ABSTRACT Non-canonical conjugation of ATG8 proteins, including LC3, to single membranes implicates the autophagy machinery in cell functions unrelated to metabolic stress. One such pathway is LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP), which aids in phagosome maturation and subsequent signaling upon cargo uptake mediated by certain innate immunity-associated receptors. Here, we show that a specific isoform of RAB5 GTPases, the molecular switches controlling early endosome traffic, is necessary for LAP. We demonstrate that RAB5c regulates phagosome recruitment and function of complexes required for phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate [PI(3)P] and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by macrophages. RAB5c facilitates phagosome translocation of the V-ATPase transmembrane core, which is needed for ATG16L1 binding and consequent LC3 conjugation. RAB5c depletion impaired macrophage elimination of the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus and disruption of the V-ATPase-ATG16L1 axis increased susceptibility in vivo . Therefore, early endosome-to-phagosome traffic is differentially regulated to promote LAP and ROS contributes to resistance against A. fumigatus by effecting LAP. HIGHLIGHTS RAB5c is required for LC3-associated phagocytosis RAB5c finetunes NAPDH oxidase assembly and ROS generation in the phagosome RAB5c regulates V-ATPase assembly on the phagosome RAB5c and V-ATPase-ATG16L1 axis are required for the killing of A. fumigatus
Product Citations: 77
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 28 March 2025 by Freitas-Filho, E. G., Zaidan, I., et al.
-
Cell Biology
In European Journal of Neuroscience on 1 September 2024 by Singh, G., Singh, K., et al.
Skeletal muscle wasting is a clinically proven pathology associated with Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) infection; however, underlying factors that govern skeletal muscle damage are yet to be explored. The current study aims to investigate the pathobiology of skeletal muscle damage using a mouse model of JEV infection. Our study reveals a significant increment in viral copy number in skeletal muscle post-JEV infection, which is associated with enhanced skeletal muscle cell death. Molecular and biochemical analysis confirms NOX2-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species, leading to autophagy flux inhibition and cell apoptosis. Along with this, an alteration in mitochondrial dynamics (change in fusion and fission process) and a decrease in the total number of mitochondria copies were found during JEV disease progression. The study represents the initial evidence of skeletal muscle damage caused by JEV and provides insights into potential avenues for therapeutic advancement.
© 2024 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Biomolecules on 4 April 2024 by Thakore, P., Clark, J. E., et al.
TRPC5 is a non-selective cation channel that is expressed in cardiomyocytes, but there is a lack of knowledge of its (patho)physiological role in vivo. Here, we examine the role of TRPC5 on cardiac function under basal conditions and during cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovascular parameters were assessed in wild-type (WT) and global TRPC5 knockout (KO) mice. Despite no difference in blood pressure or activity, heart rate was significantly reduced in TRPC5 KO mice. Echocardiography imaging revealed an increase in stroke volume, but cardiac contractility was unaffected. The reduced heart rate persisted in isolated TRPC5 KO hearts, suggesting changes in basal cardiac pacing. Heart rate was further investigated by evaluating the reflex change following drug-induced pressure changes. The reflex bradycardic response following phenylephrine was greater in TRPC5 KO mice but the tachycardic response to SNP was unchanged, indicating an enhancement in the parasympathetic control of the heart rate. Moreover, the reduction in heart rate to carbachol was greater in isolated TRPC5 KO hearts. To evaluate the role of TRPC5 in cardiac pathology, mice were subjected to abdominal aortic banding (AAB). An exaggerated cardiac hypertrophy response to AAB was observed in TRPC5 KO mice, with an increased expression of hypertrophy markers, fibrosis, reactive oxygen species, and angiogenesis. This study provides novel evidence for a direct effect of TRPC5 on cardiac function. We propose that (1) TRPC5 is required for maintaining heart rate by regulating basal cardiac pacing and in response to pressure lowering, and (2) TRPC5 protects against pathological cardiac hypertrophy.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Brain, Behavior, and Immunity on 1 November 2023 by Liu, X., Lei, Z., et al.
Approximately 20-68% of traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients exhibit trauma-associated olfactory deficits (OD) which can compromise not only the quality of life but also cognitive and neuropsychiatric functions. However, few studies to date have examined the impact of experimental TBI on OD. The present study examined inflammation and neuronal dysfunction in the olfactory bulb (OB) and the underlying mechanisms associated with OD in male mice using a controlled cortical impact (CCI) model. TBI caused a rapid inflammatory response in the OB as early as 24 h post-injury, including elevated mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines, increased numbers of microglia and infiltrating myeloid cells, and increased IL1β and IL6 production in these cells. These changes were sustained for up to 90 days after TBI. Moreover, we observed significant upregulation of the voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 and NOX2 expression levels, which were predominantly localized in microglia/macrophages and accompanied by increased reactive oxygen species production. In vivo OB neuronal firing activities showed early neuronal hyperexcitation and later hypo-neuronal activity in both glomerular layer and mitral cell layer after TBI, which were improved in the absence of Hv1. In a battery of olfactory behavioral tests, WT/TBI mice displayed significant OD. In contrast, neither Hv1 KO/TBI nor NOX2 KO/TBI mice showed robust OD. Finally, seven days of intranasal delivery of a NOX2 inhibitor (NOX2ds-tat) ameliorated post-traumatic OD. Collectively, these findings highlight the importance of OB neuronal networks and its role in TBI-mediated OD. Thus, targeting Hv1/NOX2 may be a potential intervention for improving post-traumatic anosmia.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 17 July 2023 by Toller-Kawahisa, J. E., Hiroki, C. H., et al.
Neutrophils rely predominantly on glycolytic metabolism for their biological functions, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Although pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) is a glycolytic enzyme known to be involved in metabolic reprogramming and gene transcription in many immune cell types, its role in neutrophils remains poorly understood. Here, we report that PKM2 regulates ROS production and microbial killing by neutrophils. Zymosan-activated neutrophils showed increased cytoplasmic expression of PKM2. Pharmacological inhibition or genetic deficiency of PKM2 in neutrophils reduced ROS production and Staphylococcus aureus killing in vitro. In addition, this also resulted in phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) accumulation and decreased dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) production, which is required for de novo synthesis of diacylglycerol (DAG) from glycolysis. In vivo, PKM2 deficiency in myeloid cells impaired the control of infection with Staphylococcus aureus. Our results fill the gap in the current knowledge of the importance of lower glycolysis for ROS production in neutrophils, highlighting the role of PKM2 in regulating the DHAP and DAG synthesis to promote ROS production in neutrophils.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
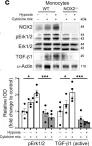
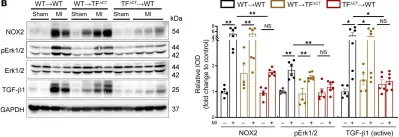
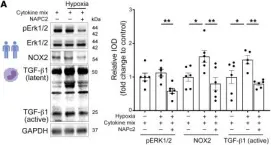
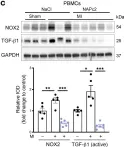
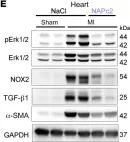
In J Clin Invest on 15 February 2023 by Garlapati, V., Molitor, M., et al.
Fig.8.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Clin Invest by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In J Clin Invest on 15 February 2023 by Garlapati, V., Molitor, M., et al.
Fig.9.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Clin Invest by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
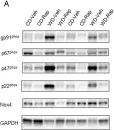
In J Clin Invest on 15 February 2023 by Garlapati, V., Molitor, M., et al.
Fig.12.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Clin Invest by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
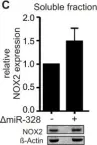
In J Clin Invest on 15 February 2023 by Garlapati, V., Molitor, M., et al.
Fig.12.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Clin Invest by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In J Clin Invest on 15 February 2023 by Garlapati, V., Molitor, M., et al.
Fig.12.E

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Clin Invest by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In Biomedicines on 30 December 2021 by La Favor, J. D., Pierre, C. J., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Biomedicines by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In Front Pharmacol on 25 June 2019 by Saul, M. J., Hegewald, A. B., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Pharmacol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In J Neuroinflammation on 29 August 2018 by Cheng, L., Chen, L., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In J Neuroinflammation on 29 August 2018 by Cheng, L., Chen, L., et al.
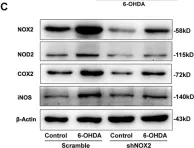
Fig.8.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In J Neuroinflammation on 29 August 2018 by Cheng, L., Chen, L., et al.
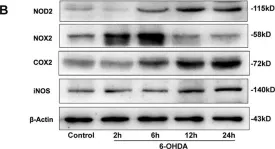
Fig.8.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
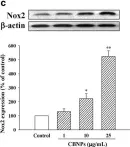
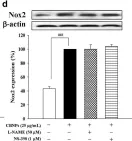
In BMC Complement Altern Med on 9 July 2018 by Hsu, H. T., Tseng, Y. T., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from BMC Complement Altern Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
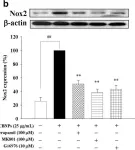
In BMC Complement Altern Med on 9 July 2018 by Hsu, H. T., Tseng, Y. T., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from BMC Complement Altern Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
In BMC Complement Altern Med on 9 July 2018 by Hsu, H. T., Tseng, Y. T., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from BMC Complement Altern Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14
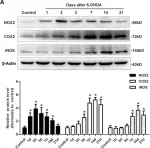
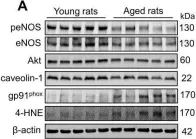
In Aging Dis on 1 April 2018 by Yang, C., DeMars, K. M., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Aging Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 14