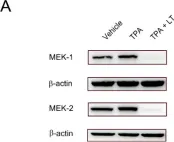
Lethal toxin (LT) is the critical virulence factor of Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax. One common symptom observed in patients with anthrax is thrombocytopenia, which has also been observed in mice injected with LT. Our previous study demonstrated that LT induces thrombocytopenia by suppressing megakaryopoiesis, but the precise molecular mechanisms behind this phenomenon remain unknown. In this study, we utilized 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced megakaryocytic differentiation in human erythroleukemia (HEL) cells to identify genes involved in LT-induced megakaryocytic suppression. Through cDNA microarray analysis, we identified Dachshund homolog 1 (DACH1) as a gene that was upregulated upon TPA treatment but downregulated in the presence of TPA and LT, purified from the culture supernatants of B. anthracis. To investigate the function of DACH1 in megakaryocytic differentiation, we employed short hairpin RNA technology to knock down DACH1 expression in HEL cells and assessed its effect on differentiation. Our data revealed that the knockdown of DACH1 expression suppressed megakaryocytic differentiation, particularly in polyploidization. We demonstrated that one mechanism by which B. anthracis LT induces suppression of polyploidization in HEL cells is through the cleavage of MEK1/2. This cleavage results in the downregulation of the ERK signaling pathway, thereby suppressing DACH1 gene expression and inhibiting polyploidization. Additionally, we found that known megakaryopoiesis-related genes, such as FOSB, ZFP36L1, RUNX1, FLI1, AHR, and GFI1B genes may be positively regulated by DACH1. Furthermore, we observed an upregulation of DACH1 during in vitro differentiation of CD34-megakaryocytes and downregulation of DACH1 in patients with thrombocytopenia. In summary, our findings shed light on one of the molecular mechanisms behind LT-induced thrombocytopenia and unveil a previously unknown role for DACH1 in megakaryopoiesis.
Product Citations: 15
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 7 March 2024 by Lin, G. L., Chang, H. H., et al.
-
WB
In Scientific Reports on 23 September 2023 by Al Shboul, S., El-Sadoni, M., et al.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is a frequently utilized approach to treat locally advanced breast cancer, but, unfortunately, a subset of tumors fails to undergo complete pathological response. Apoptosis and therapy-induced senescence (TIS) are both cell stress mechanisms but their exact role in mediating the pathological response to NAC is not fully elucidated. We investigated the change in expression of PAMIP1, the gene encoding for the pro-apoptotic protein, NOXA, following NAC in two breast cancer gene datasets, and the change in NOXA protein expression in response to NAC in 55 matched patient samples (pre- and post-NAC). PAMIP1 expression significantly declined in post-NAC in the two sets, and in our cohort, 75% of the samples exhibited a downregulation in NOXA post-NAC. Matched samples that showed a decline in NOXA post-NAC were examined for TIS based on a signature of downregulated expression of Lamin-B1 and Ki-67 and increased p16INK4a, and the majority exhibited a decrease in Lamin B1 (66%) and Ki-67 (80%), and increased p16INK4a (49%). Since our cohort consisted of patients that did not develop complete pathological response, such findings have clinical implications on the role of TIS and NOXA downregulation in mediating suboptimal responses to the currently established NAC.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
Cardiomyocyte cohesion is increased after ADAM17 inhibition.
In Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology on 4 February 2023 by Shoykhet, M., Waschke, J., et al.
A Disintegrin And Metalloprotease (ADAM) family proteins are involved in several cardiac diseases, and some ADAMs have been associated with cardiomyopathies. ADAM17 is known to cleave desmoglein 2 (DSG2), one of the proteins involved in the pathogenesis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (AC). Desmosomal stability is impaired in AC, an inheritable genetic disease, the underlying causes of which can be mutations in genes coding for proteins of the desmosome, such as DSG2, desmoplakin (DP), plakoglobin (PG), plakophilin 2 or desmocollin 2. Stabilizing desmosomal contacts can therefore be a treatment option. In the heart of the murine Jup -/- AC model, (Jup being the gene coding for PG) mice, elevated levels of p38MAPK, an activator of ADAM17, were found. However, ADAM17 levels were unaltered in Jup -/- mice hearts. Nonetheless, inhibition of ADAM17 led to enhanced cardiomyocyte cohesion in both Jup +/+ and Jup -/- mice, and in HL-1 cardiomyocytes. Further, enhanced cohesion in HL-1 cardiomyocytes after acute inhibition of ADAM17 was paralleled by enhanced localization of DSG2 and DP at the membrane, whereas no changes in desmosomal assembly or the desmosomal complex were observed. In conclusion, acute inhibition of ADAM17 might lead to reduced cleavage of DSG2, thereby stabilizing the desmosomal adhesion, evidenced by increased DSG2 and DP localization at cell borders and eventually cardiomyocyte cohesion. We believe that similar mechanisms exist in AC.
Copyright © 2023 Shoykhet, Waschke and Yeruva.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Frontiers in Oncology on 7 March 2019 by Moriguchi, M., Watanabe, T., et al.
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is defined as a rare subtype of non-Hodgkin's B-cell lymphoma which is caused by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) in immunosuppressed patients. PEL is an aggressive lymphoma and is frequently resistant to conventional chemotherapies. Therefore, it is critical to investigate novel therapeutic options for PEL. Capsaicin is a pungent component of chili pepper and possesses unique pharmacological effects, such as pain relief, anti-microbial and anti-cancer properties. Here, we demonstrate that capsaicin markedly inhibited the growth of KSHV latently infected PEL cells by inhibiting ERK, p38 MAPK and expression hIL-6, which are known to contribute to PEL growth and survival. The underlying mechanism of action by capsaicin was through the inhibition of ERK and p38 MAPK phosphorylation and signaling that affected hIL-6 expression. As a result, capsaicin induced apoptosis in PEL cells in a caspase-9 dependent manner. In line with these results, ERK (U0126) and p38 MAPK (SB203580) specific signaling inhibitors suppressed hIL-6 expression and attenuated cell growth in PEL cells. Furthermore, the addition of hIL-6 neutralizing antibody to culture medium suppressed the growth of PEL cells. We also demonstrate that capsaicin suppressed PEL cell growth in the absence of nascent viral replication. Finally, we confirmed ex vivo treatment of capsaicin attenuated PEL development in SCID mice. Taken together, capsaicin could represent a lead compound for PEL therapy without the risk of de novo KSHV infection.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
BRAF-inhibitor Associated MEK Mutations Increase RAF-Dependent and -Independent Enzymatic Activity.
In Molecular Cancer Research on 1 October 2017 by Emery, C. M., Monaco, K. A., et al.
Alterations in MEK1/2 occur in cancers, both in the treatment-naïve state and following targeted therapies, most notably BRAF and MEK inhibitors in BRAF-V600E-mutant melanoma and colorectal cancer. Efforts were undertaken to understand the effects of these mutations, based upon protein structural location, and MEK1/2 activity. Two categories of MEK1/2 alterations were evaluated, those associated with either the allosteric pocket or helix-A. Clinically, MEK1/2 alterations of the allosteric pocket are rare and we demonstrate that they confer resistance to MEK inhibitors, while retaining sensitivity to BRAF inhibition. Most mutations described in patients fall within, or are associated with, helix-A. Mutations in this region reduce sensitivity to both BRAF and MEK inhibition and display elevated phospho-ERK1/2 levels, independent from increases in phospho-MEK1/2. Biochemical experiments with a representative helix-A variant, MEK1-Q56P, reveal both increased catalytic efficiency of the activated enzyme, and phosphorylation-independent activity relative to wild-type MEK1. Consistent with these findings, MEK1/2 alterations in helix A retain sensitivity to downstream antagonism via pharmacologic inhibition of ERK1/2. This work highlights the importance of classifying mutations based on structural and phenotypic consequences, both in terms of pathway signaling output and response to pharmacologic inhibition.Implications: This study suggests that alternate modes of target inhibition, such as ERK inhibition, will be required to effectively treat tumors harboring these MEK1/2-resistant alleles. Mol Cancer Res; 15(10); 1431-44. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Int J Mol Sci on 7 March 2024 by Lin, G. L., Chang, H. H., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1