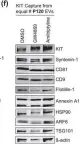
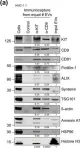
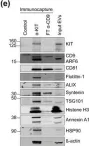
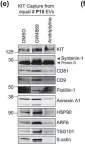
The converging biology between enveloped viruses and extracellular vesicles (EVs) has raised interest in the application of engineered EVs as antiviral therapeutics. Following the recent COVID-19 pandemic, EVs engineered with either the ACE2-receptor or Spike-protein have been proposed as strategy to either decoy SARS-CoV-2, or to compete with its cell entry. For generic use as a platform for future pandemic preparedness, a systematic and quantitative comparison of both strategies is required to assess their limitations and benefits across different variants of concern.
Here we generated EVs decorated with either the ACE2-receptor or the Spike-protein of (Wuhan)-SARS-CoV-2 and used single vesicle imaging for in-depth quantitative characterisation. These vesicles were then systematically tested for anti-viral activity across SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern using both, pseudotype and live virus cellular infection models including primary human bronchial and nasal explants.
Spike-protein EVs or ACE2-EVs recovered from transiently transfected HEK293T cells comprised only a small fraction of the EV secretome (5% or 20%, respectively) and were primarily derived from the plasma membrane rather than multivesicular bodies. Redirecting intracellular trafficking of the Spike protein by mutating its transmembrane or subcellular localisation domains did not increase the yields of Spike-EVs. Both types of vesicles inhibited SARS-CoV-2 (D614G) in a dose dependent manner with kinetics and immunohistochemistry consistent with an inhibition at the initial cell entry stage. ACE2-EVs were more potent than Spike-EVs and at least 500-1000 times more potent than soluble antibodies in a pseudotype model. Surprisingly, ACE2-EVs switched from an inhibitory to an enhancer activity for the Omicron BA.1 variant whereas Spike-EVs retained their activity across all variants of concern.
While our data show that both types of engineered EVs potently inhibit SARS-CoV, the decoy versus competition strategy may result in diverging outcomes when considering viral evolution into new variants of concern. While Spike-EVs retain their competition for receptor binding even against higher affinity viral Spike mutations, the formation of complexes between ACE2-EVs and the virus may not only result in inhibition by decoy. As EVs are actively internalised by cells themselves, they may shuttle the virus into cells, resulting in a productive alternative cell entry route for variants such as Omicron, that diverge from strict plasma membrane protease cleavage to the use of endosomal proteases for release of their genome.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 129
In Cell Communication and Signaling : CCS on 2 July 2025 by Schürz, M., Pagani, I., et al.
-
COVID-19
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
Glucosylceramide induced ectosomes propagate pathogenic α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 16 February 2025 by Jacquemyn, J., Mariott, B., et al.
Intercellular transmission of α-synuclein contributes to Parkinson’s disease pathology. Yet, the mechanisms of α-synuclein spread are not fully understood. Here, we used live-cell microscopy to examine the impact of Parkinson’s disease associated lipid alterations on α-synuclein release. We discovered that increased glucosylceramides induce ectosome shedding from primary neurons, and from dopaminergic neurons derived from Parkinson’s disease patient iPSCs harboring mutations in GBA1 (N370S, L444P and W378G) and LRRK2 (G2019S and R1441H) compared to their isogenic control. We show that elevated glucosylceramide similarly increases vesicle release and uptake by other neurons in living mouse brains using 2-photon microscopy. Finally, we show that ectosomes are loaded with pathogenic α-synuclein and lead to the transmission of α-synuclein pathology to neighbouring neurons. These data reveal ectosomes as the predominant route for α-synuclein transmission that can only be appreciated by live-cell imaging technologies.
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 29 January 2025 by Naito, M., Takeda, Y., et al.
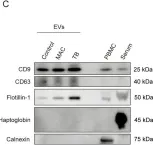
Nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD), mainly caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), and pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) are emerging health problems worldwide. However, because their clinical features are often similar, it remains difficult to differentiate NTM-PD from TB when the diagnosis cannot be made by sputum culture. To investigate potential serum biomarkers, we conducted non-targeted proteome analysis on serum extracellular vesicles (EVs) collected from 10 patients with MAC pulmonary disease (MAC-PD), 7 patients with TB, and 10 healthy controls. A total of 2614 proteins were identified in the discovery cohort. The EV protein signature from patients with NTM-PD and TB reflected infectious diseases and inflammatory response pathways. Among the identified proteins, the expression of Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 2 (NHERF2) was significantly elevated in patients with MAC-PD compared with healthy controls and patients with TB. Moreover, upregulation of NHERF2 was confirmed by immunoblotting of serum EVs and immunohistochemistry of lungs with mycobacterial infection. Our findings highlight that NHERF2 in serum EVs might be a potential biomarker for distinguishing MAC-PD from TB, possibly reflecting the pathogenesis of MAC-PD.
-
WB
-
Cardiovascular biology
Tau filaments are tethered within brain extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer's disease.
In Nature Neuroscience on 1 January 2025 by Fowler, S. L., Behr, T. S., et al.
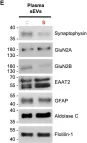
The abnormal assembly of tau protein in neurons is a pathological hallmark of multiple neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Assembled tau associates with extracellular vesicles (EVs) in the central nervous system of individuals with AD, which is linked to its clearance and prion-like propagation. However, the identities of the assembled tau species and EVs, as well as how they associate, are not known. Here, we combined quantitative mass spectrometry, cryo-electron tomography and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy to study brain EVs from individuals with AD. We found tau filaments composed mainly of truncated tau that were enclosed within EVs enriched in endo-lysosomal proteins. We observed multiple filament interactions, including with molecules that tethered filaments to the EV limiting membrane, suggesting selective packaging. Our findings will guide studies into the molecular mechanisms of EV-mediated secretion of assembled tau and inform the targeting of EV-associated tau as potential therapeutic and biomarker strategies for AD.
© 2024. Crown.
-
Neuroscience
In Cell Death & Disease on 23 October 2024 by Toledano-Zaragoza, A., Enríquez-Zarralanga, V., et al.
Niemann-Pick disease Type C (NPC) is caused by mutations in the cholesterol transport protein NPC1 leading to the endolysosomal accumulation of the lipid and to psychiatric alterations. Using an NPC mouse model (Npc1nmf164) we show aberrant mGluR5 lysosomal accumulation and reduction at plasma membrane in NPC1 deficient neurons. This phenotype was induced in wild-type (wt) neurons by genetic and pharmacological NPC1 silencing. Extraction of cholesterol normalized mGluR5 distribution in NPC1-deficient neurons. Intracellular accumulation of mGluR5 was functionally active leading to enhanced mGluR-dependent long-term depression (mGluR-LTD) in Npc1nmf164 hippocampal slices. mGluR-LTD was lower or higher in Npc1nmf164 slices compared with wt when stimulated with non-membrane-permeable or membrane-permeable mGluR5 agonists, respectively. Oral treatment with the mGluR5 antagonist 2-chloro-4-((2,5-dimethyl-1-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl)ethynyl)pyridine (CTEP) reduced mGluR-LTD and ameliorated psychiatric anomalies in the Npc1nmf164 mice. Increased neuronal mGluR5 levels were found in an NPC patient. These results implicate mGluR5 alterations in NPC psychiatric condition and provide a new therapeutic strategy that might help patients suffering from this devastating disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
In Int J Mol Sci on 29 January 2025 by Naito, M., Takeda, Y., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Biol Res on 28 September 2024 by Sánchez-Rubio, M., Abarzua-Catalan, L., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Biol Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Biol Res on 28 September 2024 by Sánchez-Rubio, M., Abarzua-Catalan, L., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Biol Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Life Sci Alliance on 1 August 2024 by Veronese, M., Kallabis, S., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Life Sci Alliance by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Biomed Sci on 27 March 2024 by Chyuan, I. T., Liao, H. J., et al.
Fig.5.E

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Biomed Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Biomed Sci on 27 March 2024 by Chyuan, I. T., Liao, H. J., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Biomed Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Cell Death Discov on 5 April 2023 by Gautheron, F., Georgievski, A., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Cell Death Discov on 5 April 2023 by Gautheron, F., Georgievski, A., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Discov by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.6.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.6.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.6.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.1.F
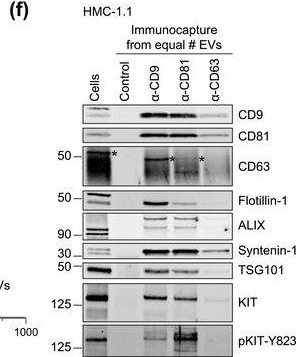
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.1.A
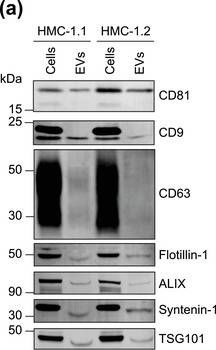
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 1 September 2022 by Pfeiffer, A., Petersen, J. D., et al.
Fig.5.B
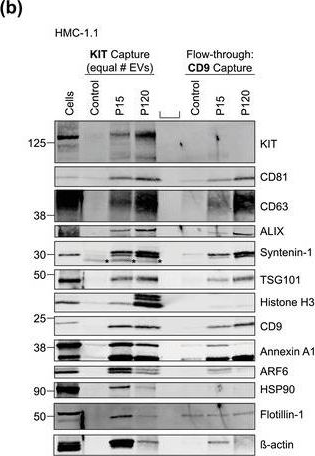
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Nat Commun on 19 March 2021 by Zhang, Y., Varela, L., et al.
Fig.9.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Biol Chem on 19 December 2020 by Zhang, L., Gui, T., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Sci Rep on 20 December 2019 by Schiano, G., Glaudemans, B., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Sci Rep on 20 December 2019 by Schiano, G., Glaudemans, B., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Extracell Vesicles on 3 July 2018 by Degosserie, J., Heymans, C., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Extracell Vesicles by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In J Cell Biol on 5 March 2018 by Verweij, F. J., Bebelman, M. P., et al.
Fig.6.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Acta Neuropathol Commun on 29 August 2017 by Gauthier, S. A., Pérez-González, R., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Acta Neuropathol Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24
In Sci Rep on 4 January 2017 by Serena, M., Parolini, F., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 24