Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) have attracted significant attention, yet the molecular mechanisms that govern their specific binding to recipient cells remain elusive. Our in vitro study utilizing single-particle tracking demonstrated that integrin heterodimers comprising α6β4 and α6β1 and ganglioside, GM1, are responsible for the binding of small EV (sEV) subtypes to laminin. EVs derived from four distinct tumor cell lines, regardless of size, exhibited high binding affinities for laminin but not for fibronectin, although fibronectin receptors are abundant in EVs and have functional roles in EV-secreting cells. Our findings revealed that integrins in EVs bind to laminin via the conventional molecular interface, facilitated by CD151 rather than by inside-out signaling of talin-1 and kindlin-2. Super-resolution movie observation revealed that sEV integrins bind only to laminin on living recipient cells. Furthermore, sEVs bound to HUVEC and induced cell branching morphogenesis in a laminin-dependent manner. Thus, we demonstrated that EVs predominantly bind to laminin on recipient cells, which is indispensable for cell responses.
© 2025 Isogai et al.
Product Citations: 119
Extracellular vesicles adhere to cells primarily by interactions of integrins and GM1 with laminin.
In The Journal of Cell Biology on 2 June 2025 by Isogai, T., Hirosawa, K. M., et al.
-
Cell Biology
In Nature Communications on 12 March 2025 by Hirosawa, K. M., Sato, Y., et al.
Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) play crucial roles in intercellular communication. However, the internalization of individual sEVs by recipient cells has not been directly observed. Here, we examined these mechanisms using state-of-the-art imaging techniques. Single-molecule imaging shows that tumor-derived sEVs can be classified into several subtypes. Simultaneous single-sEV particle tracking and observation of super-resolution movies of membrane invaginations in living cells reveal that all sEV subtypes are internalized via clathrin-independent endocytosis mediated by galectin-3 and lysosome-associated membrane protein-2C, while some subtypes that recruited raft markers are internalized through caveolae. Integrin β1 and talin-1 accumulate in recipient cell plasma membranes beneath all sEV subtypes. Paracrine, but not autocrine, sEV binding triggers Ca2+ mobilization induced by the activation of Src family kinases and phospholipase Cγ. Subsequent Ca2+-induced activation of calcineurin-dynamin promotes sEV internalization, leading to the recycling pathway. Thus, we clarified the detailed mechanisms of sEV internalization driven by paracrine adhesion signaling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
In Molecular Biology Reports on 30 January 2025 by Schurr, A. F., Dave, C. S., et al.
von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) hereditary cancer syndrome is caused by mutations in the VHL tumor suppressor gene and is characterized by a predisposition to form various types of tumors, including renal cell carcinomas, hemangioblastomas, and pheochromocytomas. The protein products of the VHL gene, pVHL, are part of an ubiquitin ligase complex that tags hypoxia inducible factor alpha (HIF-α) for proteosomal degradation. pVHL has also been reported to bind to atypical protein kinase C (aPKC).
To better understand the relationship between pVHL and aPKC, the PKC iota (PKCι) isoform of aPKC was knocked out in renal carcinoma cells, both pVHL-negative and those with replaced pVHL. Cellular properties associated with pVHL function were assayed. Knockout of PKCι in pVHL-expressing cells led to greater downregulation of HIF-α than seen with pVHL alone, suggesting that the presence of PKCι opposes complete regulation of HIF-α by pVHL. In contrast, absence of either pVHL or PKCι disrupted tight junction formation and led to upregulated levels of α5 integrin, both of which were phenocopied by lysosomal inhibition. LAMP1 (lysosome associated membrane protein 1), a marker for lysosomes, showed dysregulated localization and altered electrophoretic gel migration in the absence of pVHL. While the upregulated α5 integrin seen in the absence of either pVHL or PKCι loss was associated with increased cell adhesion, loss of pVHL caused increased cell motility whereas loss of PKCι decreased motility.
These data are consistent with a known role of PKCι in endocytosis of α5 integrin and suggest a subsequent novel role of pVHL in targeting a pool of endocytosed α5 integrin for lysosomal degradation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
The GTPase RAB6 is required for stem cell maintenance and cell migration in the gut epithelium.
In Development (Cambridge, England) on 1 November 2024 by Simonin, P., Guerrero, G. L., et al.
Intestinal epithelial cells, which are instrumental in nutrient absorption, fluid regulation, and pathogen defense, undergo continuous proliferation and differentiation within the intestinal crypts, migrating towards the luminal surface where they are eventually shed. RAB GTPases are key regulators of intracellular vesicular trafficking and are involved in various cellular processes, including cell migration and polarity. Here, we investigated the role of RAB6 in the development and maintenance of the gut epithelium. We generated conditional knockout mice with RAB6 specifically deleted in the gut epithelium. We found that deletion of the Rab6a gene resulted in embryonic lethality. In adult mice, RAB6 depletion led to altered villus architecture and impaired junction integrity without affecting the segregation of apical and basolateral membrane domains. Further, RAB6 depletion slowed down cell migration and adversely affected both cell proliferation and stem cell maintenance. Notably, the absence of RAB6 resulted in a diminished number of functional stem cells, as evidenced by the rapid death of isolated crypts from Rab6a KO mice when cultured as 3D organoids. Together, these results underscore the essential role of RAB6 in maintaining gut epithelial homeostasis.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
RAB6 GTPase is required for stem cell maintenance and cell migration in the gut epithelium.
In Development (Cambridge, England) on 21 October 2024 by Simonin, P., Guerrero, G. L., et al.
Intestinal epithelial cells, instrumental in nutrient absorption, fluid regulation, and pathogen defense, undergo continuous proliferation and differentiation within the intestinal crypts, migrating towards the luminal surface where they are eventually shed. RAB GTPases are key regulators of intracellular vesicular trafficking, and are involved in various cellular processes, including cell migration and polarity. Here, we investigated the role of RAB6 in the development and maintenance of the gut epithelium. We have generated conditional knockout mice with RAB6 specifically deleted in the gut epithelium. We found that deletion of the Rab6a gene resulted in embryonic lethality. In adult mice, RAB6 depletion led to altered villi architecture, impaired junction integrity without affecting the segregation of apical and basolateral membrane domains. Further, RAB6 depletion slowed down cell migration and adversely affected both cell proliferation and stem cell maintenance. Notably, the absence of RAB6 resulted in a diminished number of functional stem cells, as evidenced by the rapid death of isolated crypts from Rab6a KO mice when cultured as 3D organoids. Together, these results underscore the essential role of RAB6 in maintaining gut epithelial homeostasis.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
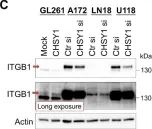
In Cells on 20 December 2021 by Chu, Y. H., Liao, W. C., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
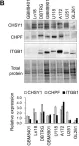
In Cells on 20 December 2021 by Chu, Y. H., Liao, W. C., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
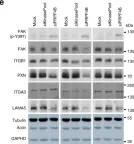
In Nat Commun on 5 July 2019 by Koedoot, E., Fokkelman, M., et al.
Fig.6.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
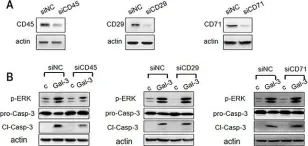
In Oncotarget on 25 July 2017 by Xue, H., Liu, L., et al.
Fig.8.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
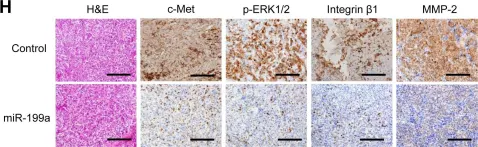
In Oncotarget on 10 May 2015 by Kinose, Y., Sawada, K., et al.
Fig.5.H

-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5