Leukotrienes (LTs) and sphingolipids are critical lipid mediators participating in numerous cellular signal transduction events and developing various disorders, such as bronchial hyperactivity leading to asthma. Enzymatic reactions initiating production of these lipid mediators involve 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)-mediated conversion of arachidonic acid to LTs and serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT)-mediated de novo synthesis of sphingolipids. Previous studies have shown that endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein ORM1-like protein 3 (ORMDL3) inhibits the activity of SPT and subsequent sphingolipid synthesis. However, the role of ORMDL3 in the synthesis of LTs is not known. In this study, we used peritoneal-derived mast cells isolated from ORMDL3 KO or control mice and examined their calcium mobilization, degranulation, NF-κB inhibitor-α phosphorylation, and TNF-α production. We found that peritoneal-derived mast cells with ORMDL3 KO exhibited increased responsiveness to antigen. Detailed lipid analysis showed that compared with WT cells, ORMDL3-deficient cells exhibited not only enhanced production of sphingolipids but also of LT signaling mediators LTB4, 6t-LTB4, LTC4, LTB5, and 6t-LTB5. The crosstalk between ORMDL3 and 5-LO metabolic pathways was supported by the finding that endogenous ORMDL3 and 5-LO are localized in similar endoplasmic reticulum domains in human mast cells and that ORMDL3 physically interacts with 5-LO. Further experiments showed that 5-LO also interacts with the long-chain 1 and long-chain 2 subunits of SPT. In agreement with these findings, 5-LO knockdown increased ceramide levels, and silencing of SPTLC1 decreased arachidonic acid metabolism to LTs to levels observed upon 5-LO knockdown. These results demonstrate functional crosstalk between the LT and sphingolipid metabolic pathways, leading to the production of lipid signaling mediators.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 14
In Journal of Lipid Research on 25 September 2021 by Bugajev, V., Paulenda, T., et al.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
In Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B on 1 June 2021 by Van Anh, T. T., Mostafa, A., et al.
Chronic inflammation results from excessive pro-inflammatory signaling and the failure to resolve the inflammatory reaction. Lipid mediators orchestrate both the initiation and resolution of inflammation. Switching from pro-inflammatory to pro-resolving lipid mediator biosynthesis is considered as efficient strategy to relieve chronic inflammation, though drug candidates exhibiting such features are unknown. Starting from a library of Vietnamese medical plant extracts, we identified isomers of the biflavanoid 8-methylsocotrin-4'-ol from Dracaena cambodiana, which limit inflammation by targeting 5-lipoxygenase and switching the lipid mediator profile from leukotrienes to specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPM). Elucidation of the absolute configurations of 8-methylsocotrin-4'-ol revealed the 2S,γS-isomer being most active, and molecular docking studies suggest that the compound binds to an allosteric site between the 5-lipoxygenase subdomains. We identified additional subordinate targets within lipid mediator biosynthesis, including microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1. Leukotriene production is efficiently suppressed in activated human neutrophils, macrophages, and blood, while the induction of SPM biosynthesis is restricted to M2 macrophages. The shift from leukotrienes to SPM was also evident in mouse peritonitis in vivo and accompanied by a substantial decrease in immune cell infiltration. In summary, we disclose a promising drug candidate that combines potent 5-lipoxygenase inhibition with the favorable reprogramming of lipid mediator profiles.
© 2021 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Structural and mechanistic insights into 5-lipoxygenase inhibition by natural products.
In Nature Chemical Biology on 1 July 2020 by Gilbert, N. C., Gerstmeier, J., et al.
Leukotrienes (LT) are lipid mediators of the inflammatory response that are linked to asthma and atherosclerosis. LT biosynthesis is initiated by 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) with the assistance of the substrate-binding 5-LOX-activating protein at the nuclear membrane. Here, we contrast the structural and functional consequences of the binding of two natural product inhibitors of 5-LOX. The redox-type inhibitor nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) is lodged in the 5-LOX active site, now fully exposed by disordering of the helix that caps it in the apo-enzyme. In contrast, the allosteric inhibitor 3-acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA) from frankincense wedges between the membrane-binding and catalytic domains of 5-LOX, some 30 Å from the catalytic iron. While enzyme inhibition by NDGA is robust, AKBA promotes a shift in the regiospecificity, evident in human embryonic kidney 293 cells and in primary immune cells expressing 5-LOX. Our results suggest a new approach to isoform-specific 5-LOX inhibitor development through exploitation of an allosteric site in 5-LOX.
-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Neurotherapeutics on 1 July 2020 by Marschallinger, J., Altendorfer, B., et al.
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) represents a huge medical need as it accounts for up to 30% of all dementia cases, and there is no cure available. The underyling spectrum of pathology is complex and creates a challenge for targeted molecular therapies. We here tested the hypothesis that leukotrienes are involved in the pathology of DLB and that blocking leukotrienes through Montelukast, a leukotriene receptor antagonist and approved anti-asthmatic drug, might alleviate pathology and restore cognitive functions. Expression of 5-lipoxygenase, the rate-limiting enzyme for leukotriene production, was indeed elevated in brains with DLB. Treatment of cognitively deficient human alpha-synuclein overexpressing transgenic mice with Montelukast restored memory. Montelukast treatment resulted in modulation of beclin-1 expression, a marker for autophagy, and in a reduction in the human alpha-synulcein load in the transgenic mice. Reducing the protein aggregation load in neurodegenerative diseases might be a novel model of action of Montelukast. Moreover, this work presents leukotriene signaling as a potential drug target for DLB and shows that Montelukast might be a promising drug candidate for future DLB therapy development.
-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Neuroscience
In Molecular Psychiatry on 1 November 2019 by di Meco, A., Li, J. G., et al.
A high circulating level of homocysteine (Hcy), also known as hyperhomocysteinemia, is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Previous studies show that elevated Hcy promotes brain amyloidosis and behavioral deficits in mouse models of AD. However, whether it directly modulates the development of tau neuropathology independently of amyloid beta in vivo is unknown. Herein, we investigate the effect of diet-induced elevated levels of brain Hcy on the phenotype of a relevant mouse model of human tauopathy. Compared with controls, tau mice fed with low folate and B vitamins diet had a significant increase in brain Hcy levels and worsening of behavioral deficits. The same mice had a significant elevation of tau phosphorylation, synaptic pathology, and astrocytes activation. In vitro studies demonstrated that Hcy effect on tau phosphorylation was mediated by an upregulation of 5-lipoxygenase via cdk5 kinase pathway activation. Our findings support the novel concept that high Hcy level in the central nervous system is a metabolic risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases, specifically characterized by the progressive accumulation of tau pathology, namely tauopathies.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Nat Commun on 11 December 2015 by Dvash, E., Har-Tal, M., et al.
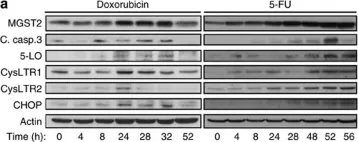
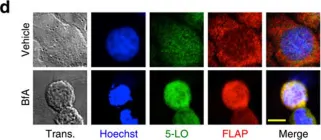
Fig.9.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Nat Commun on 11 December 2015 by Dvash, E., Har-Tal, M., et al.
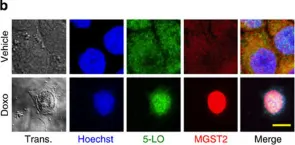
Fig.9.B

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Nat Commun on 11 December 2015 by Dvash, E., Har-Tal, M., et al.
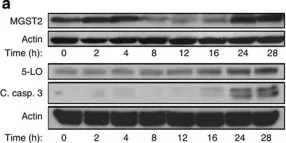
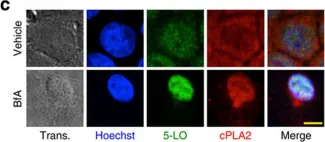
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Nat Commun on 11 December 2015 by Dvash, E., Har-Tal, M., et al.
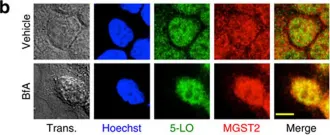
Fig.1.B

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Nat Commun on 11 December 2015 by Dvash, E., Har-Tal, M., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Nat Commun on 11 December 2015 by Dvash, E., Har-Tal, M., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
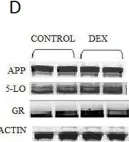
In PLoS One on 22 January 2011 by Puccio, S., Chu, J., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
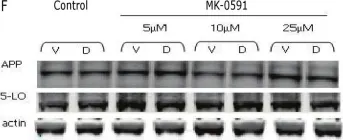
In PLoS One on 22 January 2011 by Puccio, S., Chu, J., et al.
Fig.3.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In PLoS One on 22 January 2011 by Puccio, S., Chu, J., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In PLoS One on 22 January 2011 by Puccio, S., Chu, J., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10