Proliferative vitreoretinopathy is a vision-threatening response to penetrating ocular injury, for which there is no satisfactory treatment. In this disorder, retinal pigment epithelial cells, abandon their attachment to Bruch's membrane on the scleral side of the retina, transform into motile fibroblast-like cells, and migrate through the retinal wound to the vitreal surface of the retina, where they secrete membrane-forming proteins. Annexin A2 is a calcium-regulated protein that, in complex with S100A10, assembles plasmin-forming proteins at cell surfaces. Here, we show that, in proliferative vitreoretinopathy, recruitment of macrophages and directed migration of retinal pigment epithelial cells are annexin A2-dependent, and stimulated by macrophage inflammatory protein-1α/β. These factors induce translocation of annexin A2 to the cell surface, thus enabling retinal pigment epithelial cell migration following injury; our studies reveal further that treatment of mice with intraocular antibody to either annexin A2 or macrophage inflammatory protein dampens the development of proliferative vitreoretinopathy in mice.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 41
In Nature Communications on 9 October 2024 by Luo, M., Almeida, D., et al.
-
Block
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS on 10 October 2023 by Price, Z. K., Lokman, N. A., et al.
Although the pro-tumorigenic functions of hyaluronan (HA) are well documented there is limited information on the effects and targets of different molecular weight HA. Here, we investigated the effects of 27 kDa, 183 kDa and 1000 kDa HA on ES-2 ovarian cancer cells overexpressing the stem cell associated protein, Notch3. 1000 kDA HA promoted spheroid formation in ES-2 cells mixed with ES-2 overexpressing Notch3 (1:3). We report disabled-2 (DAB2) as a novel protein regulated by 1000 kDa HA and further investigated its role in ovarian cancer. DAB2 was downregulated in ovarian cancer compared to normal tissues but increased in metastatic ovarian tumors compared to primary tumors. High DAB2 expression was associated with poor patient outcome and positively correlated with HA synthesis enzyme HAS2, HA receptor CD44 and EMT and macrophage markers. Stromal DAB2 immunostaining was significantly increased in matched ovarian cancer tissues at relapse compared to diagnosis and associated with reduced survival. The proportion of DAB2 positive macrophages was significantly increased in metastatic ovarian cancer tissues compared to primary cancers. However, DAB2 overexpression significantly reduced invasion by both A2780 and OVCAR3 cells in vivo. Our research identifies a novel relationship between HA signalling, Notch3 and DAB2. We highlight a complex relationship of both pro-tumorigenic and tumor suppressive functions of DAB2 in ovarian cancer. Our findings highlight that DAB2 has a direct tumor suppressive role on ovarian cancer cells. The pro-tumorigenic role of DAB2 may be mediated by tumour associated macrophages and requires further investigation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
Preprint on Research Square on 12 July 2023 by Price, Z. K., Lokman, N. A., et al.
Although the pro-tumorigenic functions of hyaluronan (HA) are well documented there is limited information on the effects and targets of different molecular weight HA. Here, we investigated the effects of 27kDa, 183kDa and 1000kDa HA on ES2 ovarian cancer cells overexpressing the stem cell associated protein, Notch3. 1000kDA HA promoted spheroid formation in ES2 cells mixed with ES-2 overexpressing Notch3 (1:3). We report disabled-2 (DAB2) as a novel protein regulated by high molecular weight HA and further investigated its role in ovarian cancer. DAB2 was downregulated in ovarian cancer compared to normal tissues but increased in metastatic ovarian tumors compared to primary tumors. High DAB2 expression was associated with poor patient outcome and positively correlated with HA synthesis enzyme HAS2 , HA receptor, CD44 and EMT and macrophage markers. Stromal DAB2 immunostaining was significantly increased in matched ovarian cancer tissues at relapse compared to diagnosis and associated with reduced survival. However, DAB2 overexpression significantly reduced invasion by both A2780 and OVCAR3 cells in vivo . Our research identifies a novel relationship between HA and DAB2. Furthermore, we highlight a complex relationship of both pro-tumorigenic and tumor suppressive functions of DAB2 in ovarian cancer. Further research should explore the pro-tumorigenic role of DAB2 within the tumor microenvironment of ovarian cancer.
-
Cancer Research
RNA-binding is an ancient trait of the Annexin family.
In Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology on 3 July 2023 by Patil, S. S., Panchal, V., et al.
Introduction: The regulation of intracellular functions in mammalian cells involves close coordination of cellular processes. During recent years it has become evident that the sorting, trafficking and distribution of transport vesicles and mRNA granules/complexes are closely coordinated to ensure effective simultaneous handling of all components required for a specific function, thereby minimizing the use of cellular energy. Identification of proteins acting at the crossroads of such coordinated transport events will ultimately provide mechanistic details of the processes. Annexins are multifunctional proteins involved in a variety of cellular processes associated with Ca2+-regulation and lipid binding, linked to the operation of both the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Furthermore, certain Annexins have been implicated in the regulation of mRNA transport and translation. Since Annexin A2 binds specific mRNAs via its core structure and is also present in mRNP complexes, we speculated whether direct association with RNA could be a common property of the mammalian Annexin family sharing a highly similar core structure. Methods and results: Therefore, we performed spot blot and UV-crosslinking experiments to assess the mRNA binding abilities of the different Annexins, using annexin A2 and c-myc 3'UTRs as well as c-myc 5'UTR as baits. We supplemented the data with immunoblot detection of selected Annexins in mRNP complexes derived from the neuroendocrine rat PC12 cells. Furthermore, biolayer interferometry was used to determine the KD of selected Annexin-RNA interactions, which indicated distinct affinities. Amongst these Annexins, Annexin A13 and the core structures of Annexin A7, Annexin A11 bind c-myc 3'UTR with KDs in the nanomolar range. Of the selected Annexins, only Annexin A2 binds the c-myc 5'UTR indicating some selectivity. Discussion: The oldest members of the mammalian Annexin family share the ability to associate with RNA, suggesting that RNA-binding is an ancient trait of this protein family. Thus, the combined RNA- and lipid-binding properties of the Annexins make them attractive candidates to participate in coordinated long-distance transport of membrane vesicles and mRNAs regulated by Ca2+. The present screening results can thus pave the way for studies of the multifunctional Annexins in a novel cellular context.
Copyright © 2023 Patil, Panchal, Røstbø, Romanyuk, Hollås, Brenk, Grindheim and Vedeler.
-
WB
-
Genetics
Preprint on Research Square on 26 June 2023 by Price, Z. K., Lokman, N. A., et al.
Objective: Although the pro-tumorigenic functions of hyaluronan (HA) are well documented in ovarian cancer, there is limited information on the effects of different molecular weight HA. The aim of this study was to analyse the effects of different molecular weight HA on ovarian cancer cells overexpressing Notch3 intracellular domain (NICD3, stem cell associated protein). Methods: : Mass spectrometry analysis of spheroids from ES-2 cells overexpressing NICD3 (ES-2-Rv-NICD3) with wild type ES-2 (ES-2:ES-2-Rv-NICD3, 1:3) treated with 27kDa, 183kDa or 1000kDa HA identified a novel protein regulated by high molecular weight HA (HMW-HA), disabled-2 (DAB2). Correlations between DAB2 and patient prognosis and pro-tumorigenic signatures were assessed in online databases. DAB2 was assessed by immunohistochemistry in a tissue microarray cohort of high grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) and matching tissues following relapse. Gain-of-function lentiviral methods were employed in A2780 and OVCAR3 ovarian cancer cells to determine the effect of DAB2 on cell survival, spheroid formation, gene expression, cell motility and invasion in vitro and in vivo using the chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay. Results: : HMW-HA (1000kDa) enhanced spheroid formation of ES-2:ES-2-Rv-NICD3 cells. Mass spectrometry identified DAB2 was upregulated 5.2 fold in HMW-HA treated ES-2:ES-2-Rv-NICD3 spheroids. Online database analysis showed DAB2 was downregulated in ovarian cancer compared to normal ovarian tissue but increased in metastatic compared to primary ovarian tumors. High DAB2 expression was associated with poor patient outcome and positively correlated with EMT markers . Stromal DAB2 immunostaining was significantly increased in matched tissues at relapse compared to diagnosis and associated with reduced survival. Furthermore, DAB2 protein co-localised with macrophage marker (CD68) in HGSOC tissues. In OVCAR3 but not A2780 cells, DAB2 overexpression enhanced carboplatin resistance and reduced cell motility and invasion in vitro . DAB2 overexpression reduced OVCAR3 and A2780 cell survival and in vivo invasion in the CAM assay. Conclusions: : Our findings highlight that DAB2 has both tumor suppressive and pro-tumorigenic functions in ovarian cancer
-
Cancer Research
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 3 July 2023 by Patil, S. S., Panchal, V., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 3 July 2023 by Patil, S. S., Panchal, V., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
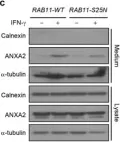
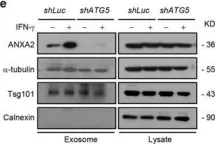
In Sci Rep on 18 July 2017 by Chen, Y. D., Fang, Y. T., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
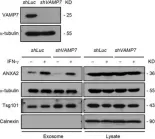
In Sci Rep on 18 July 2017 by Chen, Y. D., Fang, Y. T., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In Sci Rep on 18 July 2017 by Chen, Y. D., Fang, Y. T., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In Sci Rep on 18 July 2017 by Chen, Y. D., Fang, Y. T., et al.
Fig.2.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
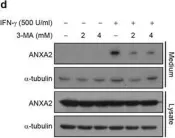
In Sci Rep on 18 July 2017 by Chen, Y. D., Fang, Y. T., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
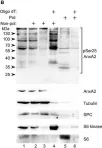
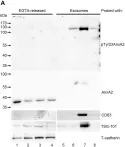
In FEBS Open Bio on 1 February 2017 by Aukrust, I., Rosenberg, L. A., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from FEBS Open Bio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
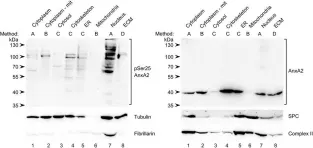
In FEBS Open Bio on 1 February 2017 by Aukrust, I., Rosenberg, L. A., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from FEBS Open Bio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In FEBS Open Bio on 1 February 2017 by Aukrust, I., Rosenberg, L. A., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from FEBS Open Bio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In FEBS Open Bio on 1 February 2017 by Aukrust, I., Rosenberg, L. A., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from FEBS Open Bio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In FEBS Open Bio on 1 February 2017 by Aukrust, I., Rosenberg, L. A., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from FEBS Open Bio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
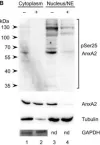
In J Cell Sci on 15 January 2016 by Grindheim, A. K., Hollås, H., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
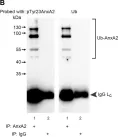
In J Cell Sci on 15 January 2016 by Grindheim, A. K., Hollås, H., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
IP
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
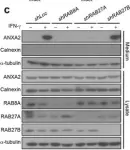
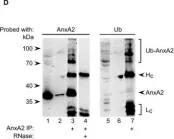
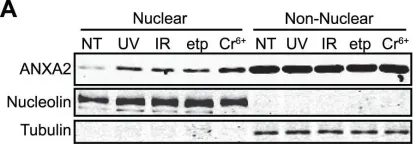
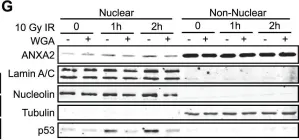
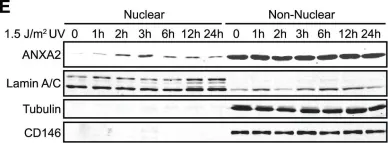
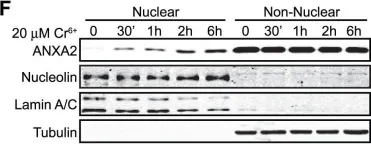
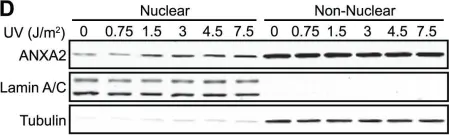
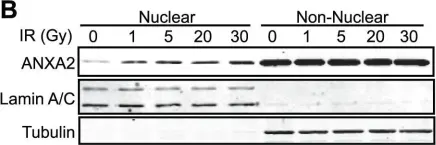
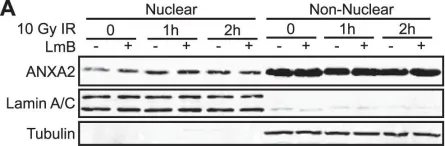
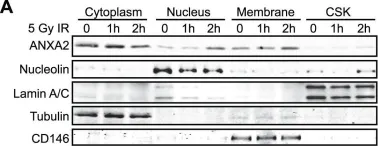
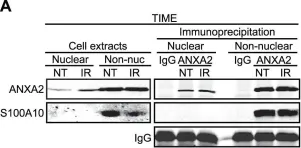
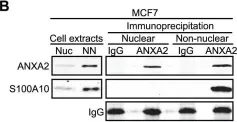
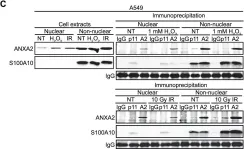
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.1.G

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.1.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25
In PLoS One on 12 December 2012 by Madureira, P. A., Hill, R., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 25