Biological patterning events that occur early in development establish proper tissue morphogenesis. Identifying the mechanisms that guide these patterning events is necessary in order to understand the molecular drivers of development and disease and to build tissues in vitro. In this study, we use an in vitro model of gastrulation to study the role of tight junctions and apical/basolateral polarity in modulating bone morphogenic protein-4 (BMP4) signaling and gastrulation-associated patterning in colonies of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs). Disrupting tight junctions via knockdown (KD) of the scaffolding tight junction protein-1 (TJP1, also known as ZO1) allows BMP4 to robustly and ubiquitously activate pSMAD1/5 signaling over time, resulting in loss of the patterning phenotype and marked differentiation bias of pluripotent stem cells to primordial germ cell-like cells (PGCLCs). These findings give important insights into how signaling events are regulated and lead to spatial emergence of diverse cell types in vitro.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 14
In Developmental Cell on 21 August 2023 by Vasić, I., Libby, A. R. G., et al.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Cell clusters adopt a collective amoeboid mode of migration in confined nonadhesive environments.
In Science Advances on 30 September 2022 by Pagès, D. L., Dornier, E., et al.
Cell migration is essential to living organisms and deregulated in cancer. Single cell's migration ranges from traction-dependent mesenchymal motility to contractility-driven propulsive amoeboid locomotion, but collective cell migration has only been described as a focal adhesion-dependent and traction-dependent process. Here, we show that cancer cell clusters, from patients and cell lines, migrate without focal adhesions when confined into nonadhesive microfabricated channels. Clusters coordinate and behave like giant super cells, mobilizing their actomyosin contractility at the rear to power their migration. This polarized cortex does not sustain persistent retrograde flows, of cells or actin, like in the other modes of migration but rather harnesses fluctuating cell deformations, or jiggling. Theoretical physical modeling shows this is sufficient to create a gradient of friction forces and trigger directed cluster motion. This collective amoeboid mode of migration could foster metastatic spread by enabling cells to cross a wide spectrum of environments.
-
IHC
In Journal of Cell Science on 15 July 2022 by Canet-Jourdan, C., Pagès, D. L., et al.
The metastatic progression of cancer remains a major issue in patient treatment. However, the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying this process remain unclear. Here, we use primary explants and organoids from patients harboring mucinous colorectal carcinoma (MUC CRC), a poor-prognosis histological form of digestive cancer, to study the architecture, invasive behavior and chemoresistance of tumor cell intermediates. We report that these tumors maintain a robust apico-basolateral polarity as they spread in the peritumoral stroma or organotypic collagen-I gels. We identified two distinct topologies - MUC CRCs either display a conventional 'apical-in' polarity or, more frequently, harbor an inverted 'apical-out' topology. Transcriptomic analyses combined with interference experiments on organoids showed that TGFβ and focal adhesion signaling pathways are the main drivers of polarity orientation. Finally, we show that the apical-out topology is associated with increased resistance to chemotherapeutic treatments in organoids and decreased patient survival in the clinic. Thus, studies on patient-derived organoids have the potential to bridge histological, cellular and molecular analyses to decrypt onco-morphogenic programs and stratify cancer patients. This article has an associated First Person interview with the first author of the paper.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
-
IHC
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
In Frontiers in Oncology on 6 April 2021 by Cruz, D. F., Mitash, N., et al.
Lemur tyrosine kinase 2 (LMTK2) is a transmembrane Ser/Thr kinase whose role has been increasingly recognized; however, when compared to other kinases, understanding of the LMTK2 networks and biological functions is still limited. Recent data have shown that transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 plays a role in modulating LMTK2 function by controlling its endocytic trafficking in human bronchial epithelial cells. Here, we aimed to unveil the LMTK2 regulatory network and elucidate how it affects cellular functions and disease pathways in either TGF-β1 dependent or independent manner. To understand how the LMTK2 and TGF-β1 pathways interconnect, we knocked down (KD) LMTK2 using small(si)RNA-mediated silencing in human bronchial epithelial CFBE41o- cells, treated cells with TGF-β1 or vehicle control, and performed differential gene expression analysis by RNA sequencing (RNAseq). In vehicle-treated cells, LMTK2 KD affected expression of 2,506 genes while it affected 4,162 genes after TGF-β1 stimulation. Bioinformatics analysis shows that LMTK2 is involved in diverse cellular functions and disease pathways, such as cell death and survival, cellular development, and cancer susceptibility. In summary, our study increases current knowledge about the LMTK2 network and its intersection with the TGF-β1 signaling pathway. These findings will serve as basis for future exploration of the predicted LMTK2 interactions and signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2021 Cruz, Mitash, Mu, Farinha and Swiatecka-Urban.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology on 3 March 2020 by Cruz, D. F., Mitash, N., et al.
The most common disease-causing mutation in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene, F508del, leads to cystic fibrosis (CF), by arresting CFTR processing and trafficking to the plasma membrane. The FDA-approved modulators partially restore CFTR function and slow down the progression of CF lung disease by increasing processing and delivery to the plasma membrane and improving activity of F508del-CFTR Cl- channels. However, the modulators do not correct compromised membrane stability of rescued F508del-CFTR. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 is a well-established gene modifier of CF associated with worse lung disease in F508del-homozygous patients, by inhibiting CFTR biogenesis and blocking the functional rescue of F508del-CFTR. Lemur tyrosine kinase 2 (LMTK2) is a transmembrane protein localized at the apical and basolateral membrane domain of human bronchial epithelial cells. Phosphorylation of the apical membrane CFTR by LMTK2 triggers its endocytosis and reduces the abundance of membrane-associated CFTR, impairing the CFTR-mediated Cl- transport. We have previously shown that LMTK2 knockdown improves the pharmacologically rescued F508del-CFTR abundance and function. Thus, reducing the LMTK2 recruitment to the plasma membrane may provide a useful strategy to potentiate the pharmacological rescue of F508del-CFTR. Here, we elucidate the mechanism of LMTK2 recruitment to the apical plasma membrane in polarized CFBE41o- cells. TGF-β1 increased LMTK2 abundance selectively at the apical membrane by accelerating its recycling in Rab11-positive vesicles without affecting LMTK2 mRNA levels, protein biosynthesis, or endocytosis. Our data suggest that controlling TGF-β1 signaling may attenuate recruitment of LMTK2 to the apical membrane thereby improving stability of pharmacologically rescued F508del-CFTR.
Copyright © 2020 Cruz, Mitash, Farinha and Swiatecka-Urban.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
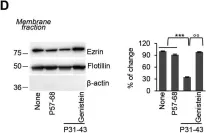
In Aging (Albany NY) on 12 April 2019 by Esposito, S., Villella, V. R., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Aging (Albany NY) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1