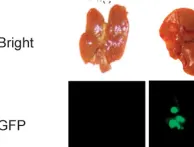
Recent characterization of spatiotemporal genomic architecture of IDH-wild-type multifocal glioblastomas (M-GBMs) suggests a clinically unobserved common-ancestor (CA) with a less aggressive phenotype, generating highly genetically divergent malignant gliomas/GBMs in distant brain regions. Using serial MRI/3D-reconstruction, whole-genome sequencing and spectral karyotyping-based single-cell phylogenetic tree building, we show two distinct types of tumor evolution in p53-mutant driven mouse models. Malignant gliomas/GBMs grow as a single mass (Type 1) and multifocal masses (Type 2), respectively, despite both exhibiting loss of Pten/chromosome 19 (chr19) and PI3K/Akt activation with sub-tetraploid/4N genomes. Analysis of early biopsied and multi-segment tumor tissues reveals no evidence of less proliferative diploid/2N lesions in Type 1 tumors. Strikingly, CA-derived relatively quiescent tumor precursors with ancestral diploid/2N genomes and normal Pten/chr19 are observed in the subventricular zone (SVZ), but are distantly segregated from multi focal Type 2 tumors. Importantly, PI3K/Akt inhibition by Rictor/mTORC2 deletion blocks distant dispersal, restricting glioma growth in the SVZ.
Product Citations: 8
In Nature Communications on 22 July 2020 by Li, Y., Li, B., et al.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
In PLoS Biology on 1 October 2019 by Sutton, L. P., Muntean, B. S., et al.
The striatum plays a fundamental role in motor learning and reward-related behaviors that are synergistically shaped by populations of D1 dopamine receptor (D1R)- and D2 dopamine receptor (D2R)-expressing medium spiny neurons (MSNs). How various neurotransmitter inputs converging on common intracellular pathways are parsed out to regulate distinct behavioral outcomes in a neuron-specific manner is poorly understood. Here, we reveal that distinct contributions of D1R-MSNs and D2R-MSNs towards reward and motor behaviors are delineated by the multifaceted signaling protein neurofibromin 1 (NF1). Using genetic mouse models, we show that NF1 in D1R-MSN modulates opioid reward, whereas loss of NF1 in D2R-MSNs delays motor learning by impeding the formation and consolidation of repetitive motor sequences. We found that motor learning deficits upon NF1 loss were associated with the disruption in dopamine signaling to cAMP in D2R-MSN. Restoration of cAMP levels pharmacologically or chemogenetically rescued the motor learning deficits seen upon NF1 loss in D2R-MSN. Our findings illustrate that multiplex signaling capabilities of MSNs are deployed at the level of intracellular pathways to achieve cell-specific control over behavioral outcomes.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Neuroscience
In Cell Reports on 10 July 2018 by Akgul, S., Li, Y., et al.
Most human cancers arise from stem and progenitor cells by the sequential accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations, while cancer modeling typically requires simultaneous multiple oncogenic events. Here, we show that a single p53 mutation, despite causing no defect in the mouse brain, promoted neural stem and progenitor cells to spontaneously accumulate oncogenic alterations, including loss of multiple chromosomal (chr) regions syntenic to human chr10 containing Pten, forming malignant gliomas with PI3K/Akt activation. Rictor/mTORC2 loss inhibited Akt signaling, greatly delaying and reducing glioma formation by suppressing glioma precursors within the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Rictor/mTORC2 loss delayed timely differentiation of granule cell precursors (GCPs) during cerebellar development, promoting sustained GCP proliferation and medulloblastoma formation, which recapitulated critical features of TP53 mutant sonic hedgehog (SHH) medulloblastomas with GLI2 and/or N-MYC amplification. Our study demonstrates that Rictor/mTORC2 has opposing functions in neural stem cells and GCPs in the adult and the developing brain, promoting malignant gliomas and suppressing SHH-medulloblastoma formation, respectively.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
In eLife on 16 January 2017 by Pal, D., Pertot, A., et al.
Many lines of evidence have indicated that both genetic and non-genetic determinants can contribute to intra-tumor heterogeneity and influence cancer outcomes. Among the best described sub-population of cancer cells generated by non-genetic mechanisms are cells characterized by a CD44+/CD24- cell surface marker profile. Here, we report that human CD44+/CD24- cancer cells are genetically highly unstable because of intrinsic defects in their DNA-repair capabilities. In fact, in CD44+/CD24- cells, constitutive activation of the TGF-beta axis was both necessary and sufficient to reduce the expression of genes that are crucial in coordinating DNA damage repair mechanisms. Consequently, we observed that cancer cells that reside in a CD44+/CD24- state are characterized by increased accumulation of DNA copy number alterations, greater genetic diversity and improved adaptability to drug treatment. Together, these data suggest that the transition into a CD44+/CD24- cell state can promote intra-tumor genetic heterogeneity, spur tumor evolution and increase tumor fitness.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
In Oncogene on 14 July 2016 by Ksionda, O., Melton, A. A., et al.
Ras GTPases are activated by RasGEFs and inactivated by RasGAPs, which stimulate the hydrolysis of RasGTP to inactive RasGDP. GTPase-impairing somatic mutations in RAS genes, such as KRAS(G12D), are among the most common oncogenic events in metastatic cancer. A different type of cancer Ras signal, driven by overexpression of the RasGEF RasGRP1 (Ras guanine nucleotide-releasing protein 1), was recently implicated in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) patients and murine models, in which RasGRP1 T-ALLs expand in response to treatment with interleukins (ILs) 2, 7 and 9. Here, we demonstrate that IL-2/7/9 stimulation activates Erk and Akt pathways downstream of Ras in RasGRP1 T-ALL but not in normal thymocytes. In normal lymphocytes, RasGRP1 is recruited to the membrane by diacylglycerol (DAG) in a phospholipase C-γ (PLCγ)-dependent manner. Surprisingly, we find that leukemic RasGRP1-triggered Ras-Akt signals do not depend on acute activation of PLCγ to generate DAG but rely on baseline DAG levels instead. In agreement, using three distinct assays that measure different aspects of the RasGTP/GDP cycle, we established that overexpression of RasGRP1 in T-ALLs results in a constitutively high GTP-loading rate of Ras, which is constantly counterbalanced by hydrolysis of RasGTP. KRAS(G12D) T-ALLs do not show constitutive GTP loading of Ras. Thus, we reveal an entirely novel type of leukemogenic Ras signals that is based on a RasGRP1-driven increased in flux through the RasGTP/GDP cycle, which is mechanistically very different from KRAS(G12D) signals. Our studies highlight the dynamic balance between RasGEF and RasGAP in these T-ALLs and put forth a new model in which IL-2/7/9 decrease RasGAP activity.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
In Elife on 16 January 2017 by Pal, D., Pertot, A., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In PLoS One on 5 March 2015 by Li, J., Chanrion, M., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2