During long-term peritoneal dialysis, peritoneal fibrosis (PF) often happens and results in ultrafiltration failure, which directly leads to the termination of dialysis. The accumulation of extracellular matrix produced from an increasing number of myofibroblasts was a hallmark characteristic of PF. To date, glucose degradation products (GDPs, i.e., methylglyoxal (MGO)) that appeared during the heating and storage of the dialysate are considered to be key components to initiating PF, but how GDPs lead to the activation of myofibroblast in fibrotic peritoneum has not yet been fully elucidated. In this study, mesothelial cell line (MeT-5A) and fibroblast cell line (MRC-5) were used to investigate the transcriptomic and proteomic changes to unveil the underlying mechanism of MGO-induced PF. Our transcriptomic data from the MGO-stimulated mesothelial cells showed upregulation of genes involved in pro-inflammatory, apoptotic, and fibrotic pathways. While no phenotypic changes were noted on fibroblasts after direct MGO, supernatant from MGO-stimulated mesothelial cells promoted fibroblasts to change into proto-myofibroblasts, activated fibroblasts in the first stage toward myofibroblasts. In conclusion, this study showed that MGO-stimulated mesothelial cells promoted fibroblast-to-proto-myofibroblast transition; however, additional involvement of other factors or cells (e.g., macrophages) may be needed to complete the transformation into myofibroblasts.
Product Citations: 238
Methylglyoxal-Stimulated Mesothelial Cells Prompted Fibroblast-to-Proto-Myofibroblast Transition.
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 19 January 2025 by Wei, Y. S., Tsai, S. Y., et al.
In International Journal of Biological Sciences on 12 December 2024 by Barilani, M., Peli, V., et al.
Extracellular vesicles (EV) have emerged as promising cell-free therapeutics in regenerative medicine. However, translating primary cell line-derived EV to clinical applications requires large-scale manufacturing and several challenges, such as replicative senescence, donor heterogeneity, and genetic instability. To address these limitations, we used a reprogramming approach to generate human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) from the young source of cord blood mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (CBMSC). Capitalizing on their inexhaustible supply potential, hiPSC offer an attractive EV reservoir. Our approach encompassed an exhaustive characterization of hiPSC-EV, aligning with the rigorous MISEV2023 guidelines. Analyses demonstrated physical features compatible with small EV (sEV) and established their identity and purity. Moreover, the sEV-shuttled non-coding (nc) RNA landscape, focusing on the microRNA and circular RNA cargo, completed the molecular signature. The kinetics of the hiPSC-sEV release and cell internalization assays unveiled robust EV production and consistent uptake by human neurons. Furthermore, hiPSC-sEV demonstrated ex vivo cell tissue-protective properties. Finally, via bioinformatics, the potential involvement of the ncRNA cargo in the hiPSC-sEV biological effects was explored. This study significantly advances the understanding of pluripotent stem cell-derived EV. We propose cord blood MSC-derived hiPSC as a promising source for potentially therapeutic sEV.
© The author(s).
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology on 15 November 2024 by Wang, X., Wang, Y., et al.
Transforming growth factor (TGF)β1 induces plasma membrane (PM) accumulation of glucose transporter 1 (Glut1) required for glycolysis of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and HSC activation. This study aimed to understand how Glut1 is anchored/docked onto the PM of HSCs.HSC expression of protein kinase M zeta isoform (PKMζ) was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), Western blotting, and immunofluorescence. PKMζ level was manipulated by short hairpin RNA (shRNA) or overexpression; HSC activation was assessed by cell expression of activation markers; PM Glut1, glucose uptake, and glycolysis of HSCs were analyzed by biotinylation, 2-NBDG-based assay, and Seahorse Glycolysis Stress Test. Phospho-mutants of vasodilator-stimulated phosphorylated protein (VASP) were created by site-directed mutagenesis. TGFβ transcriptome was obtained by RNA sequencing. Single-cell RNA sequencing datasets and immunofluorescence were leveraged to analyze PKMζ expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) of colorectal liver metastases. Function of HSC PKMζ was determined by tumor/HSC co-implantation study.Primary human and murine HSCs express PKMζ, but not full-length PKCζ. PKMζ knockdown suppresses, whereas PKMζ overexpression potentiates PM accumulation of Glut1, glycolysis, and HSC activation induced by TGFβ1. Mechanistically, PKMζ binds to and induces VASP phosphorylation at serines 157 and 239 facilitating anchoring/docking of Glut1 onto the PM of HSCs. PKMζ expression is increased in the CAFs of murine and patient colorectal liver metastases compared with quiescent HSCs. Targeting PKMζ suppresses transcriptome, CAF activation of HSCs, and colorectal tumor growth in mice.Because HSCs are also a major contributor of liver fibrosis, our data highlight PKMζ and VASP as targets to inhibit metabolic reprogramming, HSC activation, liver fibrosis, and the pro-metastatic microenvironment of the liver.Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 14 September 2024 by Tessier, C., Derrien, J., et al.
Tumor heterogeneity and plasticity, driven by Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT), enable cancer therapeutic resistance. We previously showed that EMT promotes primary cilia formation, which enables stemness and tumorigenesis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Here, we establish a role for primary cilia in human TNBC chemotherapeutic resistance. We developed patient-derived organoids, and showed that these recapitulated the cellular heterogeneity of TNBC biopsies. Notably, one of the identified cell states bore a quasi-mesenchymal phenotype, primary cilia, and stemness signatures. We treated our TNBC organoids with chemotherapeutics and observed partial killing. The surviving cells with organoid-reconstituting capacity showed selective enrichment for the quasi-mesenchymal ciliated cell subpopulation. Genomic analyses argue that this enrichment reflects a combination of pre-existing cells and ones that arose through drug-induced cellular plasticity. We developed a family of small-molecule inhibitors of ciliogenesis and show that these, or genetic ablation of primary cilia, suppress chemoresistance. We conclude that primary cilia help TNBC to evade chemotherapy.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 27 August 2024 by Liao, C. Y., Hundscheid, J. H., et al.
ABSTRACT In fibrotic tissues, activated fibroblasts remodel the collagen-rich extracellular matrix (ECM). Intervening with this process represents a candidate therapeutic strategy to attenuate disease progression. Models that generate quantitative data on 3D fibroblast-mediated ECM remodeling with the reproducibility and throughput needed for drug testing are lacking. Here, we develop a model that fits this purpose and produces combined quantitative information on drug efficacy and cytotoxicity. We use microinjection robotics to design patterns of fibrillar collagen-embedded fibroblast clusters and apply automated microscopy and image analysis to quantify ECM remodeling between-, and cell viability within clusters of TGFβ-activated primary human skin or lung fibroblasts. We apply this assay to compound screening and reveal actionable targets to suppress fibrotic ECM remodeling. Strikingly, we find that after an initial phase of fibroblast activation by TGFβ, canonical TGFβ signaling is dispensable and, instead, non-canonical activation of MEK-ERK signaling drives ECM remodeling. Moreover, we reveal that higher concentrations of two TGFβ receptor inhibitors while blocking canonical TGFβ signaling, in fact stimulate this MEK-mediated profibrotic ECM remodeling activity.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
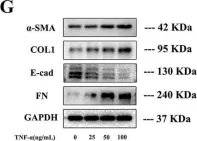
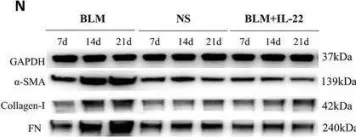
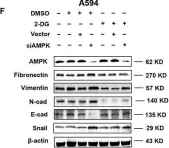
In Cell Death Discov on 28 July 2023 by Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
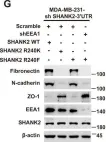
Fig.1.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
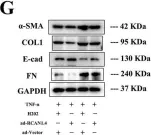
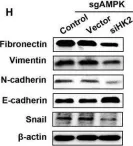
In Cell Death Discov on 28 July 2023 by Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
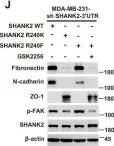
Fig.2.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
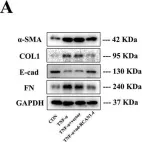
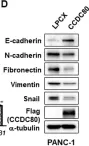
In Cell Death Discov on 28 July 2023 by Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
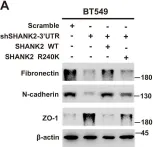
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
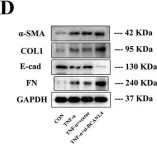
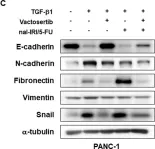
In Cell Death Discov on 28 July 2023 by Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
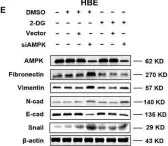
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Cell Death Discov on 28 July 2023 by Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Cell Death Discov on 28 July 2023 by Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Cell Death Discov on 28 July 2023 by Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., et al.
Fig.5.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
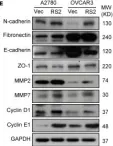
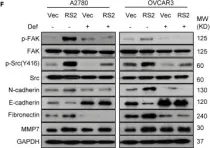
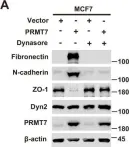
In Cancers (Basel) on 29 March 2023 by Galappaththi, S. L., Katz, B., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
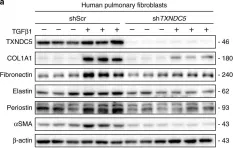
In iScience on 21 October 2022 by Pan, R., Yu, Y., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from iScience by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In iScience on 21 October 2022 by Pan, R., Yu, Y., et al.
Fig.4.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from iScience by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
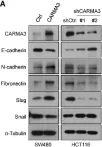
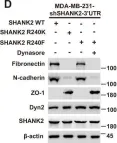
In Cancers (Basel) on 26 November 2021 by Chang, T. Y., Wu, C. T., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
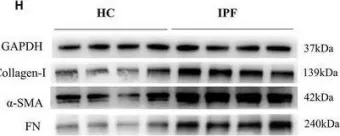
In Clin Transl Med on 1 August 2021 by Gu, P., Wang, D., et al.
Fig.2.H

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Clin Transl Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Clin Transl Med on 1 August 2021 by Gu, P., Wang, D., et al.
Fig.4.N

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Clin Transl Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Elife on 26 August 2020 by Liu, Y., Li, L., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Nat Commun on 26 August 2020 by Lee, T. H., Yeh, C. F., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Elife on 26 August 2020 by Liu, Y., Li, L., et al.
Fig.7.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Elife on 26 August 2020 by Liu, Y., Li, L., et al.
Fig.7.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Elife on 26 August 2020 by Liu, Y., Li, L., et al.
Fig.7.J

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Elife on 26 August 2020 by Liu, Y., Li, L., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In J Cell Mol Med on 1 July 2020 by Feng, S., Zhang, L., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Cell Mol Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In J Cell Mol Med on 1 July 2020 by Feng, S., Zhang, L., et al.
Fig.4.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Cell Mol Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In J Cell Mol Med on 1 July 2020 by Feng, S., Zhang, L., et al.
Fig.5.H

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Cell Mol Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Sci Rep on 19 February 2020 by Hong, E., Park, S., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
In Sci Rep on 19 February 2020 by Hong, E., Park, S., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41
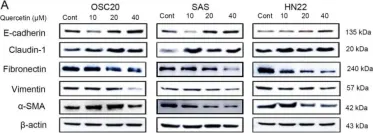
In Molecules on 10 February 2020 by Kim, S. R., Lee, E. Y., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Molecules by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 41