An oxysterol, 25-Hydroxycholesterol (25OHChol), is produced through cholesterol oxidation and is involved in various cellular processes, including apoptosis. However, the precise mechanisms underlying 25OHChol-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells remain unclear. The aim of this study was to elucidate the detailed molecular mechanisms by which 25OHChol induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cells. This study explores the apoptotic effects of 25OHChol and the associated signaling pathways in BE(2)-C cells, a widely used human neuroblastoma cell model for neuronal differentiation and cancer research. To evaluate the cytotoxicity of 25OHChol, cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 assay, which demonstrated a concentration-dependent decline, indicating a potential induction of cell death. Morphological changes characteristic of apoptosis, such as nuclear condensation and fragmentation, were confirmed via DAPI staining. Additionally, Annexin V/PI flow cytometry analysis revealed an increase in late apoptotic cell populations, further corroborating apoptosis induction. To investigate the molecular mechanisms, we analyzed the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins via Western blotting. The results showed an elevated Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, suggesting activation of the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. This was further supported by a reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), as measured by flow cytometry. Increased caspase-9 and caspase-3/7 activity provided additional evidence for caspase-mediated apoptosis. Moreover, treatment with the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK led to a dose-dependent increase in cell viability, confirming the essential role of caspases in 25OHChol-induced apoptosis. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that 25OHChol triggers apoptosis in BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cells through activation of the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. These findings provide new insights into the cytotoxic effects of 25OHChol and its potential role in neuroblastoma cell death.
Product Citations: 85
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 19 August 2025 by Kim, J., Kim, K., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
AKT Inhibition Sensitizes to Polo-Like Kinase 1 Inhibitor Onvansertib in Prostate Cancer.
In Molecular Cancer Therapeutics on 1 October 2024 by Nouri, M., Varkaris, A., et al.
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitors have had limited antitumor efficacy as single agents, and focus of current efforts is on combination therapies. We initially confirmed that the PLK1-specific inhibitor onvansertib (ONV) could enhance responses to a PARP inhibitor (olaparib) in prostate cancer xenografts. To identify more effective combinations, we screened a library of bioactive compounds for efficacy in combination with ONV in LNCaP prostate cancer cells, which identified a series of compounds including multiple AKT inhibitors. We confirmed in vitro synergy between ONV and the AKT inhibitor ipatasertib (IPA) and found that the combination increased apoptosis. Mechanistic studies showed that ONV increased expression of the antiapoptotic protein SURVIVIN and that this was mitigated by IPA. Studies in three PTEN-deficient prostate cancer xenograft models showed that cotreatment with IPA and ONV led to significant tumor growth inhibition compared with monotherapies. Together, these in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate that the efficacy of PLK1 antagonists can be enhanced by PARP or AKT inhibition and support further development of these combination therapies.
©2024 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
In Brain Sciences on 22 March 2024 by Zhang, M. X., Hong, H., et al.
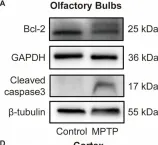
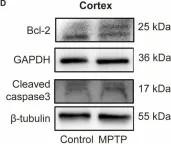
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized not only by motor symptoms but also by non-motor dysfunctions, such as olfactory impairment; the cause is not fully understood. Our study suggests that neuronal loss and inflammation in brain regions along the olfactory pathway, such as the olfactory bulb (OB) and the piriform cortex (PC), may contribute to olfactory dysfunction in PD mice, which might be related to the downregulation of the trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) in these areas. In the striatum, although only a decrease in mRNA level, but not in protein level, of TAAR1 was detected, bioinformatic analyses substantiated its correlation with PD. Moreover, we discovered that neuronal death and inflammation in the OB and the PC in PD mice might be regulated by TAAR through the Bcl-2/caspase3 pathway. This manifested as a decrease of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and an increase of the pro-apoptotic protein cleaved caspase3, or through regulating astrocytes activity, manifested as the increase of TAAR1 in astrocytes, which might lead to the decreased clearance of glutamate and consequent neurotoxicity. In summary, we have identified a possible mechanism to elucidate the olfactory dysfunction in PD, positing neuronal damage and inflammation due to apoptosis and astrocyte activity along the olfactory pathway in conjunction with the downregulation of TAAR1.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Cancer Communications (London, England) on 1 January 2024 by Raab, M., Kostova, I., et al.
The cellular tumor protein p53 (TP53) is a tumor suppressor gene that is frequently mutated in human cancers. Among various cancer types, the very aggressive high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) exhibits the highest prevalence of TP53 mutations, present in >96% of cases. Despite intensive efforts to reactivate p53, no clinical drug has been approved to rescue p53 function. In this study, our primary objective was to administer in vitro-transcribed (IVT) wild-type (WT) p53-mRNA to HGSOC cell lines, primary cells, and orthotopic mouse models, with the aim of exploring its impact on inhibiting tumor growth and dissemination, both in vitro and in vivo.
To restore the activity of p53, WT p53 was exogenously expressed in HGSOC cell lines using a mammalian vector system. Moreover, IVT WT p53 mRNA was delivered into different HGSOC model systems (primary cells and patient-derived organoids) using liposomes and studied for proliferation, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, colony formation, and chromosomal instability. Transcriptomic alterations induced by p53 mRNA were analyzed using RNA sequencing in OVCAR-8 and primary HGSOC cells, followed by ingenuity pathway analysis. In vivo effects on tumor growth and metastasis were studied using orthotopic xenografts and metastatic intraperitoneal mouse models.
Reactivation of the TP53 tumor suppressor gene was explored in different HGSOC model systems using newly designed IVT mRNA-based methods. The introduction of WT p53 mRNA triggered dose-dependent apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and potent long-lasting inhibition of HGSOC cell proliferation. Transcriptome analysis of OVCAR-8 cells upon mRNA-based p53 reactivation revealed significant alterations in gene expression related to p53 signaling, such as apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, and DNA damage. Restoring p53 function concurrently reduces chromosomal instability within the HGSOC cells, underscoring its crucial contribution in safeguarding genomic integrity by moderating the baseline occurrence of double-strand breaks arising from replication stress. Furthermore, in various mouse models, treatment with p53 mRNA reduced tumor growth and inhibited tumor cell dissemination in the peritoneal cavity in a dose-dependent manner.
The IVT mRNA-based reactivation of p53 holds promise as a potential therapeutic strategy for HGSOC, providing valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying p53 function and its relevance in ovarian cancer treatment.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
In Current Oncology (Toronto, Ont.) on 4 March 2023 by Wu, J., Fan, S., et al.
Mitophagy plays an important role in maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis by clearing damaged mitochondria. Sphingosine kinase 2 (SK2), a type of sphingosine kinase, is an important metabolic enzyme involved in generating sphingosine-1-phosphate. Its expression level is elevated in many cancers and is associated with poor clinical outcomes. However, the relationship between SK2 and mitochondrial dysfunction remains unclear. We found that the genetic downregulation of SK2 or treatment with ABC294640, a specific inhibitor of SK2, induced mitophagy and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cell lines. We showed that mitophagy correlates with apoptosis induction and likely occurs through the SET/PP2AC/PARK2 pathway, where inhibiting PP2AC activity may rescue this process. Furthermore, we found that PP2AC and PARK2 form a complex, suggesting that they might regulate mitophagy through protein-protein interactions. Our study demonstrates the important role of SK2 in regulating mitophagy and provides new insights into the mechanism of mitophagy in multiple myeloma.
-
WB
In Brain Sci on 22 March 2024 by Zhang, M. X., Hong, H., et al.
Fig.7.A
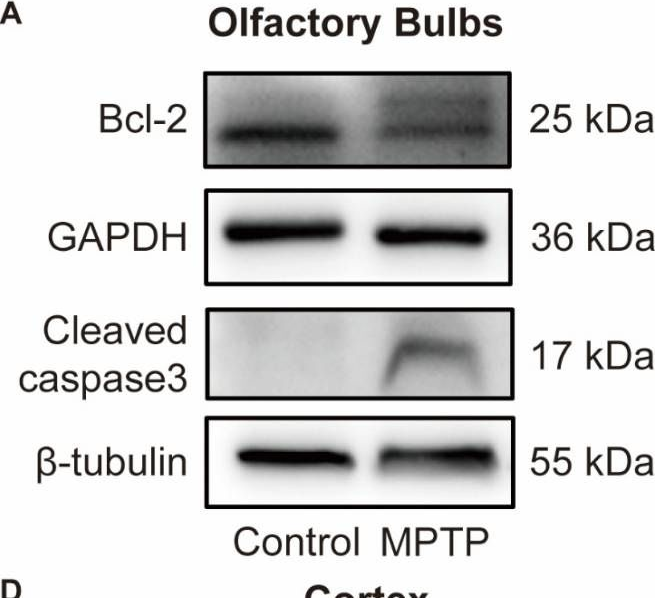
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Brain Sciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In Brain Sci on 22 March 2024 by Zhang, M. X., Hong, H., et al.
Fig.7.D
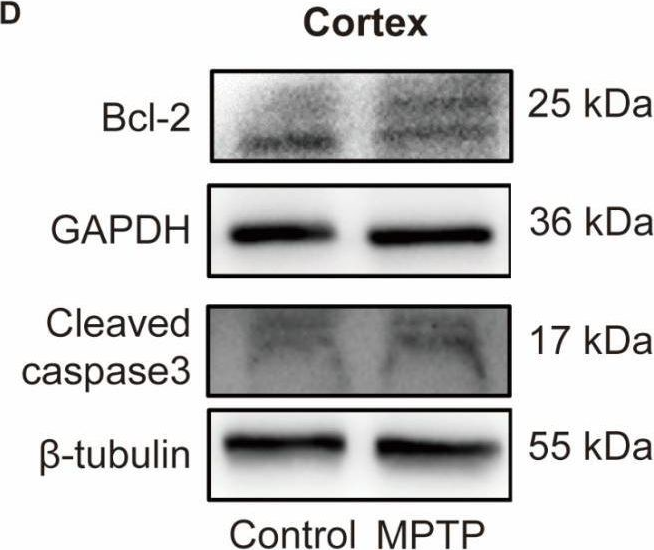
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Brain Sciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In Curr Oncol on 4 March 2023 by Wu, J., Fan, S., et al.
Fig.3.C
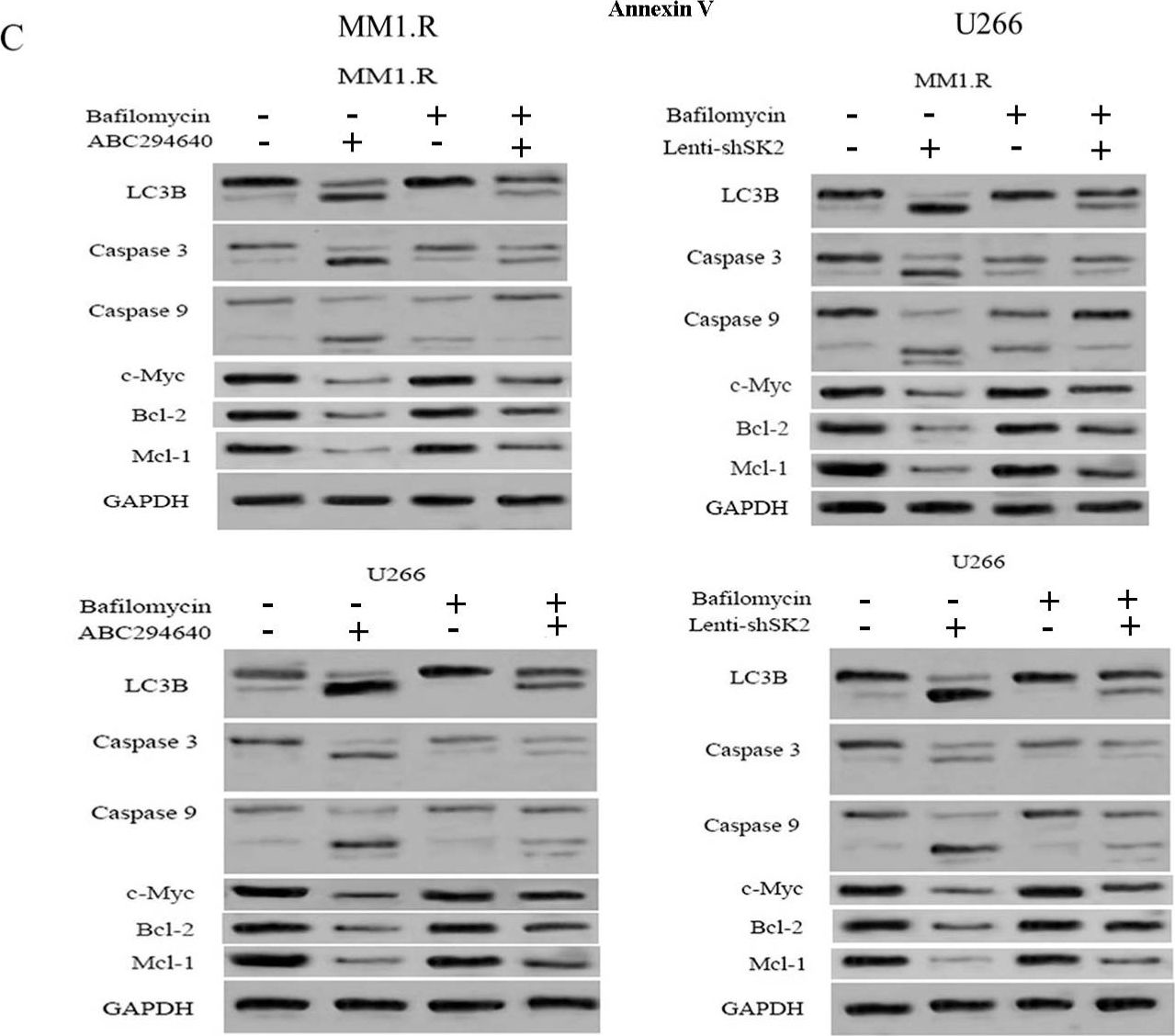
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Current Oncology (Toronto, Ont.) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
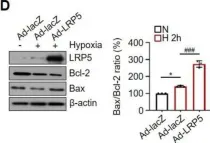
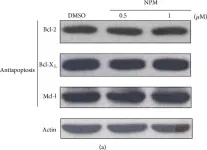
In Int J Mol Sci on 19 June 2021 by Ju, S., Lim, L., et al.
Fig.1.G
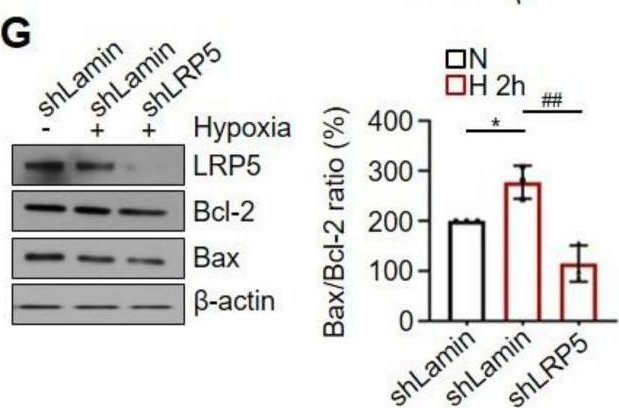
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from International Journal of Molecular Sciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
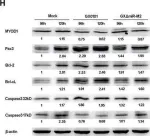
In Int J Mol Sci on 19 June 2021 by Ju, S., Lim, L., et al.
Fig.1.D
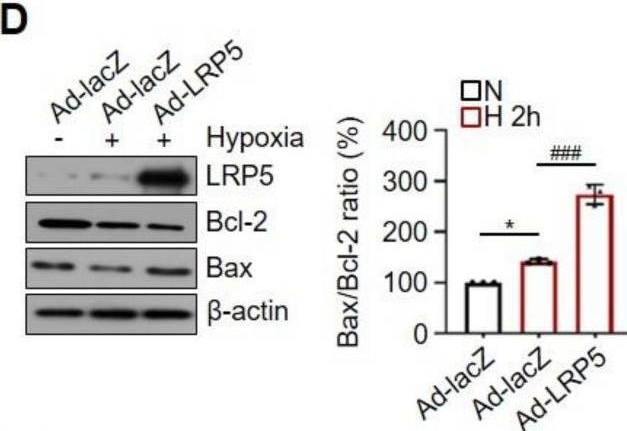
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from International Journal of Molecular Sciences by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
In Front Microbiol on 24 November 2020 by Zhu, Z. J., Teng, M., et al.
Fig.7.H
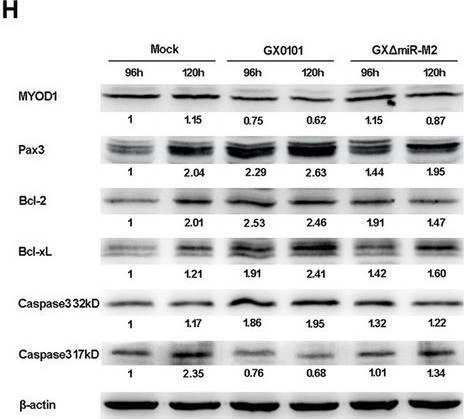
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Microbiology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
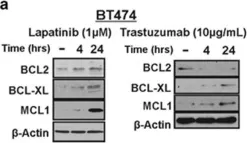
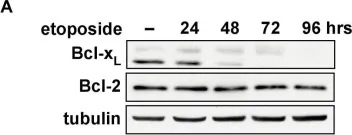
In Oncotarget on 25 April 2017 by Lei, X., Cai, S., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
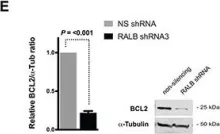
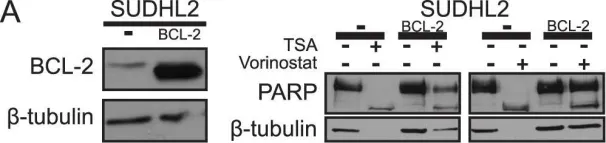
In Oncotarget on 4 October 2016 by Eckfeldt, C. E., Pomeroy, E. J., et al.
Fig.4.E
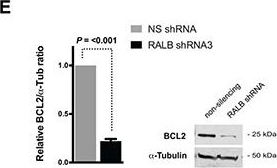
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
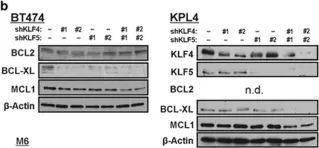
In Cell Death Dis on 19 March 2015 by Farrugia, M. K., Sharma, S. B., et al.
Fig.5.A
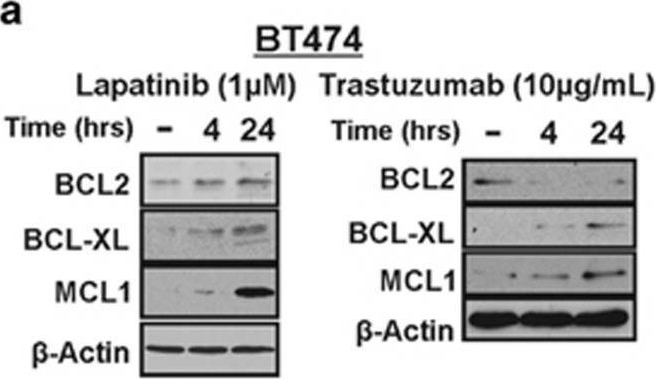
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death & Disease by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
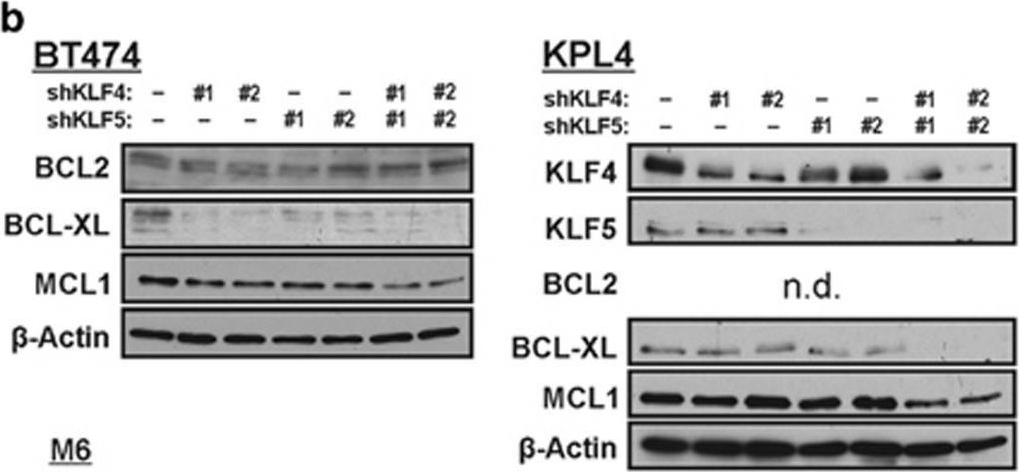
In Cell Death Dis on 19 March 2015 by Farrugia, M. K., Sharma, S. B., et al.
Fig.5.B
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death & Disease by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
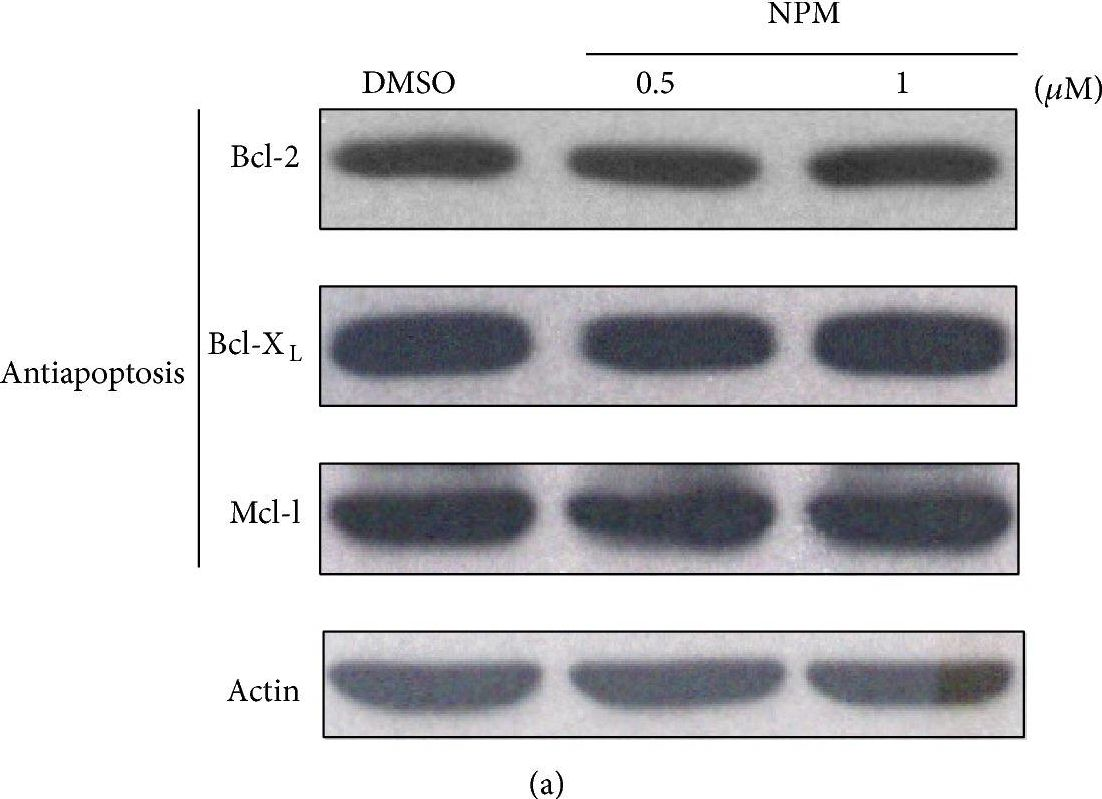
In Biomed Res Int on 30 January 2015 by Huang, P. R., Hung, S. C., et al.
Fig.5.A
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from BioMed Research International by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
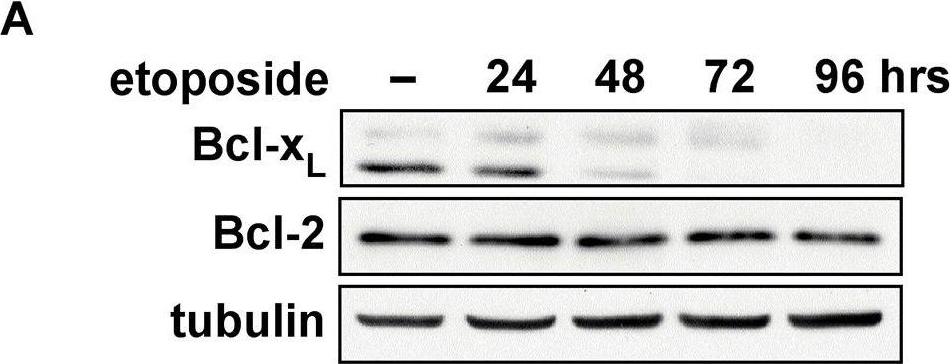
In PLoS Biol on 5 July 2013 by Dho, S. H., Deverman, B. E., et al.
Fig.4.A
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13
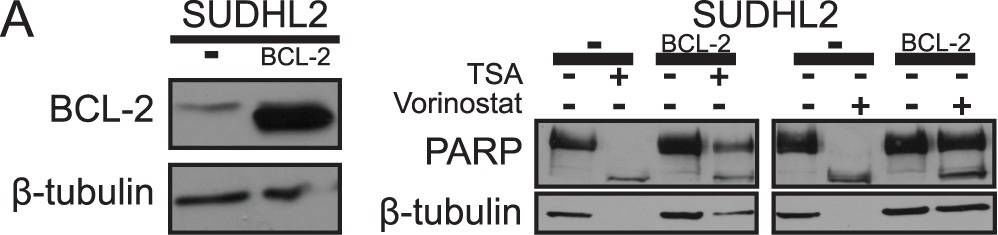
In PLoS One on 15 May 2013 by Thompson, R. C., Vardinogiannis, I., et al.
Fig.3.A
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS ONE by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 13