Oxidative stress and apoptosis are highly engaged in development of diabetic nephropathy (DN). In monotherapy, dapagliflozin and pioglitazone positively modulate target organ damage even independently of their hypoglycaemic effect. This study evaluated whether a simultaneous PPARγ activation and SGLT cotransporter inhibition offer superior protection against DN-related oxidative and apoptotic processes in a T1DM rat model. Diabetes was induced in Wistar rats using streptozotocin (55 mg/kg, i.p.). The rats received daily chow containing dapagliflozin (10 mg/kg), pioglitazone (12 mg/kg) or their combination. Six weeks after STZ administration, histological and molecular analyses were performed in excised kidneys. STZ-induced DN was demonstrated by the propagation of apoptotic (Bax, p53, Casp3) and oxidative reactions (Gp91phox, MnSOD) and disrupted nitric oxide signalling (eNOS, Hsp90, Cav1). Kidney damage molecule expression (Kim1, Nphs1) revealed a deceleration of kidney damage by pioglitazone and dapagliflozine monotherapies. The monotherapy also reduced apoptosis, oxidative stress, and partially restored NO signalling. The combined therapy ameliorated glomerulosclerosis but in other measured parameters, it reached the effect of the monotherapies except for Hsp90 expression modulation. Both dapagliflozin and pioglitazone exert protective character in kidneys when used in monotherapy. The combined therapy does not exhibit an expected additive effect within modulating oxidative stress, NO signalling or apoptosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 66
In Scientific Reports on 9 January 2025 by Čináková, A., Vavrincova-Yaghi, D., et al.
-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
In Environmental Toxicology on 1 December 2024 by Kao, S. W., Chang, Y. C., et al.
Inflammation is an intrinsic protective mechanism against various forms of cellular injuries in humans; however, its undesired activation results in tissue damage and cell death. The onset of chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are the key characteristics of autoimmune inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), for which an effective treatment is yet to be developed. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the protective effects and molecular mechanisms of a novel herbal preparation, Jing-Si herbal tea (JS), against H2O2-induced inflammation and cellular damage in HIG-82 synoviocytes. We found that JS did not show any significant alterations in cell viability at <188 μg/mL; however, a cytotoxic effect was observed at 188-1883 μg/mL concentrations tested. We found that expressions of inflammation associated extracellular matrix (ECM)-degrading proteases MMP-13, ADAMTS-2, -8, and -17 were abnormally enhanced under H2O2-induced pathological oxidative stress (ROS) in HIG-82 cells. Interestingly, JS treatment not only reduced the ROS levels but also significantly repressed the protein expressions of collagen degrading proteases in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment with JS showed enhanced cell viability against H2O2-induced toxic ROS levels. The expressions of cell protective aggrecan, Collagen II, and Bcl-2 were increased, whereas MMP-13, ADAMTS-2, Cytochrome C, and cleaved Caspase 3 were decreased by JS under inflammatory agents H2O2, MIA, LPS, and TNF-α treatment, respectively, in HIG-82 cells. Interestingly, the cytoprotective effect of JS treatment was attributed to a decreased mitochondrial localization of Bax and a reduction of Cytochrome C release into the cytoplasm of H2O2-treated HIG-82 cells. Collectively, our results suggest a novel protective mechanism of JS for RA treatment, which could be potentially applied as a complementary treatment or as an alternative therapeutic approach to mitigate inflammatory diseases.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Current Research in Toxicology on 30 November 2023 by Wen, S. Y., Ng, S. C., et al.
Diallyl trisulfide (DATS), an organosulfide compound derived from garlic, is renowned for its potent antioxidant properties, particularly in countering the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). It has also gained recognition as a potential agent for preventing heart-related conditions. Doxorubicin (Dox), a commonly used chemotherapeutic drug, is known to induce severe cardiac complications by promoting ROS production. Therefore, it was imperative to investigate whether DATS possesses cardioprotective capabilities against Dox-induced cardiac apoptosis and elucidate the underlying mechanisms. In this study, we observed that the intracellular ROS levels and cardiac apoptosis were heightened in H9c2 cells exposed to Dox (1 μM). However, treatment with 10 μM DATS effectively mitigated the Dox-induced ROS generation and apoptotic signaling, concurrently activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Notably, the anti-apoptotic effects of DATS were attenuated when PI3K siRNA and the LY294002 PI3K inhibitor were employed. Furthermore, the TUNEL assay results demonstrated a significant reduction in Dox-induced apoptosis with DATS treatment. In summary, our findings indicate that DATS can activate the PI3K/Akt pathway, reducing ROS production in cardiac cells exposed to Dox, and subsequently rescue cardiac cells from apoptosis.
© 2023 The Authors.
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Cardiovascular biology
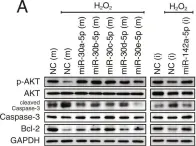
In Aging (Albany NY) on 20 February 2023 by Chen, W. S., Lin, T. Y., et al.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common disorder attributed to the loss of midbrain dopamine (mDA) neurons and reduced dopamine secretion. Currently, the treatment regimes for PD comprise deep brain stimulations, however, it attenuates the PD progression marginally and does not improve neuronal cell death. We investigated the function of Ginkgolide A (GA) to reinforce Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells (WJMSCs) for treating the in vitro model of PD. GA enhanced the self-renewal, proliferation, and cell homing function of WJMSCs as assessed by MTT and transwell co-culture assay with a neuroblastoma cell line. GA pre-treated WJMSCs can restore 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced cell death in a co-culture assay. Furthermore, exosomes isolated from GA pre-treated WJMSCs significantly rescued 6-OHDA-induced cell death as determined by MTT assay, flow cytometry, and TUNEL assay. Western blotting showed that apoptosis-related proteins were decreased following GA-WJMSCs exosomal treatment which further improved mitochondrial dysfunction. We further demonstrated that exosomes isolated from GA-WJMSCs could restore autophagy using immunofluorescence staining and immunoblotting assay. Finally, we used the alpha-synuclein recombinant protein and found that exosomes derived from GA-WJMSCs led to the reduced aggregation of alpha-synuclein compared to that in control. Our results suggested that GA could be a potential candidate for strengthening stem cell and exosome therapy for PD.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Neuroscience
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
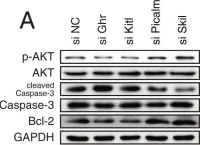
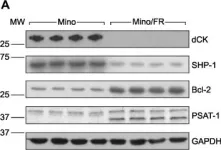
In Cancers on 26 October 2022 by Khaled, N. B., Hammer, K., et al.
Chemotherapy, the standard treatment for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), has only a modest effect on the outcome of patients with late-stage disease. Investigations of the genetic features of PDAC have demonstrated a frequent occurrence of mutations in genes involved in homologous recombination (HR), especially in the breast cancer susceptibility gene 2 (BRCA2). Olaparib, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, is approved as a maintenance treatment for patients with advanced PDAC with germline BRCA1/2 mutations following a platinum-containing first-line regimen. Limitations to the use of PARP inhibitors are represented by the relatively small proportion of patients with mutations in BRCA1/2 genes and the modest capability of these substances of inducing objective response. We have previously shown that pancreatic cancer with BRCA2 mutations exhibits a remarkably enhanced sensitivity towards tumor-necrosis-factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor-stimulating agents. We thus aimed to investigate the effect of combined treatment with PARP inhibitors and TRAIL receptor-stimulating agents in pancreatic cancer and its dependency on the BRCA2 gene status. The respective effects of TRAIL-targeting agents and the PARP inhibitor olaparib or of their combination were assessed in pancreatic cancer cell lines and patient-derived organoids. In addition, BRCA2-knockout and -complementation models were investigated. The effects of these agents on apoptosis, DNA damage, cell cycle, and receptor surface expression were assessed by immunofluorescence, Western blot, and flow cytometry. PARP inhibition and TRAIL synergized to cause cell death in pancreatic cancer cell lines and PDAC organoids. This effect proved independent of BRCA2 gene status in three independent models. Olaparib and TRAIL in combination caused a detectable increase in DNA damage and a concentration-dependent cell cycle arrest in the G2/M and S cell cycle phases. Olaparib also significantly increased the proportion of membrane-bound death receptor 5. Our results provide a preclinical rationale for the combination of PARP inhibitors and TRAIL receptor agonists for the treatment of pancreatic cancer and suggest that the use of PARP inhibitors could be extended to patients without BRCA2 mutations if used in combination with TRAIL agonists.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
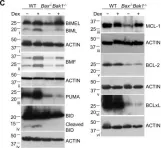
In Cell Death Dis on 8 June 2020 by Dong, L. & Vaux, D. L.
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
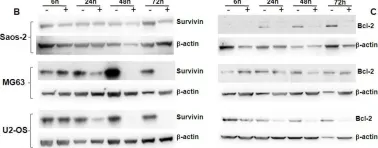
In Cells on 30 December 2019 by Chua, K. V., Fan, C. S., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Kim, J. O., Park, J. H., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Kim, J. O., Park, J. H., et al.
Fig.8.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
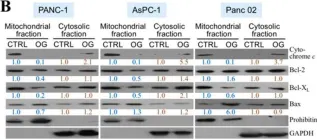
In Oncotarget on 31 August 2018 by Wirries, A., Jabari, S., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
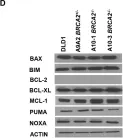
In Oncotarget on 23 February 2016 by De Toni, E. N., Ziesch, A., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
In PLoS One on 19 August 2015 by Lorkova, L., Scigelova, M., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8
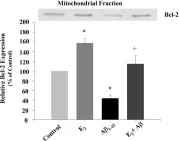
In BMC Neurosci on 3 November 2006 by Nilsen, J., Chen, S., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from BMC Neurosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 8