This work identifies CD8-NOS2+COX2+ and CD8-NOS2-COX2+ unique cellular neighborhoods that drive the tumor immune spatial architecture of CD8+ T cells predictive of clinical outcome and can be targeted with clinically available NOS inhibitors and NSAIDs.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Product Citations: 45
In Cancer Res Commun on 1 October 2024 by Ridnour, L. A., Heinz, W. F., et al.
-
IHC
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In JCI Insight on 21 May 2024 by Ridnour, L. A., Cheng, R. Y., et al.
Immune therapy is the new frontier of cancer treatment. Therapeutic radiation is a known inducer of immune response and can be limited by immunosuppressive mediators including cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) that is highly expressed in aggressive triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). A clinical cohort of TNBC tumors revealed poor radiation therapeutic efficacy in tumors expressing high COX2. Herein, we show that radiation combined with adjuvant NSAID (indomethacin) treatment provides a powerful combination to reduce both primary tumor growth and lung metastasis in aggressive 4T1 TNBC tumors, which occurs in part through increased antitumor immune response. Spatial immunological changes including augmented lymphoid infiltration into the tumor epithelium and locally increased cGAS/STING1 and type I IFN gene expression were observed in radiation-indomethacin-treated 4T1 tumors. Thus, radiation and adjuvant NSAID treatment shifts "immune desert phenotypes" toward antitumor M1/TH1 immune mediators in these immunologically challenging tumors. Importantly, radiation-indomethacin combination treatment improved local control of the primary lesion, reduced metastatic burden, and increased median survival when compared with radiation treatment alone. These results show that clinically available NSAIDs can improve radiation therapeutic efficacy through increased antitumor immune response and augmented local generation of cGAS/STING1 and type I IFNs.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 23 December 2023 by Ridnour, L. A., Cheng, R. Y., et al.
Multiple immunosuppressive mechanisms exist in the tumor microenvironment that drive poor outcomes and decrease treatment efficacy. The co-expression of NOS2 and COX2 is a strong predictor of poor prognosis in ER- breast cancer and other malignancies. Together, they generate pro-oncogenic signals that drive metastasis, drug resistance, cancer stemness, and immune suppression. Using an ER- breast cancer patient cohort, we found that the spatial expression patterns of NOS2 and COX2 with CD3+CD8+PD1- T effector (Teff) cells formed a tumor immune landscape that correlated with poor outcome. NOS2 was primarily associated with the tumor-immune interface, whereas COX2 was associated with immune desert regions of the tumor lacking Teff cells. A higher ratio of NOS2 or COX2 to Teff was highly correlated with poor outcomes. Spatial analysis revealed that regional clustering of NOS2 and COX2 was associated with stromal-restricted Teff, while only COX2 was predominant in immune deserts. Examination of other immunosuppressive elements, such as PDL1/PD1, Treg, B7H4, and IDO1, revealed that PDL1/PD1, Treg, and IDO1 were primarily associated with restricted Teff, whereas B7H4 and COX2 were found in tumor immune deserts. Regardless of the survival outcome, other leukocytes, such as CD4 T cells and macrophages, were primarily in stromal lymphoid aggregates. Finally, in a 4T1 model, COX2 inhibition led to a massive cell infiltration, thus validating the hypothesis that COX2 is an essential component of the Teff exclusion process and, thus, tumor evasion. Our study indicates that NOS2/COX2 expression plays a central role in tumor immunosuppression. Our findings indicate that new strategies combining clinically available NOS2/COX2 inhibitors with various forms of immune therapy may open a new avenue for the treatment of aggressive ER- breast cancers.
-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
NOS2 and COX2 Provide Key Spatial Targets that Determine Outcome in ER-Breast Cancer
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 23 December 2023 by Ridnour, L. A., Heinz, W. F., et al.
Estrogen receptor-negative (ER-) breast cancer is an aggressive breast cancer subtype with limited therapeutic options. Upregulated expression of both inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2) and cyclo-oxygenase (COX2) in breast tumors predicts poor clinical outcomes. Signaling molecules released by these enzymes activate oncogenic pathways, driving cancer stemness, metastasis, and immune suppression. The influence of tumor NOS2/COX2 expression on the landscape of immune markers using multiplex fluorescence imaging of 21 ER-breast tumors were stratified for survival. A powerful relationship between tumor NOS2/COX2 expression and distinct CD8+ T cell phenotypes was observed at 5 years post-diagnosis. These results were confirmed in a validation cohort using gene expression data showing that ratios of NOS2 to CD8 and COX2 to CD8 are strongly associated with poor outcomes in high NOS2/COX2-expressing tumors. Importantly, multiplex imaging identified distinct CD8+ T cell phenotypes relative to tumor NOS2/COX2 expression in Deceased vs Alive patient tumors at 5-year survival. CD8+NOS2-COX2-phenotypes defined fully inflamed tumors with significantly elevated CD8+ T cell infiltration in Alive tumors expressing low NOS2/COX2. In contrast, two distinct phenotypes including inflamed CD8+NOS2+COX2+ regions with stroma-restricted CD8+ T cells and CD8-NOS2-COX2+ immune desert regions with abated CD8+ T cell penetration, were significantly elevated in Deceased tumors with high NOS2/COX2 expression. These results were supported by applying an unsupervised nonlinear dimensionality-reduction technique, UMAP, correlating specific spatial CD8/NOS2/COX2 expression patterns with patient survival. Moreover, spatial analysis of the CD44v6 and EpCAM cancer stem cell (CSC) markers within the CD8/NOS2/COX2 expression landscape revealed positive correlations between EpCAM and inflamed stroma-restricted CD8+NOS2+COX2+ phenotypes at the tumor/stroma interface in deceased patients. Also, positive correlations between CD44v6 and COX2 were identified in immune desert regions in deceased patients. Furthermore, migrating tumor cells were shown to occur only in the CD8-NOS2+COX2+ regions, identifying a metastatic hot spot. Taken together, this study shows the strength of spatial localization analyses of the CD8/NOS2/COX2 landscape, how it shapes the tumor immune microenvironment and the selection of aggressive tumor phenotypes in distinct regions that lead to poor clinical outcomes. This technique could be beneficial for describing tumor niches with increased aggressiveness that may respond to clinically available NOS2/COX2 inhibitors or immune-modulatory agents.
-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) on 18 August 2023 by Francolino, R., Martino, M., et al.
Rosmarinus officinalis L. is an aromatic evergreen plant from the Lamiaceae family. The purpose of this study was to compare the chemical profile and bioactivities of hydroalcoholic extracts derived from wild and cultivated R. officinalis. The chemical composition of the extracts was evaluated via LC-MS analysis, which revealed the presence of a wide range of phenolic compounds, including flavonoids, phenolic and terpenes. Both extracts showed a similar interesting antioxidant activity, probably related to their content of phenol and flavonoids. The analysis of anti-acetylcholinesterase (AChE), anti-butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), and anti-α-amylase activities showed analogous inhibition, except for AChE, in which the wild type was more active than the cultivated one. Finally, in vitro studies were performed using the J774A.1 murine macrophage cell line, to characterize the anti-inflammatory and the antioxidant effects of the extracts. As expected, pretreatment with the extracts significantly reduced the production proinflammatory cytokines and ROS through modulation of the nitric oxide pathway and the mitochondrial activity. Importantly, it is observed that the anti-inflammatory effect of the extracts was explicated through the inhibition of NF-kB and its downstream mediator COX-2. Collectively, these results demonstrated that these extracts could represent a starting point for developing novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of inflammation-based diseases. Moreover, since no significant changes were observed in terms of composition and activity, both wild and cultivated R. officinalis extracts can be recommended for food and pharmaceutical purposes.
-
WB
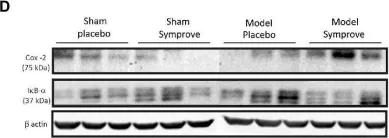
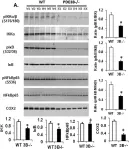
In Front Aging Neurosci on 7 February 2023 by Sancandi, M., De Caro, C., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Aging Neurosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
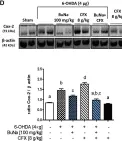
In Int J Mol Sci on 7 June 2022 by Avagliano, C., Coretti, L., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
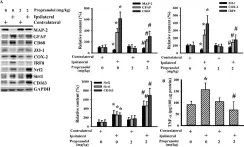
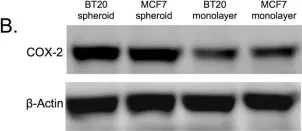
In Cells on 1 June 2020 by Lin, S. Y., Wang, Y. Y., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
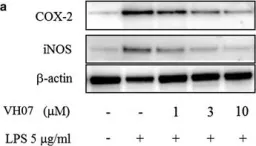
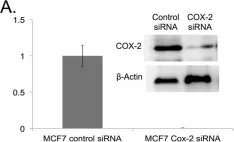
In Chem Cent J on 13 February 2018 by Ha, D. T., Long, P. T., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Chem Cent J by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
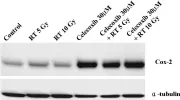
In Sci Rep on 20 June 2016 by Ahmad, F., Chung, Y. W., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In PLoS One on 25 October 2014 by Chandrasekaran, S., Marshall, J. R., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In PLoS One on 25 October 2014 by Chandrasekaran, S., Marshall, J. R., et al.
Fig.8.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 11 November 2008 by Park, W., Oh, Y. T., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Exp Clin Cancer Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8