptosis is a form of programmed cell death that is defined by activation of the kinase RIPK3 and subsequent cell membrane permeabilization by the effector MLKL. RIPK3 activation can also promote immune responses via production of cytokines and chemokines. How active cytokine production is coordinated with the terminal process of necroptosis is unclear. Here, we report that cytokine production continues within necroptotic cells even after they have lost cell membrane integrity and irreversibly committed to death. This continued cytokine production is dependent on mRNA translation and requires maintenance of endoplasmic reticulum integrity that remains after plasma membrane integrity is lost. The continued translation of cytokines by cellular corpses contributes to necroptotic cell uptake by innate immune cells and priming of adaptive immune responses to antigens associated with necroptotic corpses. These findings imply that cell death and production of inflammatory mediators are coordinated to optimize the immunogenicity of necroptotic cells.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In J Clin Invest on 1 November 2022 by de Souza, C. O., Paschoal, V. A., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Clin Invest by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1