PCK2, which encodes mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK-M), is upregulated in various cancers. We demonstrated high expression of PEPCK-M in approximately half of triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) previously. TNBC is associated with an aggressive phenotype and a high metastasis rate. In this study, we investigated the role of PCK2 in TNBC. PCK2 knockdown suppressed proliferation and mTOR signaling in TNBC cells. In addition, cell invasion/migration ability and the expression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers were positively correlated with PCK2 expression in TNBC cells via regulation of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)/SMAD3 signaling. SMAD3 was positively regulated by PCK2 in TNBC cells. Knockdown of SMAD3 in PCK2-overexpressing TNBC cells reduced the expression levels of EMT markers, Snail and Slug, and suppressed cell invasion/migration. In addition, PCK2 knockdown attenuated the stimulatory effect of TGF-β on SMAD3 phosphorylation in TNBC cells. PEPCK-M promotes the protein and mRNA expression of SMAD3 via competitive binding to tripartite motif-containing 67 (TRIM67), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, to reduce SMAD3 ubiquitination, which leads to promoting nuclear translocation of SMAD3 and autoregulation of SMAD3 transcription. Moreover, high PCK2 mRNA expression was significantly associated with poor survival in TNBC patients. In conclusion, our study revealed for the first time that PCK2 activates TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling by regulating the expression and phosphorylation of SMAD3 by inhibiting TRIM67-mediated SMAD3 ubiquitination and promoting the stimulatory effect of TGF-β to promote TNBC invasion. The regulatory effect of PCK2 on mTOR and TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling suggests that PCK2 is a potential therapeutic target for suppressing TNBC progression.
Product Citations: 257
In Cancer Biology & Therapy on 1 December 2025 by Chang, T. M., Fang, W. Y., et al.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
In Scientific Reports on 2 July 2025 by Varlı, M., Lee, K., et al.
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a critical process in cancer cell motility and metastasis. Monoterpene indole alkaloids (MIAs) have been widely investigated for biological activities, but rarely been explored for cell motility inhibition. This study aimed to discover natural products, especially focusing on MIAs, that inhibit EMT in cancer cells, based on our screening using multiple plant extracts. We found that an extract of the aerial parts of Uncaria scandens (Sm.) Wall. (Rubiaceae) decreased cancer cell motility. Targeted isolation exhibited eight MIAs. Among them, strictosamide and mitraphylline suppressed the invasion and migration of the cells. The alteration of the mRNA expression of the EMT effectors and transcription factors suggested that the EMT signaling pathway is related to the suppression of cancer cell motility by both compounds. RT-PCR gene array suggested inhibition of integrin α4 signaling as a potential mechanism of the EMT inhibition, which was supported by the quantitative analysis of the mRNA expressions of the related genes. Together, present study is the first report highlighting the cell motility-suppressive effects of strictosamide and mitraphylline. Our results suggested the potential applicability of strictosamide and mitraphylline for the prevention of metastasis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
In Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology on 9 June 2025 by Josvai, M., Lawson, J., et al.
Cardiac fibroblasts deposit and turnover the extracellular matrix in the heart, as well as secrete soluble factors that play critical roles in development, homeostasis, and disease. Coculture of CFs and human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived cardiomyocytes (CMs) enhances CM mechanical output, yet the mechanism remains unclear.
Here, we use an in vitro engineered platform to compare the effects on CM mechanical function of direct CM-CF Coculture and soluble signaling alone through CF Conditioned Medium to a CM Only monoculture. Mechanical analysis is performed using digital image correlation and custom software to quantify the coordination and organization of CM contractile behavior.
CM-CF Coculture induces larger CM contractile strains, and an increased rate of spontaneous contraction compared to CM Only. Additionally, CM-CF Cocultures have increased contractile anisotropy and myofibril alignment and faster kinetics. The paracrine effects of fibroblast conditioned medium (FCM) are sufficient to induce larger contractile strains and faster contraction kinetics with these effects remaining after the removal of FCM. However, FCM does not influence CM spontaneous rate, contractile alignment, anisotropy, or relaxation kinetics compared to CM Only control.
These data suggest that hiPSC-CFs exert dynamic and multifactorial effects on the mechanical function of hiPSC-CMs and highlight the importance of CFs in both the native heart and in vitro cardiac models. Further, this work demonstrates the applicability of the coculture-conditioned medium-monoculture paradigm to decouple the effects of paracrine factor and cell-cell signaling on hiPSC-CM mechanical function and maturation.
Copyright © 2025 Josvai, Lawson, Kanade, Kalluri, Anderson, Zhang, Stempien, Eckhardt, Kamp and Crone.
-
Cardiovascular biology
Lamotrigine promotes reentrant ventricular tachycardia in murine hearts.
In Epilepsia on 1 May 2025 by Dias, P., Meng, X., et al.
In 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration issued a safety warning concerning lamotrigine use in patients with underlying cardiac disorders. This warning was based on in vitro data that predicted class Ib antiarrhythmic activity for lamotrigine. Therefore, we investigated the proarrhythmic potential of lamotrigine in the murine heart and compared its effect with flecainide.
Murine hearts were perfused with clinically relevant concentrations of lamotrigine 3.8 μg/mL (15 μmol·L-1) or flecainide .4 μg/mL (1 μmol·L-1).
Ex vivo electrocardiography revealed a high prevalence of ventricular tachycardia (VT) in lamotrigine-perfused hearts (7/9 hearts), whereas only two hearts exposed to flecainide evidenced VT. Optical voltage mapping showed that lamotrigine preferentially decreased ventricular conduction velocity (CV) in the longitudinal direction at all pacing frequencies tested (-22% ± 8.6%, -30% ± 15.4%, and -33% ± 13.3% for pacing frequency of 200-ms, 180-ms, and 150-ms cycle length, respectively, p ≤ .05) compared to the transverse direction, which only slowed CV at the fastest pacing frequency (-15% ± 16% for pacing frequency of 150-ms cycle length, p ≤ .01). Notably, the preferential CV slowing in the longitudinal direction altered the anisotropic ratio, giving rise to a functional substrate for reentrant VT. In contrast, flecainide slowed CV uniformly in both longitudinal and transverse directions (-30% ± 8.5% vs. -27% ± 5.3%, -32% ± 9.4% vs. -29% ± 6.9%, and - 29% ± 8.3% vs. -27% ± 10% for pacing frequency of 200-ms, 180-ms, and 150-ms cycle length, respectively, p ≤ .05).
Our findings provide mechanistic insight into the proarrhythmic impact of lamotrigine.
© 2025 The Author(s). Epilepsia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
The proteasome maturation factor POMP moonlights as a stress-induced transcriptional regulator
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 27 April 2025 by Giandomenico, S. L., Mueller, M., et al.
Summary Proteostasis - the maintenance of proteins at proper concentrations, conformations, and subcellular locations - is essential for cellular function and is governed by tightly regulated protein synthesis and degradation pathways. The Proteasome Maturation Protein (POMP) is a key chaperone involved in assembling the proteasome, the primary complex responsible for protein degradation. Despite the conserved role of POMP, its loss produces contrasting proteostatic effects in yeast and mammalian cells, pointing to additional, unexplored functions. In this study, we investigated the possibility that POMP plays a moonlighting role in proteostasis regulation. We discovered that upon proteasome disruption, POMP rapidly accumulates in the nucleolus in a manner dependent on HSF1 and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Proteomic analysis of POMP interactors revealed RNA processing factors and transcriptomic profiling showed that nucleolar POMP orchestrates a protective transcriptional program. Our findings indicate POMP is a built-in sensor and effector within the proteasome assembly pathway, capable of buffering disturbances in proteasome function through a novel, non-canonical role. Notably, this mechanism is developmentally controlled and active in neurodegenerative disease contexts. Abstract Figure
-
WB
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
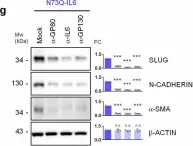
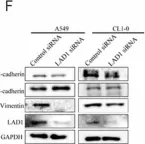
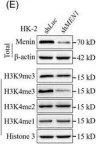
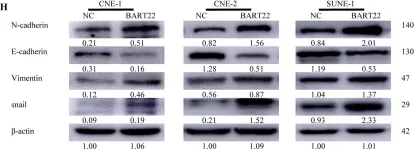
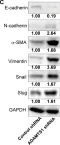
In Mol Cancer on 11 October 2024 by Ryu, K. J., Lee, K. W., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Mol Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
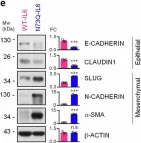
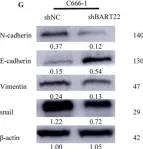
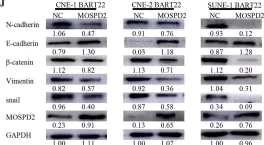
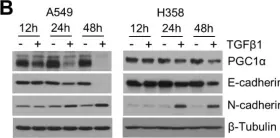
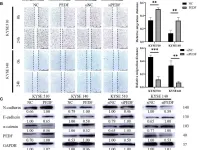
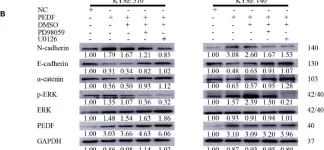
In Nat Commun on 9 September 2024 by Hung, C. H., Wu, S. Y., et al.
Fig.3.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
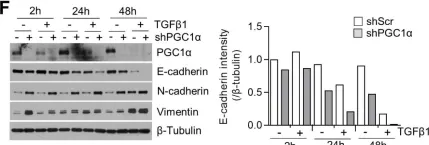
In Nat Commun on 9 September 2024 by Hung, C. H., Wu, S. Y., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
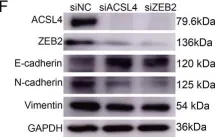
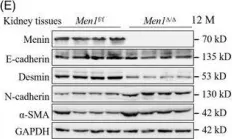
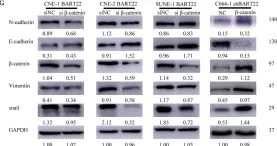
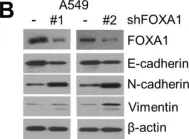
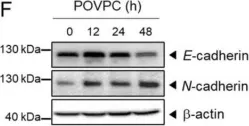
In Elife on 11 December 2023 by Lin, J., Zhang, P., et al.
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
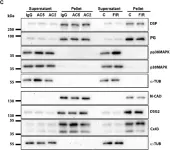
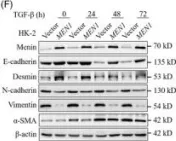
In Cell Mol Life Sci on 14 July 2023 by Yeruva, S., Stangner, K., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Mol Life Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Int J Mol Sci on 27 December 2022 by Chang, C. Y., Huang, Y. C., et al.
Fig.7.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In J Biol Chem on 1 November 2022 by Suphakhong, K., Terashima, M., et al.
Fig.1.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from J Biol Chem by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Clin Transl Med on 1 August 2022 by Jin, B., Zhu, J., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Clin Transl Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Clin Transl Med on 1 August 2022 by Jin, B., Zhu, J., et al.
Fig.4.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Clin Transl Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Clin Transl Med on 1 August 2022 by Jin, B., Zhu, J., et al.
Fig.5.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Clin Transl Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Cell Death Dis on 30 July 2022 by Zhang, T., Chen, Z., et al.
Fig.5.G

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Cell Death Dis on 30 July 2022 by Zhang, T., Chen, Z., et al.
Fig.7.J

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Cell Death Dis on 30 July 2022 by Zhang, T., Chen, Z., et al.
Fig.6.G

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Cell Death Dis on 30 July 2022 by Zhang, T., Chen, Z., et al.
Fig.4.H

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Int J Mol Sci on 26 July 2022 by Fang, X. Q., Lee, M., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Int J Mol Sci on 26 July 2022 by Fang, X. Q., Lee, M., et al.
Fig.3.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Int J Mol Sci on 26 July 2022 by Fang, X. Q., Lee, M., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Biology (Basel) on 16 May 2022 by Lee, H. C., Chang, C. Y., et al.
Fig.7.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Biology (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Front Oncol on 16 March 2021 by Chen, Z., Che, D., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Front Oncol on 16 March 2021 by Chen, Z., Che, D., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
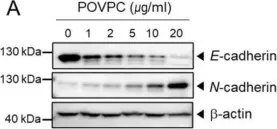
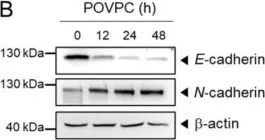
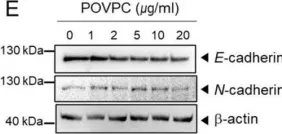
In Cells on 4 March 2021 by Seok, J. K., Hong, E. H., et al.
Fig.1.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Cells on 4 March 2021 by Seok, J. K., Hong, E. H., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Cells on 4 March 2021 by Seok, J. K., Hong, E. H., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
In Cells on 4 March 2021 by Seok, J. K., Hong, E. H., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70
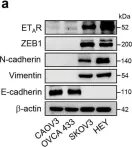
In Commun Biol on 13 November 2020 by Sestito, R., Cianfrocca, R., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Commun Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 70