Mechanistic aspects of type I procollagen biosynthesis in cells are poorly understood. To provide more insight into this process we designed a system to directly image type I procollagen biogenesis by co-expression of fluorescently labeled full size procollagen α1(I) and one α2(I) polypeptides. High resolution images show that collagen α1(I) and α2(I) polypeptides are produced in coordination in discrete structures on the ER membrane, which we termed the collagenosomes. Collagenosomes are disk shaped bodies, 0.5-1 μM in diameter and 200-400 nm thick, in the core of which folding of procollagen takes place. Collagenosomes are intimately associated with the ER membrane and their formation requires intact translational machinery, suggesting that they are the sites of nascent procollagen biogenesis. Collagenosomes show little co-localization with the COPII transport vesicles, which export type I procollagen from the ER, suggesting that these two structures are distinct. LARP6 is the protein which regulates translation of type I collagen mRNAs. The characteristic organization of collagenosomes depends on binding of LARP6 to collagen mRNAs. Without LARP6 regulation, collagenosomes are poorly organized and the folding of α1(I) and α2(I) polypeptides into procollagen in their cores is diminished. This indicates that formation of collagenosomes is dependent on regulated translation of collagen mRNAs. In live cells the size, number and shape of collagenosomes show little change within several hours, suggesting that they are stable structures of type I procollagen biogenesis. This is the first report of structural organization of type I collagen biogenesis in collagenosomes, while the fluorescent reporter system based on simultaneous imaging of both type I collagen polypeptides will enable the detailed elucidation of their structure and function.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Product Citations: 7
In Matrix Biology Plus on 1 December 2021 by Stefanovic, B., Stefanovic, L., et al.
-
WB
-
ICC-IF
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Nature Communications on 23 November 2020 by Jin, L., Chen, Y., et al.
Alternative splicing (AS) is involved in cell fate decisions and embryonic development. However, regulation of these processes is poorly understood. Here, we have identified the serine threonine kinase receptor-associated protein (STRAP) as a putative spliceosome-associated factor. Upon Strap deletion, there are numerous AS events observed in mouse embryoid bodies (EBs) undergoing a neuroectoderm-like state. Global mapping of STRAP-RNA binding in mouse embryos by enhanced-CLIP sequencing (eCLIP-seq) reveals that STRAP preferably targets transcripts for nervous system development and regulates AS through preferred binding positions, as demonstrated for two neuronal-specific genes, Nnat and Mark3. We have found that STRAP involves in the assembly of 17S U2 snRNP proteins. Moreover, in Xenopus, loss of Strap leads to impeded lineage differentiation in embryos, delayed neural tube closure, and altered exon skipping. Collectively, our findings reveal a previously unknown function of STRAP in mediating the splicing networks of lineage commitment, alteration of which may be involved in early embryonic lethality in mice.
-
WB
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Oncogenic STRAP Supports Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth by Enhancing Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.
In Molecular Cancer Research on 1 February 2019 by Wang, W., Li, S., et al.
Aberrant activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays a key role in the onset and development of hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC), with about half of them acquiring mutations in either CTNNB1 or AXIN1. The serine/threonine kinase receptor-associated protein (STRAP), a scaffold protein, was recently shown to facilitate the aberrant activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancers. However, the function of STRAP in HCC remains completely unknown. Here, increased levels of STRAP were observed in human and mouse HCCs. RNA sequencing of STRAP knockout clones generated by gene editing of Huh6 and Huh7 HCC cells revealed a significant reduction in expression of various metabolic and cell-cycle-related transcripts, in line with their general slower growth observed during culture. Importantly, Wnt/β-catenin signaling was impaired in all STRAP knockout/down cell lines tested, regardless of the underlying CTNNB1 or AXIN1 mutation. In accordance with β-catenin's role in (cancer) stem cell maintenance, the expressions of various stem cell markers, such as AXIN2 and LGR5, were reduced and concomitantly differentiation-associated genes were increased. Together, these results show that the increased STRAP protein levels observed in HCC provide growth advantage among others by enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. These observations also identify STRAP as a new player in regulating β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular cancers. IMPLICATIONS: Elevated STRAP levels in hepatocellular cancers provide a growth advantage by enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
IHC
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
STRAP Promotes Stemness of Human Colorectal Cancer via Epigenetic Regulation of the NOTCH Pathway.
In Cancer Research on 15 October 2017 by Jin, L., Vu, T., et al.
NOTCH signaling exerts essential roles in normal and malignant intestinal physiology and the homeostasis of cancer stem-like cells (CSC), but the basis for this latter role remains obscure. The signaling scaffold protein STRAP is upregulated in several cancers, where it promotes tumorigenicity and metastasis. Here we report a novel oncogenic function for STRAP in maintaining CSC subpopulations in a heterogeneous mixture by antagonizing formation of the chromatin modifier PRC2 and by epigenetically activating NOTCH signals in human colorectal cancer. Silencing STRAP sensitized colorectal cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs in vitro and in vivo STRAP depletion also contributed to a reduced stem-like phenotype of colorectal cancer cells, as indicated by reduced expression of the CSC signature and NOTCH signaling regulators in vitro and by diminished tumorigenesis in vivo Genes encoding some upstream activators of NOTCH were highly enriched for H3K27me3, which forms repressive chromatin domains upon STRAP silencing. Mechanistically, STRAP competitively disrupted association of the PRC2 subunits EZH2 and SUZ12, thereby inhibiting PRC2 assembly. Restoring the NOTCH pathway by lentiviral expression of NICD1 or HES1 in STRAP-depleted tumor cells reversed the CSC phenotype. In 90 colorectal cancer clinical specimens, a significant positive correlation was documented between the expression of STRAP and HES1. Overall, our findings illuminated a novel STRAP-NOTCH1-HES1 molecular axis as a CSC regulator in colorectal cancer, with potential implications to improve treatment of this disease. Cancer Res; 77(20); 5464-78. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
-
IP
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
mTORC1 phosphorylates LARP6 to stimulate type I collagen expression.
In Scientific Reports on 23 January 2017 by Zhang, Y. & Stefanovic, B.
Excessive deposition of type I collagen causes fibrotic diseases. Binding of La ribonucleoprotein domain family, member 6 (LARP6) to collagen mRNAs regulates their translation and is necessary for high type I collagen expression. Here we show that mTORC1 phosphorylates LARP6 on S348 and S409. The S348A/S409A mutant of LARP6 acts as a dominant negative protein in collagen biosynthesis, which retards secretion of type I collagen and causes excessive posttranslational modifications. Similar effects are seen using mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin or by knocking down raptor. The S348A/S409A mutant weakly interacts with the accessory protein STRAP, needed for coordinated translation of collagen mRNAs. The interaction of wt LARP6 and STRAP is also attenuated by rapamycin and by raptor knockdown. Additionally, in the absence of S348/S409 phosphorylation LARP6 is sequestered in increasing amounts at the ER membrane. We postulate that phosphorylation of S348/S409 by mTORC1 stimulates the interaction of LARP6 and STRAP to coordinate translation of collagen mRNAs and to release LARP6 from the ER for new round of translation. These mechanisms contribute to high level of collagen expression in fibrosis.
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
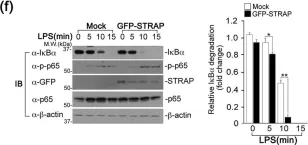
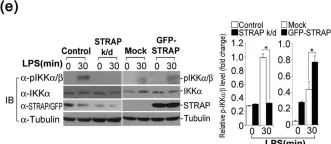
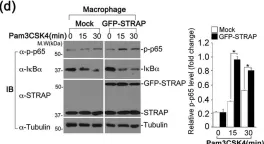
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
Fig.2.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
Fig.2.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
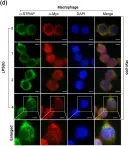
Fig.4.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Sci Rep on 9 December 2016 by Huh, H. D., Ra, E. A., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9