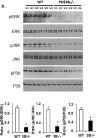
Themis is important in regulating positive selection of thymocytes during T cell development, but its role in peripheral T cells is less understood. Here, we investigated T cell activation and its sequelae using a tamoxifen-mediated, acute Themis deletion mouse model. We find that proliferation, effector functions including anti-tumor killing, and up-regulation of energy metabolism are severely compromised. This study reveals the phenomenon of peripheral adaptation to loss of Themis, by demonstrating direct TCR-induced defects after acute deletion of Themis that were not evident in peripheral T cells chronically deprived of Themis in dLck-Cre deletion model. Peripheral adaptation to long-term loss was compared using chronic versus acute tamoxifen-mediated deletion and with the (chronic) dLck-Cre deletion model. We found that upon chronic tamoxifen-mediated Themis deletion, there was modulation in the gene expression profile for both TCR and cytokine signaling pathways. This profile overlapped with (chronic) dLck-Cre deletion model. Hence, we found that peripheral adaptation induced changes to both TCR and cytokine signaling modules. Our data highlight the importance of Themis in the activation of CD8+ T cells.
© 2023 Gautam et al.
Product Citations: 49
Themis controls T cell activation, effector functions, and metabolism of peripheral CD8+ T cells.
In Life Science Alliance on 1 December 2023 by Gautam, N., Wojciech, L., et al.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports Medicine on 21 February 2023 by Wu, L., Brzostek, J., et al.
Signal transduction induced by chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) is generally believed to rely on the activity of the SRC family kinase (SFK) LCK, as is the case with T cell receptor (TCR) signaling. Here, we show that CAR signaling occurs in the absence of LCK. This LCK-independent signaling requires the related SFK FYN and a CD28 intracellular domain within the CAR. LCK-deficient CAR-T cells are strongly signaled through CAR and have better in vivo efficacy with reduced exhaustion phenotype and enhanced induction of memory and proliferation. These distinctions can be attributed to the fact that FYN signaling tends to promote proliferation and survival, whereas LCK signaling promotes strong signaling that tends to lead to exhaustion. This non-canonical signaling of CAR-T cells provides insight into the initiation of both TCR and CAR signaling and has important clinical implications for improvement of CAR function.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Food and Chemical Toxicology : An International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association on 1 December 2020 by Hossain, K. F. B., Hosokawa, T., et al.
Mercury (Hg) is a toxic metal, well-known for its dangerous health effects on human. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is a phenolic component generally consumed as a food additive as an antioxidant. However, BHT induced antioxidant properties against heavy metals-influenced toxicity are little studied. We hypothesized that BHT has a regulatory effect on Hg-induced cytotoxicity. The objective of this research was to assess the protecting effects of BHT against inorganic Hg (iHg)-toxicity in PC12 cells, where cells were treated with/without HgCl2 (Hg2+) (5 μM) and BHT (100 μM) for 48 h and analyzed further. Cells treated by Hg caused a significant cell viability reduction, membrane damage, glutathione reduction, DNA fragmentation, ROS generation, with suppressed expressions of akt, mTOR, ERK1, Nrf2 and HO1; and elevated apoptotic expressions of p53, Bax, cytochrome c and active caspase 3. However, BHT and Hg2+ co-exposure showed prevention against Hg2+-toxicity by improving GSH content and inhibiting ROS generation and oxidative stress mediated damages. Additionally, BHT co-treatment inverted the pro-apoptotic proteins by augmenting pro-survival regulatory proteins akt, mTOR, ERK1, Nrf2 and HO1. These findings proved that BHT inhibits Hg2+-toxicity, hindering ROS generation and intrinsic apoptosis, via enhancing glutathione and antioxidants; and suggested BHT implications as therapeutic.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Cell Biology
A Dual Inhibitor of Cdc7/Cdk9 Potently Suppresses T Cell Activation.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 14 August 2019 by Chen, E. W., Tay, N. Q., et al.
T cell activation is mediated by signaling pathways originating from the T cell receptor (TCR). Propagation of signals downstream of the TCR involves a cascade of numerous kinases, some of which have yet to be identified. Through a screening strategy that we have previously introduced, PHA-767491, an inhibitor of the kinases Cdc7 and Cdk9, was identified to impede TCR signaling. PHA-767491 suppressed several T cell activation phenomena, including the expression of activation markers, proliferation, and effector functions. We also observed a defect in TCR signaling pathways upon PHA-767491 treatment. Inhibition of Cdc7/Cdk9 impairs T cell responses, which could potentially be detrimental for the immune response to tumors, and also compromises the ability to resist infections. The Cdc7/Cdk9 inhibitor is a strong candidate as a cancer therapeutic, but its effect on the immune system poses a problem for clinical applications.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 13 July 2018 by Zhao, X., Sankaran, S., et al.
Foreign antigens are presented by antigen-presenting cells in the presence of abundant endogenous peptides that are nonstimulatory to the T cell. In mouse T cells, endogenous, nonstimulatory peptides have been shown to enhance responses to specific peptide antigens, a phenomenon termed coagonism. However, whether coagonism also occurs in human T cells is unclear, and the molecular mechanism of coagonism is still under debate since CD4 and CD8 coagonism requires different interactions. Here we show that the nonstimulatory, HIV-derived peptide GAG enhances a specific human cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to HBV-derived epitopes presented by HLA-A*02:01. Coagonism in human T cells requires the CD8 coreceptor, but not T-cell receptor (TCR) binding to the nonstimulatory peptide-MHC. Coagonists enhance the phosphorylation and recruitment of several molecules involved in the TCR-proximal signaling pathway, suggesting that coagonists promote T-cell responses to antigenic pMHC by amplifying TCR-proximal signaling.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
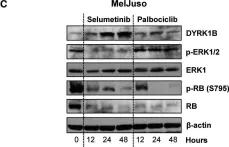
In Sci Rep on 20 June 2016 by Ahmad, F., Chung, Y. W., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
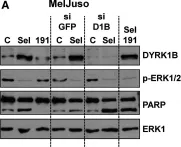
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 1 February 2016 by Ashford, A. L., Dunkley, T. P., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Mol Life Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 1 February 2016 by Ashford, A. L., Dunkley, T. P., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Mol Life Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 1 February 2016 by Ashford, A. L., Dunkley, T. P., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Mol Life Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 1 February 2016 by Ashford, A. L., Dunkley, T. P., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Mol Life Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 1 February 2016 by Ashford, A. L., Dunkley, T. P., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Mol Life Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
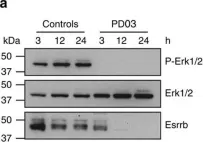
In Nat Commun on 24 July 2015 by Latos, P. A., Gonçalves, A., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
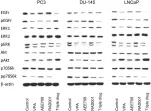
In BMC Cancer on 25 August 2011 by Wedel, S., Hudak, L., et al.
Fig.8.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from BMC Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8