The poor prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is attributed to tumor microenvironment driven by hypoxia regulated carbonic anhydrase IX. Our study elucidates the ability of Methazolamide, a CAIX inhibitor to sensitize resistant PDAC cells. The effect of Methazolamide alone and in combination with gemcitabine on proliferation, migration, tumor inhibition along with its impact on metastasis by influencing HIF-1α/PTEN/Glut1/Glut3 signalling through the expression of CAIX was assessed. Methazolamide induced cytotoxicity in several PDAC cells including patient derived with IC50 0.7-4.09 mM and 0.29-2.56 mM in monolayer and clonogenic assays respectively. Methazolamide alone and in combination significantly downregulated hypoxia induced expression of HIF-1α and CAIX together with proliferation (Ki-67, Cyclin D1), invasion (Rac-1, Snail), stem cell (Oct-4, Sox-2), angiogenesis (VEGF), glycolysis (Glut1, Glut3) and apoptosis (Bax, Bc1-2 and PTEN) markers in MIA PaCa-2 and PANC-1 cells. In vivo study in PAXF 546L PDX model exhibited profound tumor growth inhibition with downregulation of CD34, Oct-4, Sox-2, C-myc, Nanog, Ki-67, and Rac-1 signalling. Considering inadequate availability of effective therapeutics and importance of CAIX in processes leading to aggressive behavior of PDAC, targeting it by using Methazolamide, a pre-approved drug in combination with gemcitabine represents promising therapeutic approach specifically in metastatic settings.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 12
In Scientific Reports on 14 May 2025 by Ghosalkar, J., Sonawane, V., et al.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
The role of a ciliary GTPase in the regulation of neuronal maturation of olfactory sensory neurons.
In Development (Cambridge, England) on 15 January 2023 by Habif, J. C., Xie, C., et al.
Olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) form embryonically and mature perinatally, innervating glomeruli and extending dendrites with multiple cilia. This process and its timing are crucial for odor detection and perception and continues throughout life. In the olfactory epithelium (OE), differentiated OSNs proceed from an immature (iOSN) to a mature (mOSN) state through well-defined sequential morphological and molecular transitions, but the precise mechanisms controlling OSN maturation remain largely unknown. We have identified that a GTPase, ARL13B, has a transient and maturation state-dependent expression in OSNs marking the emergence of a primary cilium. Utilizing an iOSN-specific Arl13b-null murine model, we examined the role of ARL13B in the maturation of OSNs. The loss of Arl13b in iOSNs caused a profound dysregulation of the cellular homeostasis and development of the OE. Importantly, Arl13b null OSNs demonstrated a delay in the timing of their maturation. Finally, the loss of Arl13b resulted in severe deformation in the structure and innervation of glomeruli. Our findings demonstrate a previously unknown role of ARL13B in the maturation of OSNs and development of the OE.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Neuroscience
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Listeria monocytogenes Co-Opts the Host Exocyst Complex To Promote Internalin A-Mediated Entry.
In Infection and Immunity on 15 December 2022 by Gyanwali, G. C., Herath, T. U. B., et al.
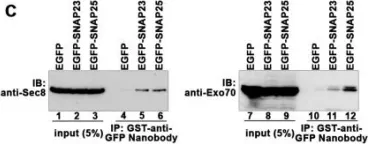
The bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes induces its internalization (entry) into intestinal epithelial cells through interaction of its surface protein, internalin A (InlA), with the human cell-cell adhesion molecule, E-cadherin. While InlA-mediated entry requires bacterial stimulation of actin polymerization, it remains unknown whether additional host processes are manipulated to promote internalization. Here, we show that interaction of InlA with E-cadherin induces the host membrane-trafficking process of polarized exocytosis, which augments uptake of Listeria. Imaging studies revealed that exocytosis is stimulated at sites of InlA-dependent internalization. Experiments inhibiting human N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) demonstrated that exocytosis is needed for efficient InlA-mediated entry. Polarized exocytosis is mediated by the exocyst complex, which comprises eight proteins, including Sec6, Exo70, and Exo84. We found that Exo70 was recruited to sites of InlA-mediated entry. In addition, depletion of Exo70, Exo84, or Sec6 by RNA interference impaired entry without affecting surface levels of E-cadherin. Similar to binding of InlA to E-cadherin, homophilic interaction of E-cadherin molecules mobilized the exocyst and stimulated exocytosis. Collectively, these results demonstrate that ligation of E-cadherin induces exocytosis that promotes Listeria entry, and they raise the possibility that the exocyst might also control the normal function of E-cadherin in cell-cell adhesion.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Shigella flexneri subverts host polarized exocytosis to enhance cell-to-cell spread.
In Molecular Microbiology on 1 November 2021 by Herath, T. U. B., Roy, A., et al.
Shigella flexneri is a gram-negative bacterial pathogen that causes dysentery. Critical for disease is the ability of Shigella to use an actin-based motility (ABM) process to spread between cells of the colonic epithelium. ABM transports bacteria to the periphery of host cells, allowing the formation of plasma membrane protrusions that mediate spread to adjacent cells. Here we demonstrate that efficient protrusion formation and cell-to-cell spread of Shigella involves bacterial stimulation of host polarized exocytosis. Using an exocytic probe, we found that exocytosis is locally upregulated in bacterial protrusions in a manner that depends on the Shigella type III secretion system. Experiments involving RNA interference (RNAi) indicate that efficient bacterial protrusion formation and spread require the exocyst, a mammalian multi-protein complex known to mediate polarized exocytosis. In addition, the exocyst component Exo70 and the exocyst regulator RalA were recruited to Shigella protrusions, suggesting that bacteria manipulate exocyst function. Importantly, RNAi-mediated depletion of exocyst proteins or RalA reduced the frequency of protrusion formation and also the lengths of protrusions, demonstrating that the exocyst controls both the initiation and elongation of protrusions. Collectively, our results reveal that Shigella co-opts the exocyst complex to disseminate efficiently in host cell monolayers.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 23 August 2021 by Guan, Y., Liang, X., et al.
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified loci for kidney disease, but the causal variants, genes, and pathways remain unknown. Here we identify two kidney disease genes Dipeptidase 1 (DPEP1) and Charged Multivesicular Body Protein 1 A (CHMP1A) via the triangulation of kidney function GWAS, human kidney expression, and methylation quantitative trait loci. Using single-cell chromatin accessibility and genome editing, we fine map the region that controls the expression of both genes. Mouse genetic models demonstrate the causal roles of both genes in kidney disease. Cellular studies indicate that both Dpep1 and Chmp1a are important regulators of a single pathway, ferroptosis and lead to kidney disease development via altering cellular iron trafficking.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
ICC-IF
-
Genetics
In Nat Commun on 3 December 2018 by Ahmed, S. M., Nishida-Fukuda, H., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
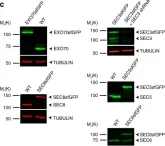
In Biol Open on 19 June 2015 by Kubo, K., Kobayashi, M., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Biol Open by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2