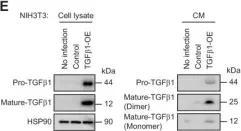
Age is a critical determinant of arterial disease, including aneurysm formation. Here, to understand the impact of aging on the arterial transcriptome, we leveraged RNA-sequencing data to define transcripts that change with advancing age in human arteries. Among the most repressed transcripts in aged individuals were those that are relevant for actomyosin structure and organization, including both myosin light chain kinase (MYLK) and smooth muscle γ-actin (ACTG2). This was associated with a reduction of serum response factor (SRF), which controls these transcripts via defined promoter elements. To determine the consequences of isolated Srf depletion, we conditionally deleted Srf in vascular smooth muscle of young mice (i8-SRF-KO mice). This led to a reduction of the SRF regulon, including Mylk and Actg2, and impaired arterial contractility, but left endothelial-dependent dilatation unaffected. Srf-depletion also increased aortic diameter and Alcian blue staining of the aortic media, which are cardinal features of aortopathy, such as aortic aneurysmal disease. Despite this, i8-SRF-KO mice were protected from aortic lesions elicited by angiotensin II (AngII). Proteomics demonstrated that Srf-depletion mimicked a protein signature of AngII treatment involving increases of the mechanoresponsive transcriptional coactivators YAP and TAZ and reduction of the Hippo kinase Lats2. Protection from aortopathy could be overcome by changing the order of KO induction and AngII administration resulting in advanced aneurysms in both i8-SRF-KO and control mice. Our work provides important insights into the molecular underpinnings of age-dependent changes in aortic function and mechanisms of adaptation in hypertension.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 278
Declining activity of serum response factor in aging aorta in relation to aneurysm progression.
In The Journal of Biological Chemistry on 1 April 2025 by Rippe, C., Bastrup, J. A., et al.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
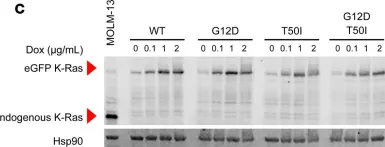
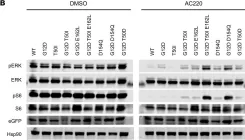
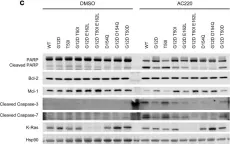
U2AF1 mutations rescue deleterious exon skipping induced by KRAS mutations
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 25 March 2025 by Walter, D. M., Cho, K., et al.
The mechanisms by which somatic mutations of splicing factors, such as U2AF1 S34F in lung adenocarcinoma, contribute to cancer pathogenesis are not well understood. Here, we used prime editing to modify the endogenous U2AF1 gene in lung adenocarcinoma cells and assessed the resulting impact on alternative splicing. These analyses identified KRAS as a key target modulated by U2AF1 S34F . One specific KRAS mutation, G12S, generates a cryptic U2AF1 binding site that leads to skipping of KRAS exon 2 and generation of a non-functional KRAS transcript. Expression of the U2AF1 S34F mutant reverts this exon skipping and restores KRAS function. Analysis of cancer genomes reveals that U2AF1 S34F mutations are enriched in KRAS G12S -mutant lung adenocarcinomas. A comprehensive analysis of splicing factor/oncogene mutation co-occurrence in cancer genomes also revealed significant co-enrichment of KRAS Q61R and U2AF1 I24T mutations. Experimentally, KRAS Q61R mutation leads to KRAS exon 3 skipping, which in turn can be rescued by the expression of U2AF1 I24T . Analysis of genomic and clinical patient data suggests that both U2AF1 mutations occur secondary to KRAS mutation and are associated with decreased overall patient survival. Our findings provide evidence that splicing factor mutations can rescue splicing defects caused by oncogenic mutations. More broadly, they demonstrate a dynamic process of cascading selection where mutational events are positively selected in cancer genomes as a consequence of earlier mutations.
Intrinsic electrical activity drives small-cell lung cancer progression.
In Nature on 1 March 2025 by Peinado, P., Stazi, M., et al.
Elevated or ectopic expression of neuronal receptors promotes tumour progression in many cancer types1,2; neuroendocrine (NE) transformation of adenocarcinomas has also been associated with increased aggressiveness3. Whether the defining neuronal feature, namely electrical excitability, exists in cancer cells and impacts cancer progression remains mostly unexplored. Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an archetypal example of a highly aggressive NE cancer and comprises two major distinct subpopulations: NE cells and non-NE cells4,5. Here we show that NE cells, but not non-NE cells, are excitable, and their action potential firing directly promotes SCLC malignancy. However, the resultant high ATP demand leads to an unusual dependency on oxidative phosphorylation in NE cells. This finding contrasts with the properties of most cancer cells reported in the literature, which are non-excitable and rely heavily on aerobic glycolysis. Additionally, we found that non-NE cells metabolically support NE cells, a process akin to the astrocyte-neuron metabolite shuttle6. Finally, we observed drastic changes in the innervation landscape during SCLC progression, which coincided with increased intratumoural heterogeneity and elevated neuronal features in SCLC cells, suggesting an induction of a tumour-autonomous vicious cycle, driven by cancer cell-intrinsic electrical activity, which confers long-term tumorigenic capability and metastatic potential.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 25 February 2025 by Lasota, M., Jankowski, D., et al.
Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor with one of the worst prognoses among solid tumors, characterized by resistance to treatment. Therefore, there is an urgent need for new methods of targeted therapy. Previous studies have shown that the overexpression of receptor tyrosine kinases such as c-KIT or PDGFR can increase proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer cells. The aim of our study was to analyze aggregates between a supramolecular carrier (Congo red, CR) and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BLU-258) as well as to investigate the effect of the free inhibitor and its aggregate with Congo red (CR-BLU-258) on selected properties of pancreatic cells, including these cells' viability and three-dimensional cell spheroid cultures. To better understand the interactions between Congo red and BLU-258, we used molecular modeling in addition to biophysical methods. These attempts allowed us to determine the optimal molar ratio, which we used for in vitro studies on pancreatic cancer cell lines. A significantly greater decrease in the viability of the tested 3D cultures was observed after 48 h of incubation with CR-BLU-258, which resulted in a lower IC50 value for the tested co-aggregate compared with BLU-258 alone. Moreover, a higher resistance of PANC-1 and BxPC3 spheroid cells to the tested compounds was noted compared with the 2D culture model. A significantly lower response was observed in 3D cell cultures (BxPC3 and PANC-1) treated with BLU-258 alone compared with the 2D culture. Thus, our results showed that both BLU-258 (alone) and in its co-aggregate with Congo red exhibit anticancer activity, inhibiting the growth of pancreatic cancer cells and reducing their viability, survival, and migration. Both tested compounds also affected the phosphorylation of the selected signaling proteins. We conclude that the selected tyrosine kinase inhibitor (alone) and in its co-aggregate with Congo red exhibit anticancer activity and should be considered as a novel effective therapy against pancreatic cancer.
-
Cancer Research
In Science Advances on 24 January 2025 by Wang, X., Zhu, R., et al.
NF2-related schwannomatosis, previously known as neurofibromatosis type 2, is a genetic disorder characterized by nerve tumors due to NF2 gene mutations. Mice with Nf2 deletion develop schwannomas slowly with low penetrance, hence inconvenient for preclinical studies. Here, we show that NF2, by recruiting E3 ubiquitin ligases β-TrCP1/2, promotes WWC1-3 ubiquitination and degradation. In NF2 mutated cells, WWC1-3 accumulation is a compensatory mechanism to prevent YAP/TAZ hyperactivation and rapid tumorigenesis. Accordingly, we generate a synthetic mouse model with complete penetrance and short latency by concurrently deleting Nf2 and Wwc1/2 in Schwann cells. This model closely resembles NF2-related schwannomatosis in patients, as confirmed by histological and single-cell transcriptome analysis. Moreover, a cell line from mouse schwannomas and a syngeneic tumor model in immune-competent mice are established. Furthermore, a screen using established models has identified candidate drugs that effectively suppress schwannoma progression. Hence, this work has developed rapid and transplantable models that will facilitate both basic and translational research on NF2-related schwannomatosis.
In Commun Biol on 17 October 2024 by Thinyakul, C., Sakamoto, Y., et al.
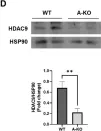
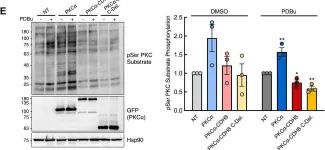
Fig.4.E

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Commun Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
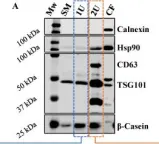
In JCI Insight on 8 September 2023 by Chen, P. Y., Huang, B. J., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
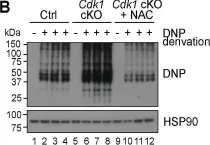
In JCI Insight on 8 September 2023 by Chen, P. Y., Huang, B. J., et al.
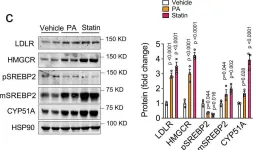
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
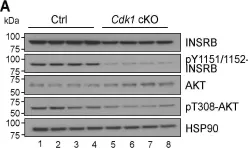
In JCI Insight on 8 September 2023 by Chen, P. Y., Huang, B. J., et al.
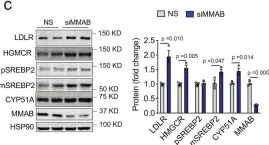
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In MBio on 31 August 2023 by Ikeda, T., Shimizu, R., et al.
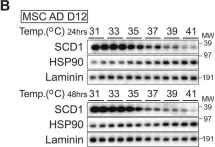
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from MBio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In MBio on 31 August 2023 by Ikeda, T., Shimizu, R., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from MBio by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In JCI Insight on 8 November 2022 by Yamane, T., Kanamori, Y., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Cells on 16 September 2022 by Abdelrahman, A. A., Bunch, K. L., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Cells on 30 August 2022 by Goo, B. M. S. S., Ahmadieh, S., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Nat Commun on 8 November 2021 by Goedeke, L., Canfrán-Duque, A., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Nat Commun on 8 November 2021 by Goedeke, L., Canfrán-Duque, A., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In PLoS Biol on 1 May 2021 by Mori, H., Dugan, C. E., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In J Biol Chem on 23 February 2021 by Van, A. N., Kunkel, M. T., et al.
Fig.6.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Int J Mol Sci on 22 January 2021 by Del Pozo-Acebo, L., López de Las Hazas, M. C., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Bos taurus (Bovine)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Elife on 21 December 2020 by Ow, J. R., Caldez, M. J., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Elife on 21 December 2020 by Ow, J. R., Caldez, M. J., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In JCI Insight on 5 November 2020 by Wong, J. C., Perez-Mancera, P. A., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In PLoS Genet on 1 November 2020 by Dewhurst, M. R., Ow, J. R., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Genet by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In PLoS Genet on 1 November 2020 by Dewhurst, M. R., Ow, J. R., et al.
Fig.2.H

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Genet by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In PLoS Genet on 1 November 2020 by Dewhurst, M. R., Ow, J. R., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Genet by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In PLoS Genet on 1 November 2020 by Dewhurst, M. R., Ow, J. R., et al.
Fig.7.T

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Genet by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In Cell Death Dis on 13 August 2020 by Gidlöf, O., Bader, K., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
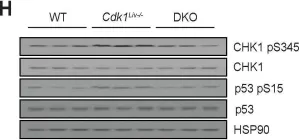
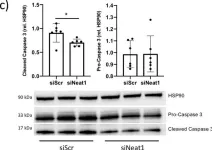
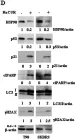
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 30 June 2020 by Garufi, A., Baldari, S., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Exp Clin Cancer Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
In J Exp Clin Cancer Res on 30 June 2020 by Garufi, A., Baldari, S., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Exp Clin Cancer Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77
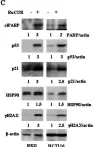
In Cancers (Basel) on 18 March 2020 by Castellví, M., Felip, E., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 77