Specificity in membrane trafficking relies on the interaction between Rab small GTPase proteins and their molecular effectors. However, the evidence that different Rab proteins can bind to common effectors challenges this view. Here, we show that molecular competition between distinct Rab GTPases for a shared protein can link diverse membrane trafficking pathways. Theoretical analysis and experimental data support a role for Zfyve26 as a part of a competitive network that modulates changes in Rab5-Rab11 abundance, activation status, and correlation at the surface of single endocytic structures. By leveraging on the Loop index, a novel metric that couples the GTP-bound fraction and the total amount of Rab GTPase, we infer the saturation of Zfyve26 molecules at the endocytic surface from time-lapse imaging data. Our findings establish that transduction in the endocytic system is governed by stoichiometric constraints determining the trade-off between different trafficking pathways at the surface of a membrane-bound organelle.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Product Citations: 18
A competition network connects Rab5 and Rab11 GTPases at the surface of endocytic structures.
In IScience on 18 April 2025 by Ferro, E., Tealdi, S., et al.
Discovery of a Small Molecule with an Inhibitory Role for RAB11.
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 9 December 2024 by Lempicki, C., Milosavljevic, J., et al.
RAB11, a pivotal RabGTPase, regulates essential cellular processes such as endocytic recycling, exocytosis, and autophagy. The protein was implicated in various human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, viral infections, and podocytopathies. However, a small-molecular inhibitor is lacking. The complexity and workload associated with potential assays make conducting large-scale screening for RAB11 challenging. We employed a tiered approach for drug discovery, utilizing deep learning-based computational screening to preselect compounds targeting a specific pocket of RAB11 protein with experimental validation by an in vitro platform reflecting RAB11 activity through the exocytosis of GFP. Further validation included the exposure of Drosophila by drug feeding. In silico pre-screening identified 94 candidates, of which 9 were confirmed using our in vitro platform for Rab11 activity. Focusing on compounds with high potency, we assessed autophagy, which independently requires RAB11, and validated three of these compounds. We further analyzed the dose-response relationship, observing a biphasic, potentially hormetic effect. Two candidate compounds specifically caused a shift in Rab11 vesicles to the cell periphery, without significant impact on Rab5 or Rab7. Drosophila larvae exposed to another candidate compound with predicted oral bioavailability exhibited minimal toxicity, subcellular dispersal of endogenous Rab11, and a decrease in RAB11-dependent nephrocyte function, further supporting an inhibitory role. Taken together, the combination of computational screening and experimental validation allowed the identification of small molecules that modify the function of Rab11. This discovery may further open avenues for treating RAB11-associated disorders.
-
ICC-IF
-
Chlorocebus aethiops (Grivet monkey)
DRG2 is required for surface localization of PD-L1 and the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy.
In Cell Death Discovery on 27 May 2024 by Choi, S. H., Mani, M., et al.
More than half of tumor patients with high PD-L1 expression do not respond to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy, and the underlying mechanisms are yet to be clarified. Here we show that developmentally regulated GTP-binding protein 2 (DRG2) is required for response of PD-L1-expressing tumors to anti-PD-1 therapy. DRG2 depletion enhanced IFN-γ signaling and increased the PD-L1 level in melanoma cells. However, it inhibited recycling of endosomal PD-L1 and reduced surface PD-L1 levels, which led to defects in interaction with PD-1. Anti-PD-1 did not expand effector-like T cells within DRG2-depleted tumors and failed to improve the survival of DRG2-depleted tumor-bearing mice. Cohort analysis revealed that patients bearing melanoma with low DRG2 protein levels were resistant to anti-PD-1 therapy. These findings identify DRG2 as a key regulator of recycling of endosomal PD-L1 and response to anti-PD-1 therapy and provide insights into how to increase the correlation between PD-L1 expression and response to anti-PD-1 therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
In Molecular Biology of the Cell on 1 March 2024 by van der Beek, J., de Heus, C., et al.
The multisubunit HOPS tethering complex is a well-established regulator of lysosome fusion with late endosomes and autophagosomes. However, the role of the HOPS complex in other stages of endo-lysosomal trafficking is not well understood. To address this, we made HeLa cells knocked out for the HOPS-specific subunits Vps39 or Vps41, or the HOPS-CORVET-core subunits Vps18 or Vps11. In all four knockout cells, we found that endocytosed cargos were trapped in enlarged endosomes that clustered in the perinuclear area. By correlative light-electron microscopy, these endosomes showed a complex ultrastructure and hybrid molecular composition, displaying markers for early (Rab5, PtdIns3P, EEA1) as well as late (Rab7, CD63, LAMP1) endosomes. These "HOPS bodies" were not acidified, contained enzymatically inactive cathepsins and accumulated endocytosed cargo and cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor (CI-MPR). Consequently, CI-MPR was depleted from the TGN, and secretion of lysosomal enzymes to the extracellular space was enhanced. Strikingly, HOPS bodies also contained the autophagy proteins p62 and LC3, defining them as amphisomes. Together, these findings show that depletion of the lysosomal HOPS complex has a profound impact on the functional organization of the entire endosomal system and suggest the existence of a HOPS-independent mechanism for amphisome formation.
-
Cell Biology
In Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS on 17 October 2022 by Keable, R., Hu, S., et al.
Beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), also known as β-secretase, is an aspartic protease. The sorting of this enzyme into Rab11-positive recycling endosomes regulates the BACE1-mediated cleavage of its substrates, however, the mechanisms underlying this targeting remain poorly understood. The neural cell adhesion molecule 2 (NCAM2) is a substrate of BACE1. We show that BACE1 cleaves NCAM2 in cultured hippocampal neurons and NCAM2-transfected CHO cells. The C-terminal fragment of NCAM2 that comprises the intracellular domain and a small portion of NCAM2's extracellular domain, associates with BACE1. This association is not affected in cells with inhibited endocytosis, indicating that the interaction of NCAM2 and BACE1 precedes the targeting of BACE1 from the cell surface to endosomes. In neurons and CHO cells, this fragment and BACE1 co-localize in Rab11-positive endosomes. Overexpression of full-length NCAM2 or a recombinant NCAM2 fragment containing the transmembrane and intracellular domains but lacking the extracellular domain leads to an increase in BACE1 levels in these organelles. In NCAM2-deficient neurons, the levels of BACE1 are increased at the cell surface and reduced in intracellular organelles. These effects are correlated with increased levels of the soluble extracellular domain of BACE1 in the brains of NCAM2-deficient mice, suggesting increased shedding of BACE1 from the cell surface. Of note, shedding of the extracellular domain of Sez6, a protein cleaved exclusively by BACE1, is reduced in NCAM2-deficient animals. These results indicate that the BACE1-generated fragment of NCAM2 regulates BACE1 activity by promoting the targeting of BACE1 to Rab11-positive endosomes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
-
WB
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 17 October 2022 by Keable, R., Hu, S., et al.
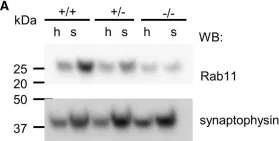
Fig.7.A
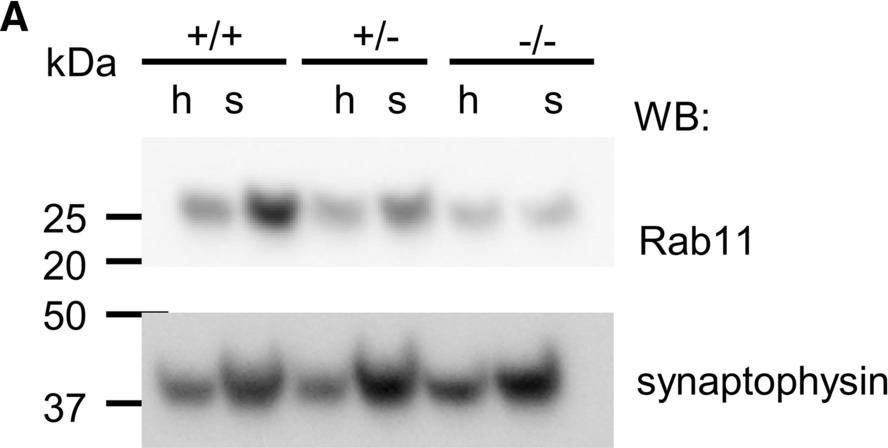
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 17 October 2022 by Keable, R., Hu, S., et al.
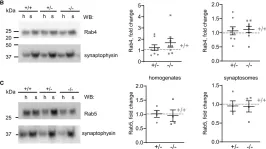
Fig.7.B
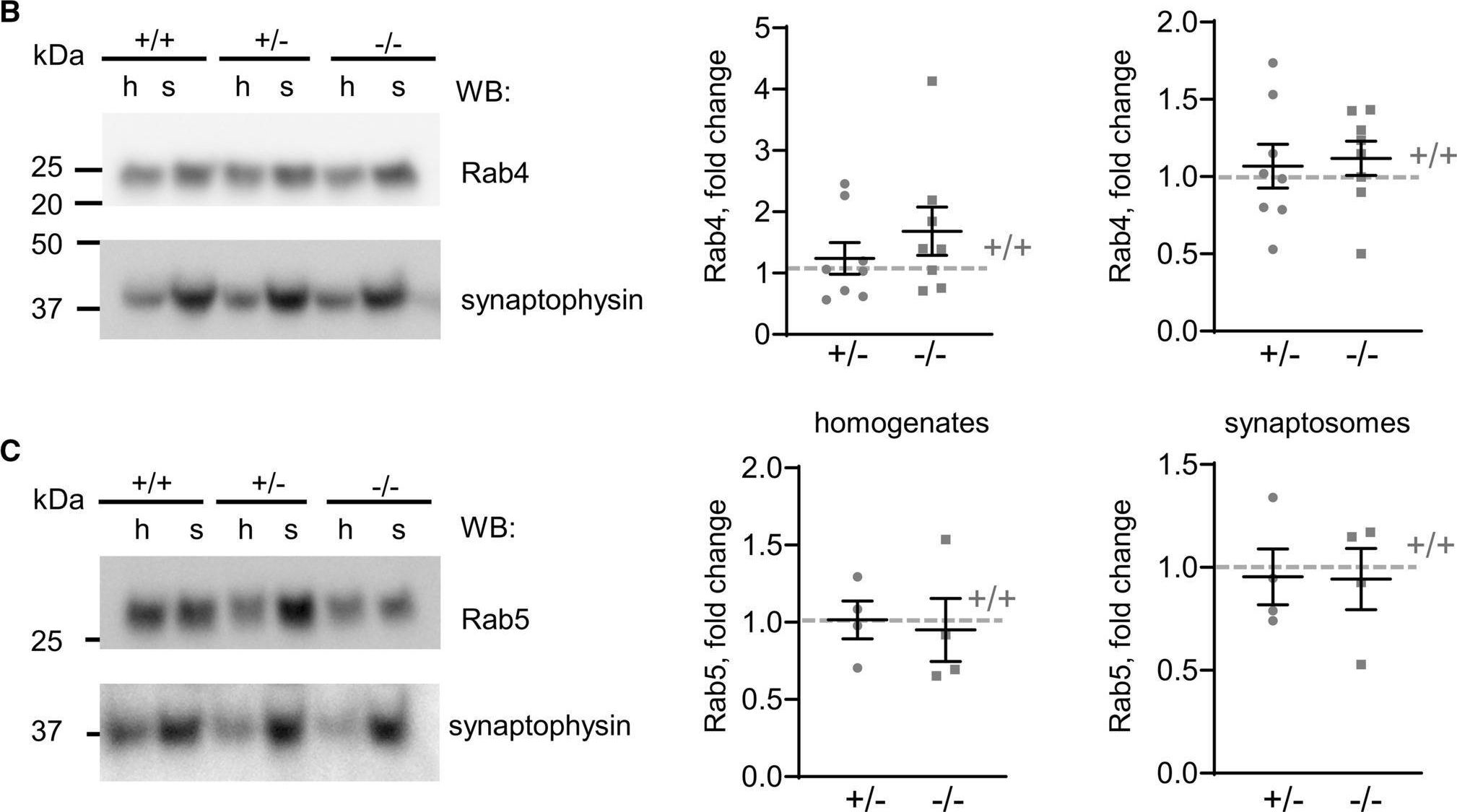
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences : CMLS by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2