Enteric bacterial pathogens pose significant threats to human health; however, the mechanisms by which they infect the mammalian gut in the face of daunting host defenses remain to be fully defined. For the attaching and effacing (A/E) bacterial family member and murine pathogen Citrobacter rodentium, its virulence strategy appears to involve penetration of the colonic mucus barrier to reach the underlying epithelium. To better define these interactions, we grew colonoids under air-liquid interface (ALI) conditions, producing a thick mucus layer that mimicked in vivo mucus composition and glycosylation. C. rodentium's penetration of ALI-derived mucus was dramatically enhanced upon exposure to sialic acid, in concert with the secretion of two serine protease autotransporter of Enterobacteriaceae (SPATE) proteins, Pic and EspC. Despite Pic being a class II SPATE, and already recognized as a mucinase, it was EspC, a class I SPATE family member, that degraded ALI-derived mucus, despite class I SPATEs not previously shown to possess mucinase activity. Confirming this finding, E. coli DH5α carrying a plasmid that expresses C. rodentium-derived EspC was able to degrade the mucus. Moreover, recombinant EspC alone also displayed mucinolytic activity in a dose-dependent manner. Collectively, our results reveal the utility of ALI-derived mucus in modeling microbe-host interactions at the intestinal mucosal surface, as well as identify EspC as an atypical class I SPATE that shows significant mucinolytic activity toward ALI-derived mucus.
Product Citations: 1,030
In Gut Microbes on 1 December 2025 by Chen, Y., Gilliland, A., et al.
In Cancer Biology & Therapy on 1 December 2025 by Chang, T. M., Fang, W. Y., et al.
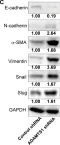
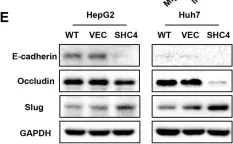
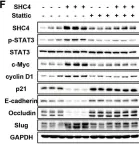
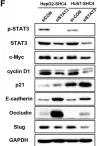
PCK2, which encodes mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK-M), is upregulated in various cancers. We demonstrated high expression of PEPCK-M in approximately half of triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) previously. TNBC is associated with an aggressive phenotype and a high metastasis rate. In this study, we investigated the role of PCK2 in TNBC. PCK2 knockdown suppressed proliferation and mTOR signaling in TNBC cells. In addition, cell invasion/migration ability and the expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers were positively correlated with PCK2 expression in TNBC cells via regulation of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)/SMAD3 signaling. SMAD3 was positively regulated by PCK2 in TNBC cells. Knockdown of SMAD3 in PCK2-overexpressing TNBC cells reduced the expression levels of EMT markers, Snail and Slug, and suppressed cell invasion/migration. In addition, PCK2 knockdown attenuated the stimulatory effect of TGF-β on SMAD3 phosphorylation in TNBC cells. PEPCK-M promotes the protein and mRNA expression of SMAD3 via competitive binding to tripartite motif-containing 67 (TRIM67), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, to reduce SMAD3 ubiquitination, which leads to promoting nuclear translocation of SMAD3 and autoregulation of SMAD3 transcription. Moreover, high PCK2 mRNA expression was significantly associated with poor survival in TNBC patients. In conclusion, our study revealed for the first time that PCK2 activates TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling by regulating the expression and phosphorylation of SMAD3 by inhibiting TRIM67-mediated SMAD3 ubiquitination and promoting the stimulatory effect of TGF-β to promote TNBC invasion. The regulatory effect of PCK2 on mTOR and TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling suggests that PCK2 is a potential therapeutic target for suppressing TNBC progression.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
A multi-tiered mechanical mechanism shapes the early neural plate.
In Nature Communications on 4 July 2025 by Inman, A., Spiritosanto, E., et al.
The formation of complex tissues during embryonic development requires an intricate spatiotemporal coordination of local mechanical processes regulating global tissue morphogenesis. Here, we uncover a novel mechanism that mechanically regulates the shape of the anterior neural plate (ANP), a vital forebrain precursor, during zebrafish gastrulation. Combining in vivo and in silico approaches we reveal that the ANP is shaped by global tissue flows regulated by distinct force-generating processes. We show that mesendoderm migration and E-cadherin-dependent differential tissue interactions control distinct flow regimes in the neuroectoderm. Initial opposing flows lead to neuroectoderm cell internalisation and progressive multilayer tissue folding which in turn provide forces driving ANP tissue reshaping. We find that convergent extension is dispensable for internalisation but required for ANP tissue extension. Our results highlight how spatiotemporal regulation and coupling of different mechanical processes between tissues in the embryo control the first internalisation and folding events of the developing brain.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Windows of susceptibility to neonatal acute kidney injury and nephron loss in a rabbit model.
In Scientific Reports on 1 July 2025 by Indugula, S., Yarlagadda, S., et al.
Nephrogenesis is completed before term birth, but preterm infants continue this process postnatally. It is unknown if preterm neonates are more susceptible to acute kidney injury (AKI) immediately after birth (during nephrogenesis) or later in postnatal development, and if this AKI timing impacts nephron number. Rabbits were exposed to gentamicin (100 mg/kg intraperitoneal) and indomethacin (5 mg/kg orally) on postnatal day (P) 0-3 (early-exposed) or P6-9 (late-exposed). Animals were euthanized three hours after last nephrotoxin dose or at 6 weeks of life. Histologic injury was assessed, and Kidney injury marker 1 (Kim1) expression was quantified. At 6 weeks, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (SCr) levels were measured. Ex vivo MRI imaging was performed with automated quantitation of nephron numbers. AKI was induced in early and late-exposed rabbits. At 6 weeks, we identified a mean of 170,972 glomeruli in the controls (n = 5), 159,655 in the early-exposed (n = 4), and 145,748 glomeruli in the late-exposed group (n = 3, a 14.8% reduction compared to control, p = 0.01). Late-exposed rabbits had elevated BUN and SCr relative to early-exposed. This study suggests that exposure to nephrotoxins during early postnatal nephrogenesis causes AKI but may have less impact on long-term nephron number than exposure during nephron maturation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Activation of Human FPR2 with AT-RvD1 Resolves Acute Sialadenitis in Vivo.
In Inflammation on 4 June 2025 by Nam, K., Dos Santos, H. T., et al.
Previous studies demonstrated that activation of the mouse G protein-coupled formyl peptide receptor 2 (mFpr2) with aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 (AT-RvD1) blocks pro-inflammatory cytokine signaling while promoting salivary gland (SG) epithelial integrity both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, mice lacking Fpr2 display alterations of SG innate and adaptive immunity. Taken together, these results indicate that Fpr2 activation with AT-RvD1 restores saliva secretion and regulates SG immunity in mice. To demonstrate the value of AT-RvD1 for use in human SG, however, we need to extend the findings above in the direction of clinical use. To this end, the current study investigated whether treatment with AT-RvD1 reduces SG inflammation and restores saliva secretion in an acute sialadenitis mouse model expressing the human formyl peptide receptor 2 (hFPR2) protein. Results indicate that mice carrying the hFPR2 and treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) display acute sialadenitis-like features as shown by increased levels of proliferating inflammatory cells, loss of epithelial integrity and reduced saliva secretion. In contrast, when these mice are treated with AT-RvD1, the sialadenitis-like features are drastically reduced as evidenced by a significant decrease in proliferating inflammatory cells as well as restoration of saliva secretion to levels comparable to phosphate buffered saline (PBS)-treated healthy controls. Finally, changes observed in mice carrying the hFPR2 and treated with LPS and AT-RvD1 were comparable to those observed in wild-type mice carrying the mFpr2. Together, these results demonstrate that activation of hFPR2 with AT-RvD1 resolves acute sialadenitis in vivo.
© 2025. The Author(s).
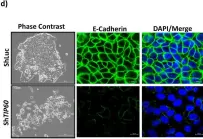
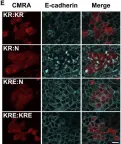
In Cells on 9 May 2025 by Mohammad, A. & Jha, S.
Fig.1.O

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
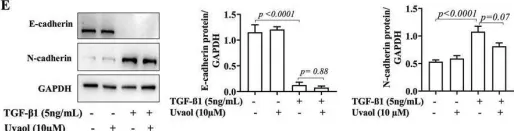
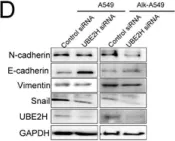
In Front Pharmacol on 22 January 2025 by Patrícia Gonçalves Tenório, L., Xavier, F. H. D. C., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Pharmacol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
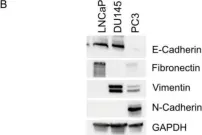
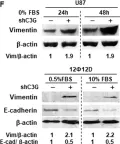
In Cancers (Basel) on 6 August 2024 by Bouchareb, E., Dallel, S., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
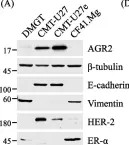
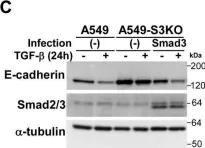
In Cancers (Basel) on 6 August 2024 by Bouchareb, E., Dallel, S., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Cell Mol Biol Lett on 31 May 2024 by Yuan, S. H., Wu, C. C., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Mol Biol Lett by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Int J Mol Sci on 10 April 2024 by Breitenecker, K., Heiden, D., et al.
Fig.2.G

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Int J Mol Sci on 25 March 2023 by De Gregorio, A., Serafino, A., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 3 March 2023 by Lucaciu, S. A., Figliuzzi, R., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Front Cell Dev Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Int J Mol Sci on 27 December 2022 by Chang, C. Y., Huang, Y. C., et al.
Fig.7.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In iScience on 22 December 2022 by Satow, R., Suzuki, Y., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from iScience by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In JCI Insight on 10 October 2022 by Yu, T. X., Kalakonda, S., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Int J Mol Sci on 29 September 2022 by Aboouf, M. A., Armbruster, J., et al.
Fig.2.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2022 by Rinaldi, A., Lazareth, H., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Biology (Basel) on 16 May 2022 by Lee, H. C., Chang, C. Y., et al.
Fig.7.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Biology (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Cancer Cell Int on 15 January 2022 by Zhang, X., Zhang, H., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancer Cell Int by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Cancer Cell Int on 15 January 2022 by Zhang, X., Zhang, H., et al.
Fig.6.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancer Cell Int by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Cancer Cell Int on 15 January 2022 by Zhang, X., Zhang, H., et al.
Fig.5.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancer Cell Int by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Cancer Cell Int on 15 January 2022 by Zhang, X., Zhang, H., et al.
Fig.5.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancer Cell Int by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Cancer Cell Int on 15 January 2022 by Zhang, X., Zhang, H., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancer Cell Int by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Int J Mol Sci on 14 January 2022 by Riccioni, V., Trionfetti, F., et al.
Fig.1.G

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Sci Rep on 23 June 2021 by Lian, P., Braber, S., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Curr Biol on 21 June 2021 by Hill, W., Zaragkoulias, A., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Curr Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Biology (Basel) on 28 April 2021 by Yen, M. C., Wu, K. L., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Biology (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In Cell Death Dis on 6 April 2021 by Manzano, S., Gutiérrez-Uzquiza, A., et al.
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 147