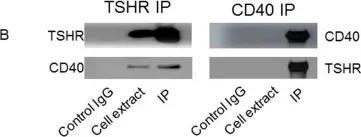
Fibrocytes appear to participate in inflammation and tissue remodeling in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO). These patients have increased frequencies of circulating TSH receptor (TSHR)- and CD40-positive fibrocytes, suggesting TSHR and CD40 may play roles in proinflammatory cytokine production, which ultimately leads to orbital inflammation and tissue remodeling.
To investigate the potential interactions between the TSHR and CD40 signaling pathways and their roles in IL-6 and TNF-α production.
CD40 expression on fibrocytes was assessed using flow cytometry; IL-6 and TNF-α protein release using Luminex technology; increased IL-6 and TNF-α mRNA abundance, using real-time PCR; TSH- and CD40 ligand (CD40L)-stimulated Akt phosphorylation in fibrocytes, by western blot analysis; TSHR-CD40 protein-protein interaction, using co-immunoprecipitation, and CD40-TSHR co-localization, using immunocytochemistry.
TSH enhances CD40 expression at a pre-translational level in fibrocytes. Production of IL-6 and TNF-α after costimulation with TSH and CD40L was greater than that after TSH or CD40L stimulation alone. TSH and CD40L costimulation also resulted in greater Akt phosphorylation. Akt and nuclear factor (NF)-κB inhibitors significantly reduced cytokine production after TSH and CD40L costimulation. TSHR and CD40L are colocalized on the cell surface and form a complex.
TSHR and CD40 in fibrocytes appear to be physically and functionally related. TSH stimulates CD40 production on the fibrocyte surface. Cytokine expression upon simultaneous stimulation of TSHR and CD40 is greater than levels achieved with TSH or CD40L alone. Increased expression of CD40 by TSH is a potential mechanism for this process.
Product Citations: 2
CD40 Expression in Fibrocytes Is Induced by TSH: Potential Synergistic Immune Activation.
In PLoS ONE on 16 September 2016 by Mester, T., Raychaudhuri, N., et al.
-
IP
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
TWEAK inhibits TRAF2-mediated CD40 signaling by destabilization of CD40 signaling complexes.
In The Journal of Immunology on 1 September 2013 by Salzmann, S., Lang, I., et al.
We found recently that TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and fibroblast growth factor-inducible-14 (Fn14) by virtue of their strong capability to reduce the freely available cytoplasmic pool of TNFR-associated factor (TRAF)2 and cellular inhibitors of apoptosis (cIAPs) antagonize the functions of these molecules in TNFR1 signaling, resulting in sensitization for apoptosis and inhibition of classical NF-κB signaling. In this study, we demonstrate that priming of cells with TWEAK also interferes with activation of the classical NF-κB pathway by CD40. Likewise, there was strong inhibition of CD40 ligand (CD40L)-induced activation of MAPKs in TWEAK-primed cells. FACS analysis and CD40L binding studies revealed unchanged CD40 expression and normal CD40L-CD40 interaction in TWEAK-primed cells. CD40L immunoprecipitates, however, showed severely reduced amounts of CD40 and CD40-associated proteins, indicating impaired formation or reduced stability of CD40L-CD40 signaling complexes. The previously described inhibitory effect of TWEAK on TNFR1 signaling has been traced back to reduced activity of the TNFR1-associated TRAF2-cIAP1/2 ubiquitinase complex and did not affect the stability of the immunoprecipitable TNFR1 receptor complex. Thus, the inhibitory effect of TWEAK on CD40 signaling must be based at least partly on other mechanisms. In line with this, signaling by the CD40-related TRAF2-interacting receptor TNFR2 was also attenuated but still immunoprecipitable in TWEAK-primed cells. Collectively, we show that Fn14 activation by soluble TWEAK impairs CD40L-CD40 signaling complex formation and inhibits CD40 signaling and thus identify the Fn14-TWEAK system as a potential novel regulator of CD40-related cellular functions.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS One on 16 September 2016 by Mester, T., Raychaudhuri, N., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1