The small GTPase Ras is an intracellular signaling hub required for long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus and for memory formation. Genetic alterations in Ras signaling (i.e., RASopathies) are linked to cognitive disorders in humans. However, it remains unclear how Ras controls synaptic plasticity, and whether different Ras isoforms play overlapping or distinct roles in neurons. Using genetically modified mice, we show here that H-Ras (the most abundant isoform in the brain) does not promote LTP, but instead long-term depression mediated by metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR-LTD). Mechanistically, H-Ras is activated locally in spines during mGluR-LTD via c-Src, and is required to trigger Erk activation and de novo protein synthesis. Furthermore, H-Ras deletion impairs object recognition as well as social and spatial memory. Conversely, K-Ras is the isoform specifically required for LTP. This functional specialization correlates with a differential synaptic distribution of the two isoforms H-Ras and K-Ras, which may have important implications for RASopathies and cognitive function.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 37
Different Ras isoforms regulate synaptic plasticity in opposite directions.
In The EMBO Journal on 1 April 2025 by López-Merino, E., Fernández-Rodrigo, A., et al.
Droj2 Facilitates Somatosensory Neurite Sculpting via GTP-Binding Protein Arf102F in Drosophila.
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 25 August 2023 by Rui, M., Kong, W., et al.
Developmental remodeling of neurite is crucial for the accurate wiring of neural circuits in the developing nervous system in both vertebrates and invertebrates, and may also contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric disorders, for instance, autism, Alzheimer's disease (AD), and schizophrenia. However, the molecular underpinnings underlying developmental remodeling are still not fully understood. Here, we have identified DnaJ-like-2 (Droj2), orthologous to human DNAJA1 and DNAJA4 that is predicted to be involved in protein refolding, as a developmental signal promoting dendrite sculpting of the class IV dendritic arborization (C4da) sensory neuron in Drosophila. We further show that Arf102F, a GTP-binding protein previously implicated in protein trafficking, serves downstream of Droj2 to govern neurite pruning of C4da sensory neurons. Intriguingly, our data consistently demonstrate that both Droj2 and Arf102F promote the downregulation of the conserved L1-type cell-adhesion molecule Neuroglian anterior to dendrite pruning. Mechanistically, Droj2 genetically interacts with Arf102F and promotes Neuroglian downregulation to initiate dendrite severing. Taken together, this systematic study sheds light on an unprecedented function of Droj2 and Arf102F in neuronal development.
-
IHC
In Neuron on 16 March 2022 by Goldsmith, J., Ordureau, A., et al.
Neurons depend on autophagy to maintain cellular homeostasis, and defects in autophagy are pathological hallmarks of neurodegenerative disease. To probe the role of basal autophagy in the maintenance of neuronal health, we isolated autophagic vesicles from mouse brain tissue and used proteomics to identify the major cargos engulfed within autophagosomes, validating our findings in rodent primary and human iPSC-derived neurons. Mitochondrial proteins were identified as a major cargo in the absence of mitophagy adaptors such as OPTN. We found that nucleoid-associated proteins are enriched compared with other mitochondrial components. In the axon, autophagic engulfment of nucleoid-enriched mitochondrial fragments requires the mitochondrial fission machinery Drp1. We proposed that localized Drp1-dependent fission of nucleoid-enriched fragments in proximity to the sites of autophagosome biogenesis enhances their capture. The resulting efficient autophagic turnover of nucleoids may prevent accumulation of mitochondrial DNA in the neuron, thus mitigating activation of proinflammatory pathways that contribute to neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cell Biology
-
Neuroscience
Assessing Rab5 Activation in Health and Disease.
In Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.) on 29 August 2021 by Pensalfini, A., Jiang, Y., et al.
The endocytic pathway is a system of dynamically communicating vesicles, known as early endosomes, that internalize, sort, and traffic nutrients, trophic factors, and signaling molecules to sites throughout the cell. In all eukaryotic cells, early endosome functions are regulated by Rab5 activity, dependent upon its binding to GTP, whereas Rab5 bound to GDP represents the biologically inactive form. An increasing number of neurodegenerative diseases are associated with endocytic dysfunction and, in the case of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Down syndrome (DS), an early appearing highly characteristic reflection of endocytic pathway dysfunction is an abnormal enlargement of Rab5 positive endosomes. In AD and DS, endosome enlargement accompanying accelerated endocytosis and fusion, upregulated transcription of endocytosis-related genes, and aberrant signaling by endosomes are caused by pathological Rab5 overactivation. In this chapter, we describe a battery of methods that have been used to assess Rab5 activation in models of AD/DS and are applicable to other cell and animal disease models. These methods include (1) fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) assay; (2) quantitative measurement of endosome size by light, fluorescence and electron microscopy; (3) detection of GTP-Rab5 by in situ immunocytochemistry in vitro and ex vivo; (4) immunoprecipitation and GTP-agarose pull-down assay; (5) biochemical detection of Rab5 in endosome-enriched subcellular fractions obtained by OptiPrep™ density gradient centrifugation of mouse brain.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
Live visualization of a functional RET-EGFP chimeric receptor in homozygous knock-in mice.
In Development, Growth Differentiation on 1 August 2021 by Sunardi, M., Ito, K., et al.
The GDNF Family Ligands (GFLs) regulate neural development and kidney organogenesis by activating the RET receptor tyrosine kinase. Many RET-dependent developmental processes involve long-distance cell-cell communications or cell polarity, which includes cell migration and axon guidance. This suggests that spatiotemporally regulated subcellular localization of RET protein and appropriate propagation of RET signaling in cells are essential for the physiological function of the GFLs. Little is known, however, about the dynamics of RET protein in cells. Addressing this issue requires development of a system that allows visualization of RET in living cells. In this study, we report generation of a novel knock-in mouse line in which the RET-EGFP chimeric receptor is expressed under the Ret promoter. Unlike Ret-deficient mice that die after birth due to the absence of the enteric nervous system (ENS) and kidneys, RetRET-EGFP/RET-EGFP mice were viable and grew to adulthood with no overt abnormality, which indicated that RET-EGFP exerts function comparable to RET. In neurons and ENS progenitors, RET-EGFP signals were detected both on the cell membrane and in the cytoplasm, the latter of which appeared as a punctate pattern. Time-lapse imaging of cultured neural cells and embryos revealed active transport of RET-EGFP puncta in neuronal axons and cell bodies. Immunohistochemical analyses detected RET-EGFP signals in early and recycling endosomes, indicating that RET-EGFP is trafficked via the endocytic pathway. RetRET-EGFP/RET-EGFP mice enable visualization of functional RET protein in vivo for the first time and provide a unique platform to examine the dynamics and physiology of RET trafficking.© 2021 Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
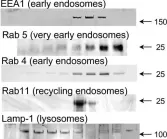
In Mol Pain on 17 July 2007 by Rodríguez-Muñoz, M., de la Torre-Madrid, E., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Molecular Pain by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1