VE-cadherin is an essential adhesion molecule in endothelial adherens junctions, and the integrity of these complexes is thought to be regulated by VE-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation. We have previously shown that adrenomedullin (AM) blockade correlates with elevated levels of phosphorylated VE-cadherin (pVE-cadherinY731) in endothelial cells, associated with impaired barrier function and a persistent increase in vascular endothelial cell permeability. However, the mechanism underlying this effect is unknown. In this article, we demonstrate that the AM-mediated dephosphorylation of pVE-cadherinY731 takes place through activation of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2, as judged by the rise of its active fraction phosphorylated at tyrosine 542 (pSHP-2Y542) in HUVECs and glioblastoma-derived-endothelial cells. Both pre-incubation of HUVECs with SHP-2 inhibitors NSC-87877 and SHP099 and SHP-2 silencing hindered AM-induced dephosphorylation of pVE-cadherinY731 in a dose dependent-manner, showing the role of SHP-2 in the regulation of endothelial cell contacts. Furthermore, SHP-2 inhibition impaired AM-induced HUVECs differentiation into cord-like structures in vitro and impeded AM-induced neovascularization in in vivo Matrigel plugs bioassays. Subcutaneously transplanted U87-glioma tumor xenograft mice treated with AM-receptors-blocking antibodies showed a decrease in pSHP-2Y542 associated with VE-cadherin in nascent tumor vasculature when compared to control IgG-treated xenografts. Our findings show that AM acts on VE-cadherin dynamics through pSHP-2Y542 to finally modulate cell-cell junctions in the angiogenesis process, thereby promoting a stable and functional tumor vasculature.
Copyright © 2021 Sigaud, Dussault, Berenguer-Daizé, Vellutini, Benyahia, Cayol, Parat, Mabrouk, Vázquez, Riveiro, Metellus and Ouafik.
Product Citations: 26
In Frontiers in Oncology on 26 October 2021 by Sigaud, R., Dussault, N., et al.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Cell Chemical Biology on 18 February 2021 by Filip, R., Desrochers, G. F., et al.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) act as cellular signal transducers through repression of protein translation. Elucidating targets using bioinformatics and traditional quantitation methods is often insufficient to uncover global miRNA function. Herein, alteration of protein function caused by miRNA-185 (miR-185), an immunometabolic miRNA, was determined using activity-based protein profiling, transcriptomics, and lipidomics. Fluorophosphonate-based activity-based protein profiling of miR-185-induced changes to human liver cells revealed that exclusively metabolic serine hydrolase enzymes were regulated in activity, some with roles in lipid and endocannabinoid metabolism. Lipidomic analysis linked enzymatic changes to levels of cellular lipid species, such as components of very-low-density lipoprotein particles. Additionally, inhibition of one miR-185 target, monoglyceride lipase, led to decreased hepatitis C virus levels in an infectious model. Overall, the approaches used here were able to identify key functional changes in serine hydrolases caused by miR-185 that are targetable pharmacologically, such that a small molecule inhibitor can recapitulate the miRNA phenotype.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In The Journal of Biological Chemistry on 17 July 2020 by Lu, W., Ai, H., et al.
Homeostatic scaling of the synapse, such as synaptic down-scaling, has been proposed to offset deleterious effects induced by sustained synaptic strength enhancement. Proper function and subcellular distribution of Src homology 2 domain-containing nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP2) are required for synaptic plasticity. However, the role of SHP2 in synaptic down-scaling remains largely unknown. Here, using biochemical assays and cell-imaging techniques, we found that synaptic SHP2 levels are temporally regulated during synaptic down-scaling in cultured hippocampal neurons. Furthermore, we observed that a Noonan syndrome-associated mutation of SHP2, resulting in a D61G substitution, prevents synaptic down-scaling. We further show that this effect is due to an inability of the SHP2-D61G variant to properly disassociate from postsynaptic density protein 95, leading to impaired SHP2 dispersion from synaptic sites after synaptic down-scaling. Our findings reveal a molecular mechanism of the Noonan syndrome-associated genetic variant SHP2-D61G that contributes to deficient synaptic down-scaling.
© 2020 Lu et al.
-
ICC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
The dual role of c-src in cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein.
In EMBO Reports on 3 July 2020 by Choi, Y. R., Kim, J. B., et al.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons located in the substantia nigra pars compacta and the presence of proteinaceous inclusions called Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in numerous brain regions. Increasing evidence indicates that Lewy pathology progressively involves additional regions of the nervous system as the disease advances, and the prion-like propagation of α-synuclein (α-syn) pathology promotes PD progression. Accordingly, the modulation of α-syn transmission may be important for the development of disease-modifying therapies in patients with PD. Here, we demonstrate that α-syn fibrils induce c-src activation in neurons, which depends on the FcγRIIb-SHP-1/-2-c-src pathway and enhances signals for the uptake of α-syn into neurons. Blockade of c-src activation inhibits the uptake of α-syn and the formation of Lewy body-like inclusions. Furthermore, the blockade of c-src activation also inhibits the release of α-syn via activation of autophagy. The brain-permeable c-src inhibitor, saracatinib, efficiently reduces α-syn propagation into neighboring regions in an in vivo model system. These results suggest a new therapeutic target against progressive PD.
© 2020 The Authors.
In The Journal of Experimental Medicine on 4 September 2017 by Luo, M., Flood, E. C., et al.
Relative or absolute hypoxia activates signaling pathways that alter gene expression and stabilize the pulmonary microvasculature. Alveolar hypoxia occurs in disorders ranging from altitude sickness to airway obstruction, apnea, and atelectasis. Here, we report that the phospholipid-binding protein, annexin A2 (ANXA2) functions to maintain vascular integrity in the face of alveolar hypoxia. We demonstrate that microvascular endothelial cells (ECs) from Anxa2-/- mice display reduced barrier function and excessive Src-related tyrosine phosphorylation of the adherens junction protein vascular endothelial cadherin (VEC). Moreover, unlike Anxa2+/+ controls, Anxa2-/- mice develop pulmonary edema and neutrophil infiltration in the lung parenchyma in response to subacute alveolar hypoxia. Mice deficient in the ANXA2-binding partner, S100A10, failed to demonstrate hypoxia-induced pulmonary edema under the same conditions. Further analyses reveal that ANXA2 forms a complex with VEC and its phosphatases, EC-specific protein tyrosine phosphatase (VE-PTP) and Src homology phosphatase 2 (SHP2), both of which are implicated in vascular integrity. In the absence of ANXA2, VEC is hyperphosphorylated at tyrosine 731 in response to vascular endothelial growth factor, which likely contributes to hypoxia-induced extravasation of fluid and leukocytes. We conclude that ANXA2 contributes to pulmonary microvascular integrity by enabling VEC-related phosphatase activity, thereby preventing vascular leak during alveolar hypoxia.
© 2017 Luo et al.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cardiovascular biology
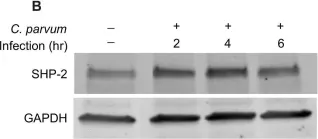
In PLoS One on 12 November 2015 by Varughese, E. A., Kasper, S., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
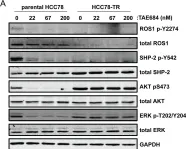
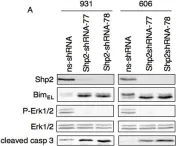
In PLoS One on 19 December 2013 by Davies, K. D., Mahale, S., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
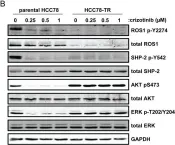
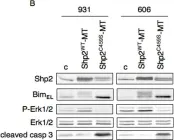
In PLoS One on 19 December 2013 by Davies, K. D., Mahale, S., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
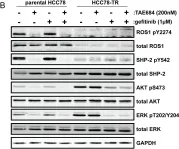
In PLoS One on 19 December 2013 by Davies, K. D., Mahale, S., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
In PLoS One on 13 November 2012 by Selimoglu-Buet, D., Gallais, I., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
In PLoS One on 13 November 2012 by Selimoglu-Buet, D., Gallais, I., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
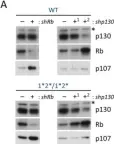
In PLoS Genet on 24 June 2010 by Burkhart, D. L., Wirt, S. E., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Genet by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7