Metastasis is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are abundant components within the tumour microenvironment, playing critical roles in metastasis. Although increasing evidence supports a role for small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) in this process, their precise contribution and molecular mechanisms remain unclear, compromising the development of antimetastatic therapies. Here, we establish that CAF-sEVs drive metastasis by mediating CAF-cancer cell interaction and hyperactivating TGF-β signalling in tumour cells. Metastasis is abolished by genetically targeting CAF-sEV secretion and consequent reduction of TGF-β signalling in cancer cells. Pharmacological treatment with dimethyl amiloride (DMA) decreases CAFs' sEV secretion, reduces TGF-β signalling levels in tumour cells and abrogates metastasis and tumour self-seeding. This work defines a new mechanism required by CAFs to drive cancer progression, supporting the therapeutic targeting of EV trafficking to disable the driving forces of metastasis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Product Citations: 61
In Journal of Extracellular Vesicles on 1 March 2025 by Teixeira, A. F., Wang, Y., et al.
-
Cancer Research
AMH regulates a mosaic population of AMHR2-positive cells in the ovarian surface epithelium.
In The Journal of Biological Chemistry on 1 November 2024 by Smith, E. R., Ye, D., et al.
The function and homeostasis of the mammalian ovary depend on complex paracrine interactions between multiple cell types. Using primary mouse tissues and isolated cells, we showed in vitro that ovarian follicles secrete factor(s) that suppresses the growth of ovarian epithelial cells in culture. Most of the growth suppressive activity was accounted for by Anti-Mullerian Hormone/Mullerian Inhibitory Substance (AMH/MIS) secreted by granulosa cells of the follicles, as determined by immune depletion experiments. Additionally, conditioned medium from granulosa cells from wild-type control, but not AMH knockout, suppressed epithelial cell growth. Tracing of the AMH-regulated cells using AMHR2 (AMH receptor 2)-Cre:ROSA26 mutant mice indicated the presence of populations of AMHR2-positive epithelial cells on the ovarian surface and oviduct epithelia. Cells isolated from the mutant mice indicated that a subpopulation of cells marked by AMHR2-Cre:ROSA26 accounted for most cell growth and expansion in ovarian surface epithelial cells, and the AMHR2 lineage-derived cells were regulated by AMH in vitro; whereas, fewer AMHR2-Cre:ROSA26-marked cells accounted for oviduct epithelial cell outgrowth. The results reveal a paracrine pathway in maintaining follicle-epithelial homeostasis in the ovary and support a subpopulation of AMHR2 lineage marked epithelial cells as ovarian epithelial stem/progenitor cells with higher proliferative potential regulatable by follicle-secreted AMH.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
In The FASEB Journal on 15 August 2024 by Itoh, Y., Miyake, K., et al.
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a pleiotropic cytokine that modulates a wide variety of cellular responses by regulating target gene expression. It principally transmits signals via receptor-activated transcription factors Smad2 and Smad3, which form trimeric complexes with Smad4 upon activation and regulate gene expression by binding to genomic DNA. Here, we examined the mechanisms by which TGF-β regulates the transcription of target genes in a cell context-dependent manner by screening a double-stranded DNA oligonucleotide library for DNA sequences bound to endogenous activated Smad complexes. Screening was performed by cyclic amplification of selected targets (CASTing) using an anti-Smad2/3 antibody and nuclear extracts isolated from three cell lines (A549, HepG2, and HaCaT) stimulated with TGF-β. The preference of the activated Smad complexes for conventional Smad-binding motifs such as Smad-binding element (SBE) and CAGA motifs was different in HepG2 than in the other two cell lines, which may indicate the distinct composition of the activated Smad complexes. Several transcription factor-binding motifs other than SBE or CAGA, including the Fos/Jun-binding motifs, were detected in the enriched sequences. Reporter assays using sequences containing these transcription factor-binding motifs together with Smad-binding motifs indicated that some of the motifs may be involved in cell type-dependent transcriptional activation by TGF-β. The results suggest that the CASTing method is useful for elucidating the molecular basis of context-dependent Smad signaling.
© 2024 The Author(s). The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
-
Genetics
In ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science on 12 April 2024 by Längle, D., Wojtowicz-Piotrowski, S., et al.
The TGFβ type II receptor (TβRII) is a central player in all TGFβ signaling downstream events, has been linked to cancer progression, and thus, has emerged as an auspicious anti-TGFβ strategy. Especially its targeted degradation presents an excellent goal for effective TGFβ pathway inhibition. Here, cellular structure-activity relationship (SAR) data from the TβRII degrader chemotype 1 was successfully transformed into predictive ligand-based pharmacophore models that allowed scaffold hopping. Two distinct 3,4-disubstituted indoles were identified from virtual screening: tetrahydro-4-oxo-indole 2 and indole-3-acetate 3. Design, synthesis, and screening of focused amide libraries confirmed 2r and 3n as potent TGFβ inhibitors. They were validated to fully recapitulate the ability of 1 to selectively degrade TβRII, without affecting TβRI. Consequently, 2r and 3n efficiently blocked endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cell migration in different cancer cell lines while not perturbing the microtubule network. Hence, 2 and 3 present novel TβRII degrader chemotypes that will (1) aid target deconvolution efforts and (2) accelerate proof-of-concept studies for small-molecule-driven TβRII degradation in vivo.
© 2024 American Chemical Society.
Spatial Single Cell Analysis of Proteins in 2D Human Gastruloids Using Iterative Immunofluorescence.
In Current Protocols on 1 October 2023 by Freeburne, E., Teague, S., et al.
During development, cell signaling instructs tissue patterning, the process by which initially identical cells give rise to spatially organized structures consisting of different cell types. How multiple signals combinatorially instruct fate in space and time remains poorly understood. Simultaneous measurement of signaling activity through multiple signaling pathways and of the cell fates they control is critical to addressing this problem. Here we describe an iterative immunofluorescence protocol and computational pipeline to interrogate pattern formation in a 2D model of human gastrulation with far greater multiplexing than is possible with standard immunofluorescence techniques. This protocol and computational pipeline together enable imaging followed by spatial and co-localization analysis of over 27 proteins in the same gastruloids. We demonstrate this by clustering single cell protein expression, using techniques familiar from scRNA-seq, and linking this to spatial position to calculate spatial distributions and cell signaling activity of different cell types. These methods are not limited to patterning in 2D gastruloids and can be easily extended to other contexts. In addition to the iterative immunofluorescence protocol and analysis pipeline, Support Protocols for 2D gastruloid differentiation and producing micropatterned multi-well slides are included. © 2023 The Authors. Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: Iterative immunofluorescence Basic Protocol 2: Computational analysis pipeline Support Protocol 1: Generating micropatterned multi-well slides Support Protocol 2: Differentiation of 2D gastruloids.
© 2023 The Authors. Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
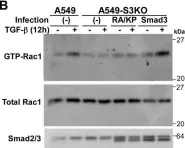
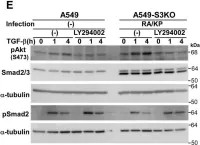
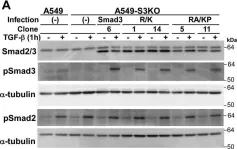
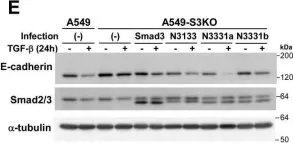
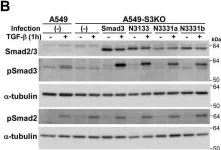
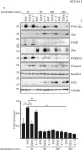
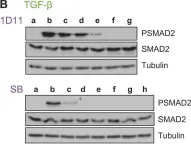
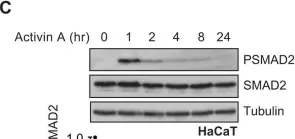
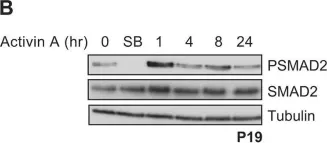
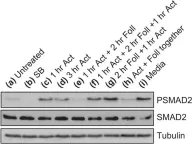
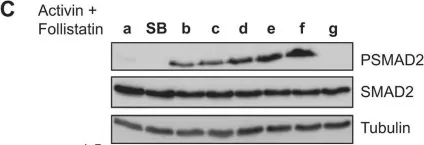
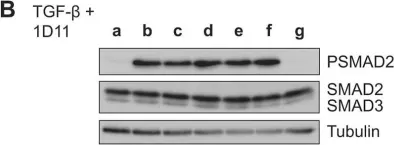
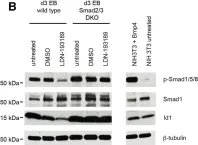
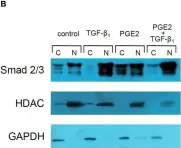
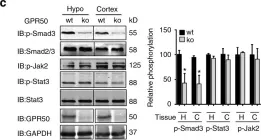
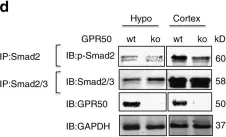
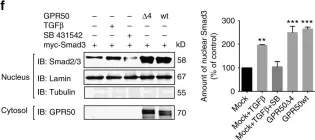
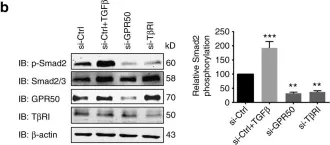
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
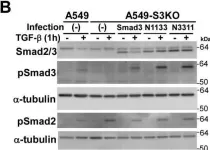
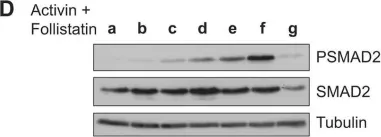
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.6.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
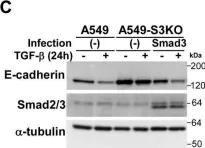
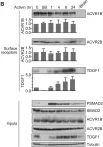
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
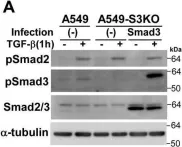
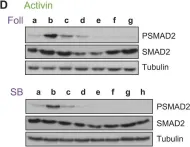
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Biol Chem on 21 March 2021 by Motizuki, M., Koinuma, D., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
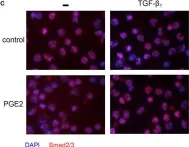
In Cells on 21 November 2019 by Sundqvist, A., Voytyuk, O., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In J Cell Sci on 15 July 2019 by Miller, D. S. J., Schmierer, B., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Cell Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In Cell Rep on 21 August 2018 by Senft, A. D., Costello, I., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cell Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In Front Immunol on 11 July 2018 by Remes Lenicov, F., Paletta, A. L., et al.
Fig.11.C

-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In Front Immunol on 11 July 2018 by Remes Lenicov, F., Paletta, A. L., et al.
Fig.11.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In Nat Commun on 23 March 2018 by Wojciech, S., Ahmad, R., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In Nat Commun on 23 March 2018 by Wojciech, S., Ahmad, R., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In Nat Commun on 23 March 2018 by Wojciech, S., Ahmad, R., et al.
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34
In Nat Commun on 23 March 2018 by Wojciech, S., Ahmad, R., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 34