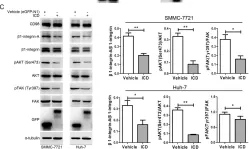
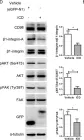
Cellular metabolism is influenced by the stiffness of the extracellular matrix. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and its binding partner, p130Cas, transmit biomechanical signals, such as substrate stiffness, to the cell to regulate a variety of cellular responses, but their roles in early transcriptional and metabolic responses remain largely unexplored. We cultured mouse embryonic fibroblasts with or without siRNA-mediated FAK or p130Cas knockdown and assessed the early transcriptional responses of these cells to placement on soft and stiff substrates by RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analyses. Exposure to the stiff substrate altered the expression of genes important for metabolic and biosynthetic processes, and these responses were influenced by knockdown of FAK and p130Cas. Our findings reveal that FAK-p130Cas signaling mechanotransduces substrate stiffness to early transcriptional changes that alter cellular metabolism and biosynthesis.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Product Citations: 128
FAK and p130Cas Modulate Stiffness-Mediated Early Transcription and Cellular Metabolism.
In Cytoskeleton (Hoboken, N.J.) on 1 March 2025 by Tumenbayar, B. I., Pham, K., et al.
-
WB
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
A fibronectin gradient remodels mixed-phase mesoderm.
In Science Advances on 19 July 2024 by Zhu, M., Gu, B., et al.
Physical processes ultimately shape tissue during development. Two emerging proposals are that cells migrate toward stiffer tissue (durotaxis) and that the extent of cell rearrangements reflects tissue phase, but it is unclear whether and how these concepts are related. Here, we identify fibronectin-dependent tissue stiffness as a control variable that underlies and unifies these phenomena in vivo. In murine limb bud mesoderm, cells are either caged, move directionally, or intercalate as a function of their location along a stiffness gradient. A modified Landau phase equation that incorporates tissue stiffness accurately predicts cell diffusivity upon loss or gain of fibronectin. Fibronectin is regulated by WNT5A-YAP feedback that controls cell movements, tissue shape, and skeletal pattern. The results identify a key determinant of phase transition and show how fibronectin-dependent directional cell movement emerges in a mixed-phase environment in vivo.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Identification of Curcumin Targets in the Brain of Epileptic Mice Using DARTS.
In ACS Omega on 28 May 2024 by Zhang, N., Lin, R., et al.
Curcumin, a compound derived from turmeric, is traditionally utilized in East Asian medicine for treating various health conditions, including epilepsy. Despite its involvement in numerous cellular signaling pathways, the specific mechanisms and targets of curcumin in epilepsy treatment have remained unclear. Our study focused on identifying the primary targets and functional pathways of curcumin in the brains of epileptic mice. Using drug affinity responsive target stabilization (DARTS) and affinity chromatography, we identified key targets in the mouse brain, revealing 232 and 70 potential curcumin targets, respectively. Bioinformatics analysis revealed a strong association of these proteins with focal adhesions and cytoskeletal components. Further experiments using DARTS, along with immunofluorescence staining and cell migration assays, confirmed curcumin's ability to regulate the dynamics of focal adhesions and influence cell migration. This study not only advances our understanding of curcumin's role in epilepsy treatment but also serves as a model for identifying therapeutic targets in neurological disorders.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Bisbiguanide analogs induce mitochondrial stress to inhibit lung cancer cell invasion.
In IScience on 19 April 2024 by Knippler, C. M., Arnst, J. L., et al.
Targeting cancer metabolism to limit cellular energy and metabolite production is an attractive therapeutic approach. Here, we developed analogs of the bisbiguanide, alexidine, to target lung cancer cell metabolism and assess a structure-activity relationship (SAR). The SAR led to the identification of two analogs, AX-4 and AX-7, that limit cell growth via G1/G0 cell-cycle arrest and are tolerated in vivo with favorable pharmacokinetics. Mechanistic evaluation revealed that AX-4 and AX-7 induce potent mitochondrial defects; mitochondrial cristae were deformed and the mitochondrial membrane potential was depolarized. Additionally, cell metabolism was rewired, as indicated by reduced oxygen consumption and mitochondrial ATP production, with an increase in extracellular lactate. Importantly, AX-4 and AX-7 impacted overall cell behavior, as these compounds reduced collective cell invasion. Taken together, our study establishes a class of bisbiguanides as effective mitochondria and cell invasion disrupters, and proposes bisbiguanides as promising approaches to limiting cancer metastasis.
© 2024 The Authors.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
FAK and p130Cas modulate stiffness-mediated early transcription and cellular metabolism
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 16 January 2024 by Tumenbayar, B., Tutino, V. M., et al.
SUMMARY Cellular metabolism is influenced by the stiffness of the extracellular matrix. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and its binding partner, p130Cas, transmit biomechanical signals about substrate stiffness to the cell to regulate a variety of cellular responses, but their roles in early transcriptional and metabolic responses remain largely unexplored. We cultured mouse embryonic fibroblasts with or without siRNA-mediated FAK or p130Cas knockdown and assessed the early transcriptional responses of these cells to placement on soft and stiff substrates by RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analyses. Exposure to the stiff ECM altered the expression of genes important for metabolic and biosynthetic processes, and these responses were influenced by knockdown of FAK and p130Cas. Our findings reveal that FAK-p130Cas signaling mechanotransduces ECM stiffness to early transcriptional changes that alter cellular metabolism and biosynthesis.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
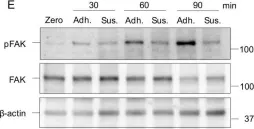
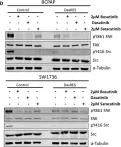
In Cells on 16 April 2022 by Kamranvar, S. A., Gupta, D. K., et al.
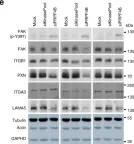
Fig.1.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
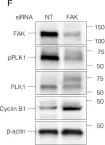
In Cells on 16 April 2022 by Kamranvar, S. A., Gupta, D. K., et al.
Fig.4.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
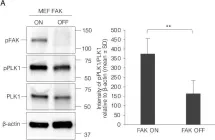
In Cells on 16 April 2022 by Kamranvar, S. A., Gupta, D. K., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
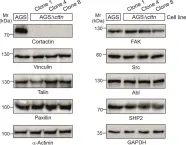
In Int J Mol Sci on 3 June 2021 by Knorr, J., Sharafutdinov, I., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In Nat Commun on 5 July 2019 by Koedoot, E., Fokkelman, M., et al.
Fig.6.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
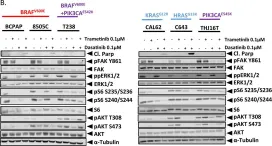
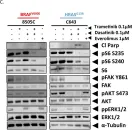
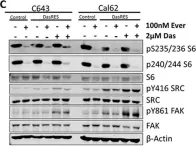
In Oncogenesis on 28 February 2018 by Beadnell, T. C., Nassar, K. W., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In Oncogenesis on 28 February 2018 by Beadnell, T. C., Nassar, K. W., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
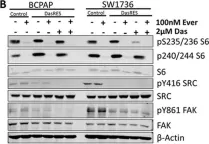
In Oncogenesis on 28 February 2018 by Beadnell, T. C., Nassar, K. W., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In Oncogenesis on 28 February 2018 by Beadnell, T. C., Nassar, K. W., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
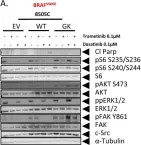
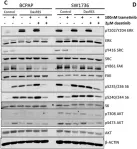
In Oncotarget on 28 November 2017 by Mishall, K. M., Beadnell, T. C., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
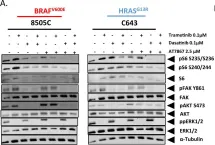
In Oncotarget on 28 November 2017 by Mishall, K. M., Beadnell, T. C., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
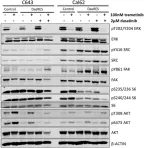
In Oncotarget on 28 November 2017 by Mishall, K. M., Beadnell, T. C., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In Oncotarget on 28 November 2017 by Mishall, K. M., Beadnell, T. C., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In Oncotarget on 28 November 2017 by Mishall, K. M., Beadnell, T. C., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In Int J Mol Sci on 10 November 2016 by Wu, B., Zhou, Y., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In Int J Mol Sci on 10 November 2016 by Wu, B., Zhou, Y., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
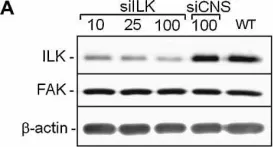
In PLoS One on 5 January 2012 by Prosperi, J. R., Khramtsov, A. I., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
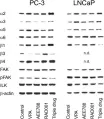
In BMC Cancer on 25 August 2011 by Wedel, S., Hudak, L., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from BMC Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In PLoS One on 10 June 2010 by Minea, R. O., Helchowski, C. M., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20
In J Cell Physiol on 1 February 2010 by Gagné, D., Groulx, J. F., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Physiol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 20